Invertible Generative Models for Beam Reconstruction: Introducing the MENT-Flow Approach
Table of Links
I. Introduction
II. Maximum Entropy Tomography
- A. Ment
- B. Ment-Flow
III. Numerical Experiments
- A. 2D reconstructions from 1D projections
- B. 6D reconstructions from 1D projections
IV. Conclusion and Extensions
V. Acknowledgments and References
B. MENT-Flow
In the absence of a method to directly optimize the Lagrange functions
\ 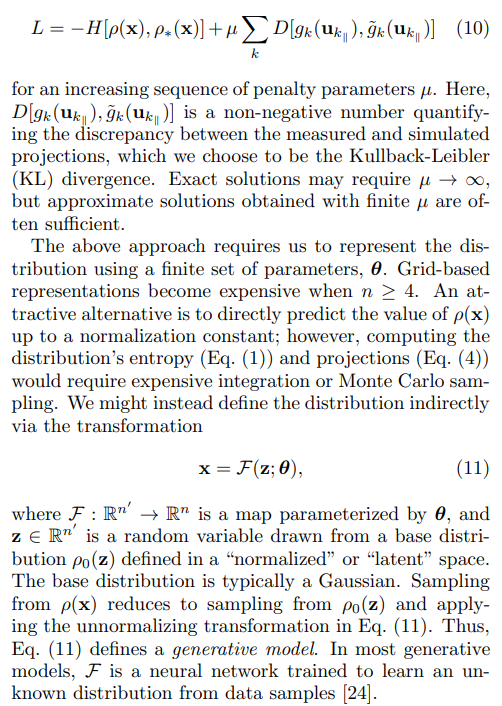
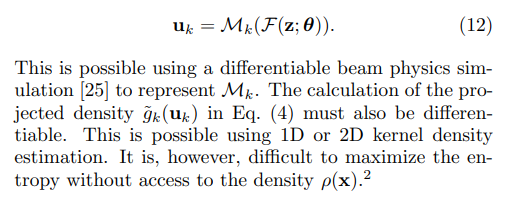
\ Roussel et al. [10] showed that generative models can also be trained to match projections of the unknown distribution. To train the model via gradient descent, the transformations from the base distribution to the measurement locations must be differentiable:
\ 
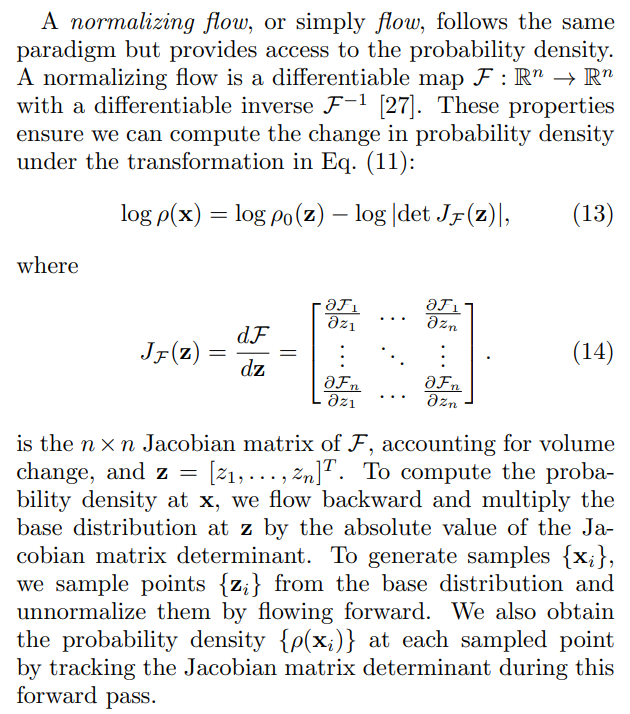
\ 
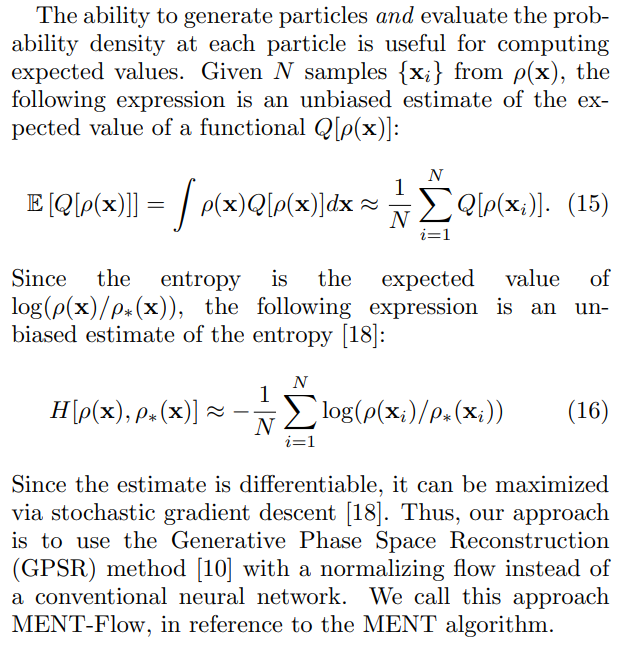
\ 
\ It is not immediately obvious whether normalizing flows can learn complex 6D distributions from projections in reasonable time. Flows preserve the topological features of the base distribution; for example, flows cannot perfectly represent disconnected modes if the base distribution has a single mode [28]. Thus, building complex flows requires layering transformations, either as a series of maps (discrete flows) or a system of differential equations (continuous flows), often leading to large models and expensive training.[3]
