Collaborative Research in Accelerator Physics: Acknowledgments and DOE Funding
Table of Links
I. Introduction
II. Maximum Entropy Tomography
- A. Ment
- B. Ment-Flow
III. Numerical Experiments
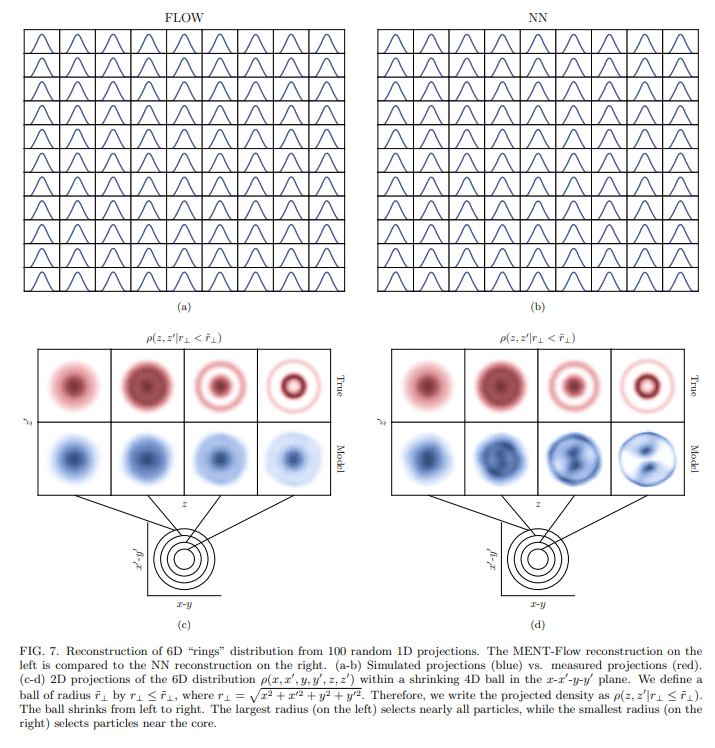
- A. 2D reconstructions from 1D projections
- B. 6D reconstructions from 1D projections
IV. Conclusion and Extensions
V. Acknowledgments and References
V. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful to Ryan Roussel (SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory), Juan Pablo Gonzalez-Aguilera (University of Chicago), and Auralee Edelen (SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory) for discussions that seeded the idea for this work and for sharing their differentiable kernel density estimation code.
\ This manuscript has been authored by UT Battelle, LLC under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725 with the U.S. Department of Energy. The United States Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a non-exclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, world-wide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for United States Government purposes. The Department of Energy will provide public access to these results of federally sponsored research in accordance with the DOE Public Access Plan (http://energy.gov/downloads/doe-public-access-plan).
\ 
[1] B. Cathey, S. Cousineau, A. Aleksandrov, and A. Zhukov, First six-dimensional phase space measurement of an accelerator beam, Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 064804 (2018).
\ [2] K. Ruisard, A. Aleksandrov, S. Cousineau, V. Tzoganis, and A. Zhukov, High dimensional characterization of the longitudinal phase space formed in a radio frequency quadrupole, Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 23, 124201 (2020).
\ [3] A. Hoover, K. Ruisard, A. Aleksandrov, A. Zhukov, and S. Cousineau, Analysis of a hadron beam in fivedimensional phase space, Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 26, 064202 (2023).
\ [4] Y. Liu, C. Long, and A. Aleksandrov, Nonintrusive measurement of time-resolved emittances of 1-gev operational hydrogen ion beam using a laser comb, Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 23, 102806 (2020).
\ [5] A. Wolski, D. C. Christie, B. L. Militsyn, D. J. Scott, and H. Kockelbergh, Transverse phase space characterization in an accelerator test facility, Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 23, 032804 (2020).
\ [6] K. Hock and A. Wolski, Tomographic reconstruction of the full 4D transverse phase space, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 726, 8 (2013).
\ [7] M. Wang, Z. Wang, D. Wang, W. Liu, B. Wang, M. Wang, M. Qiu, X. Guan, X. Wang, W. Huang, and S. Zheng, Four-dimensional phase space measurement using multiple two-dimensional profiles, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 943, 162438 (2019).
\ [8] B. Marchetti, A. Grudiev, P. Craievich, R. Assmann, H.- H. Braun, N. Catalan Lasheras, F. Christie, R. D’Arcy, R. Fortunati, R. Ganter, et al., Experimental demonstration of novel beam characterization using a polarizable x-band transverse deflection structure, Scientific reports 11, 3560 (2021).
\ [9] A. Wolski, M. A. Johnson, M. King, B. L. Militsyn, and P. H. Williams, Transverse phase space tomography in an accelerator test facility using image compression and machine learning, Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 25, 122803 (2022).
\ [10] R. Roussel, A. Edelen, C. Mayes, D. Ratner, J. P. Gonzalez-Aguilera, S. Kim, E. Wisniewski, and J. Power, Phase space reconstruction from accelerator beam measurements using neural networks and differentiable simulations, Physical Review Letters 130, 145001 (2023).
\ [11] A. Scheinker, F. Cropp, and D. Filippetto, Adaptive autoencoder latent space tuning for more robust machine learning beyond the training set for six-dimensional phase space diagnostics of a time-varying ultrafast electron-diffraction compact accelerator, Phys. Rev. E 107, 045302 (2023).
\ [12] S. Jaster-Merz, R. W. Assmann, R. Brinkmann, F. Burkart, W. Hillert, M. Stanitzki, and T. Vinatier, 5D tomographic phase-space reconstruction of particle bunches, Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 27, 072801 (2024).
