A Guide on How to Eliminate Thread Explosions in iOS: GCD and Swift Concurrency
Introduction
Thread explosion is a situation where multiple threads run simultaneously, causing performance degradation and memory overhead. In this article, we explore how to eliminate thread explosions and how Swift Concurrency helps prevent them.
Thread Explosion in GCD
Foundation
The system doesn’t provide an exact answer to how many threads we have. Based on WWDC Swift Concurrency Behind the Scenes, we can conclude that there are 16 threads per CPU core.
\ Let’s consider the following code:
import Foundation let queue = DispatchQueue(label: "com.nsvasilev.concurrent-queue", attributes: .concurrent) for _ in 0...127 { queue.async { sleep(5) } }
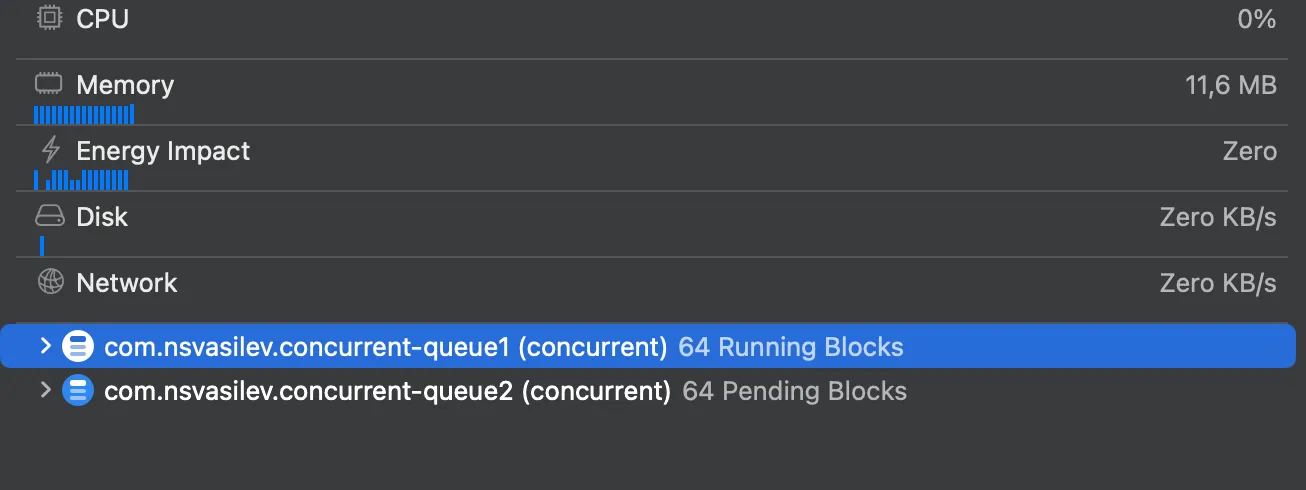
\ The queue is a concurrent queue, and it schedules 128 tasks concurrently without limiting the number of active threads. Each task simulates a real-world heavy operation. Due to concurrent execution, the system might spawn numerous threads, causing performance degradation and increased CPU usage.
The output is separated into two groups, each containing 64 elements, due to a thread limit of 64. These 64 operations can be executed in any order because we are dealing with a concurrent queue.
\ Grand Central Dispatch (GCD) doesn’t have a built-in mechanism to prevent thread explosion. Next, we examine thread explosion in concurrent and serial GCD queues.
Deadlocks in Concurrent Queues
The thread explosion may lead to deadlocks in concurrent queues. Let’s consider the following example:
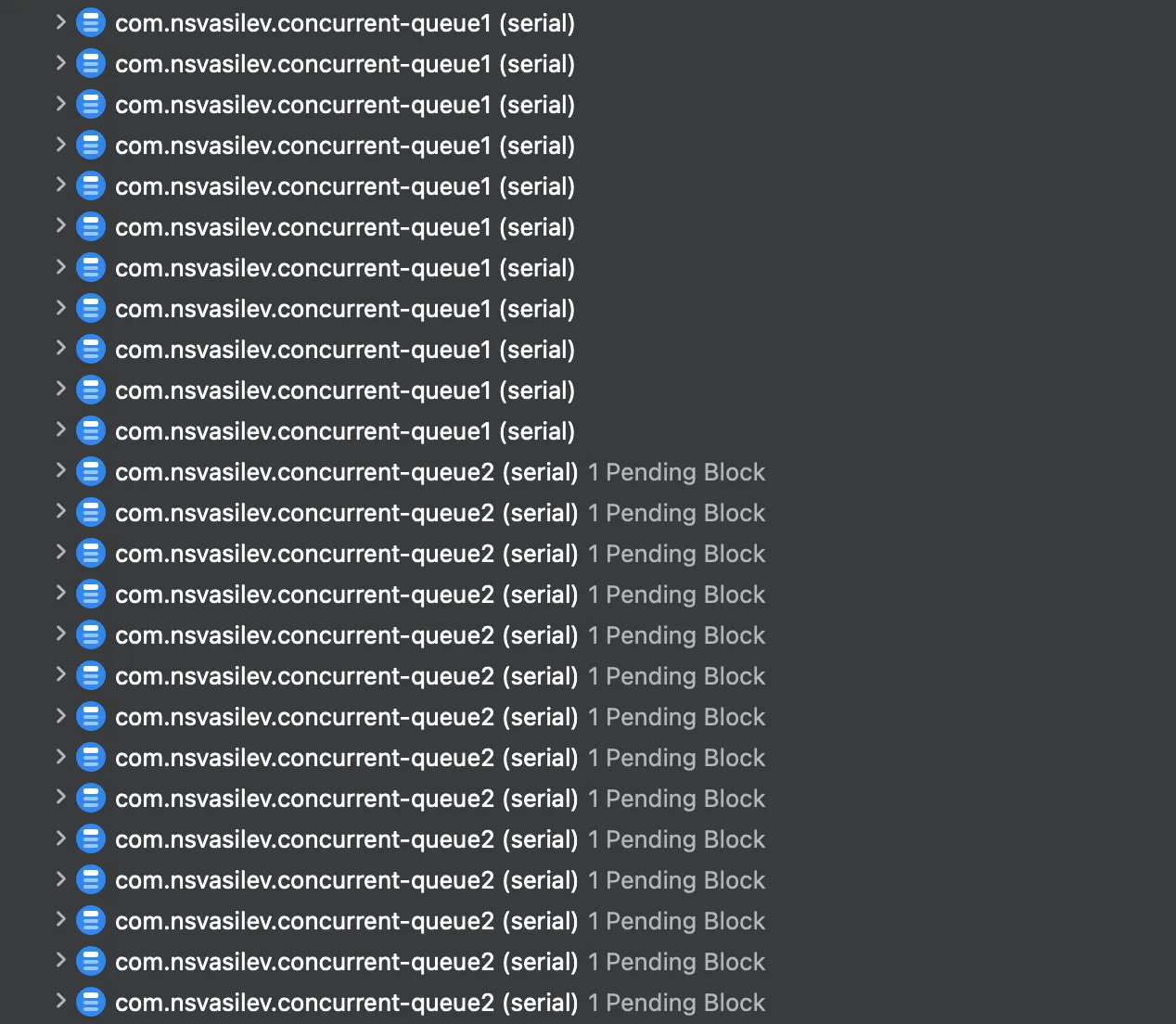
import Foundation let queue1 = DispatchQueue(label: "com.nsvasilev.concurrent-queue1", attributes: .concurrent) let queue2 = DispatchQueue(label: "com.nsvasilev.concurrent-queue2", attributes: .concurrent) let dispatchSemaphore = DispatchSemaphore(value: 0) (0..<64).forEach { _ in queue1.async { dispatchSemaphore.wait() } } (0..<64).forEach { _ in queue2.async { dispatchSemaphore.signal() } }
\ It may not be obvious that this code will cause a deadlock. The first concurrent queue schedules 64 tasks, each waiting on a semaphore. In this particular case, the thread limit is 64, meaning all available threads are occupied by these tasks. However, none of the tasks can proceed because they are all blocked, waiting for a signal from the second queue. Meanwhile, the second queue is also trying to run its tasks, which involve signaling the semaphore.
\
But, since all threads are blocked by the first queue’s wait() calls, none of the signals from queue2 can be processed, resulting in a deadlock where both queues are waiting for each other indefinitely.
\ There are three possible solutions.
-
Use