\ 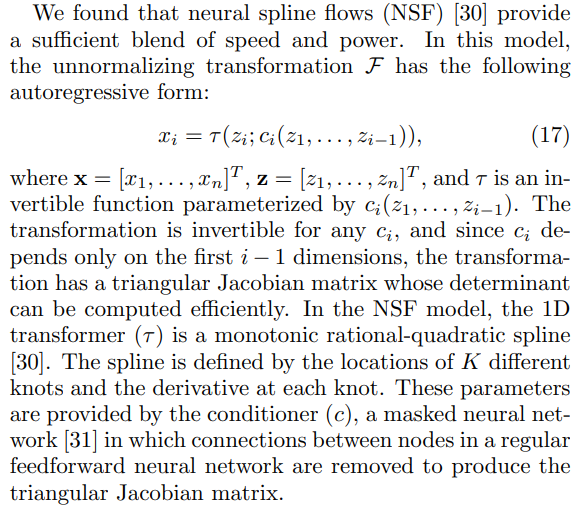
\ The model’s representational power increases with the number of parameters in the masked neural network and the number of knots in the rational-quadratic splines. We can also define more than one flow layer. For the composition of T layers
\ 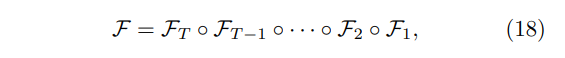
\ and transformed coordinates
\ 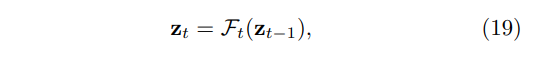
\ the Jacobian determinant is available from
\ 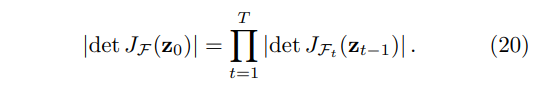
\ Compared to MENT, MENT-Flow increases the reconstruction model complexity and does not guarantee an exact entropy maximum. However, MENT-Flow scales straightforwardly to n-dimensional phase space and immediately generates independent and identically distributed samples from the reconstructed distribution function.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Austin Hoover, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 37830, USA (hooveram@ornl.gov);
(2) Jonathan C. Wong, Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\ 
You May Also Like

Ripple (XRP) CEO Brad Garlinghouse Makes Another Statement Regarding the Anticipated US Cryptocurrency Legislation

Trump Dismisses Stock Market Dip as Minor While Solana and XRP Stand to Gain