\ [13] R. Roussel, J. P. Gonzalez-Aguilera, A. Edelen, E. Wisniewski, A. Ody, W. Liu, Y.-K. Kim, and J. Power, Efficient 6-dimensional phase space reconstruction from experimental measurements using generative machine learning (2024).
\ [14] S. Press´e, K. Ghosh, J. Lee, and K. A. Dill, Principles of maximum entropy and maximum caliber in statistical physics, Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 1115 (2013).
\ [15] J. Skilling and S. F. Gull, Bayesian maximum entropy image reconstruction, Lecture Notes-Monograph Series , 341 (1991).
\ [16] R. D. Rosenkrantz, ET Jaynes: Papers on probability, statistics and statistical physics, Vol. 158 (Springer Science & Business Media, 2012).
\ [17] A. Giffin, Maximum Entropy: The Universal Method for Inference, Ph.D. thesis, University at Albany, State University of New York, Albany, NY, USA (2008).
\ [18] G. Loaiza-Ganem, Y. Gao, and J. P. Cunningham, Maximum entropy flow networks, in International Conference on Learning Representations (2016).
\ [19] J. C. Wong, A. Shishlo, A. Aleksandrov, Y. Liu, and C. Long, 4D transverse phase space tomography of an operational hydrogen ion beam via noninvasive 2d measurements using laser wires, Physical Review Accelerators and Beams 25, 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.25.042801 (2022).
\ [20] C. Mottershead, Maximum entropy tomography, in Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Workshop on Maximum Entropy and Bayesian Methods, Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA (Springer, 1996) pp. 425–430.
\ [21] G. Minerbo, MENT: A maximum entropy algorithm for reconstructing a source from projection data, Computer Graphics and Image Processing 10, 48 (1979).
\ [22] N. J. Dusaussoy and I. E. Abdou, The extended MENT algorithm: a maximum entropy type algorithm using prior knowledge for computerized tomography, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 39, 1164 (1991).
\ [23] A. Tran and Y. Hao, Beam tomography with coupling using maximum entropy technique, in Proc. 14th International Particle Accelerator Conference, 14 (JACoW Publishing, Geneva, Switzerland, 2023) pp. 3944–3947.
\ [24] S. Bond-Taylor, A. Leach, Y. Long, and C. G. Willcocks, Deep generative modelling: A comparative review of vaes, gans, normalizing flows, energy-based and autoregressive models, IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 44, 7327 (2021).
\ [25] J. Kaiser, C. Xu, A. Eichler, and A. Santamaria Garcia, Bridging the gap between machine learning and particle accelerator physics with high-speed, differentiable simulations, Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 27, 054601 (2024).
\ [26] Z. Ao and J. Li, Entropy estimation via normalizing flow, in Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vol. 36 (2022) pp. 9990–9998.
\ [27] G. Papamakarios, E. Nalisnick, D. J. Rezende, S. Mohamed, and B. Lakshminarayanan, Normalizing flows for probabilistic modeling and inference, The Journal of Machine Learning Research 22, 2617 (2021).
\ [28] V. Stimper, B. Sch¨olkopf, and J. M. Hern´andez-Lobato, Resampling base distributions of normalizing flows, in Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, Vol. 151 (PMLR, 2022) pp. 4915–4936.
\ [29] G. M. Green, Y.-S. Ting, and H. Kamdar, Deep potential: Recovering the gravitational potential from a snapshot of phase space, The Astrophysical Journal 942, 26 (2023).
\ [30] C. Durkan, A. Bekasov, I. Murray, and G. Papamakarios, Neural spline flows, Advances in neural information processing systems 32 (2019).
\ [31] G. Papamakarios, T. Pavlakou, and I. Murray, Masked autoregressive flow for density estimation, Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017).
\ [32] A. Hoover, MENT-Flow: maximum-entropy phase space tomography using normalizing flows, 10.5281/zenodo.11110801 (2024).
\ [33] A. Aleksandrov, S. Cousineau, and K. Ruisard, Understanding beam distributions in hadron linacs in the presence of space charge, Journal of Instrumentation 15 (7), P07025.
\ [34] M. Laszkiewicz, J. Lederer, and A. Fischer, Marginal tailadaptive normalizing flows, in Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, Vol. 162, edited by K. Chaudhuri, S. Jegelka, L. Song, C. Szepesvari, G. Niu, and S. Sabato (PMLR, 2022) pp. 12020–12048.
\ [35] S. Basir and I. Senocak, An adaptive augmented lagrangian method for training physics and equality constrained artificial neural networks, arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.04904 (2023).
\ [36] B. Dai and U. Seljak, Sliced iterative normalizing flows, in Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, Vol. 139, edited by M. Meila and T. Zhang (PMLR, 2021) pp. 2352–2364.
\ [37] B. Klartag, A central limit theorem for convex sets, Inventiones mathematicae 168, 91 (2007).
\ [38] J. Qiang, Differentiable self-consistent space-charge simulation for accelerator design, Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 26, 024601 (2023).
\ [39] M. Mardani, J. Song, J. Kautz, and A. Vahdat, A variational perspective on solving inverse problems with diffusion models, arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.04391 (2023).
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Austin Hoover, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 37830, USA (hooveram@ornl.gov);
(2) Jonathan C. Wong, Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

MYX Finance price surges again as funding rate points to a crash

Fed Day Dry Powder: Cryptoquant Analyst Tracks $7.6B Stablecoin Pile on Exchanges