OperationQueueto limit simultaneous tasks.let operationQueue = OperationQueue() operationQueue.maxConcurrentOperationCount = 5 operationQueue.qualityOfService = .backgroundlet queue = DispatchQueue(label: "com.nsvasilev.concurrent-queue2", attributes: .concurrent) let dispatchSemaphore = DispatchSemaphore(value: 0)(0..<64).forEach { _ in operationQueue.addOperation { dispatchSemaphore.wait() } }(0..<64).forEach { _ in queue.async { dispatchSemaphore.signal() } }\
-
Use
DispatchSemaphoreto limit simultaneous tasks.let queue = DispatchQueue(label: "com.nsvasilev.concurrent-queue", attributes: .concurrent) let dispatchSemaphore = DispatchSemaphore(value: 3)(0..<128).forEach { index in dispatchSemaphore.wait() queue.async { dispatchSemaphore.signal() } }\
DispatchSemaphore controls access to the queue and does not allow performing more than 3 operations at a time.
-
Use Swift Concurrency to prevent thread explosion.
\
Swift Concurrency can manage thread explosion. We will explore how it prevents thread explosion later in this article.
Deadlocks in Serial Queues
Deadlocks can occur in serial queues as well. The GCD thread limit for both concurrent and serial queues is capped at 512.
let dispatchSemaphore = DispatchSemaphore(value: 0) for _ in 0...511 { let queue1 = DispatchQueue(label: "com.nsvasilev.concurrent-queue1") queue1.async { dispatchSemaphore.wait() } } for _ in 0...511 { let queue2 = DispatchQueue(label: "com.nsvasilev.concurrent-queue2") queue2.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 1.0) { dispatchSemaphore.signal() } }
\
\ The inner for-loop creates 512 serial queues, consuming all available threads. As a result, the first loop occupies all threads, causing a deadlock because there are no threads left to execute the second loop’s queue operations.
Swift Concurrency
Swift Concurrency prevents thread explosion, and in this part, we are going to take a look at how it works. Let’s explore how Swift Concurrency manages tasks efficiently and avoids creating excessive threads.
Priorities
In Swift Concurrency, we have only three task priorities: .userInitiated, .utility, .background.
.userInitiatedis a high-priority task for user-initiated actions..utilityis a medium-priority task for background processing..backgroundis for low-priority tasks that can run in the background.
\ Let’s consider some examples:
// The high-priority task for user-initiated actions. Task(priority: .userInitiated) { await loadSomeData() } // The medium-priority task for background processing. Task(priority: .utility) { await processDataInBackground() } // The low-priority tasks that can run in the background. Task(priority: .background) { await performBackgroundCleanup() }
\ In this example, await loadSomeData() is assigned the highest priority with .userInitiated, indicating that it is a user-focused task requiring prompt execution. Background tasks, such as cleanup, are set to .background priority, allowing them to run without blocking critical operations.
How Swift Concurrency Is Managing Threads
Let’s consider examples that convert the cases from the previous section, but using Swift Concurrency. The task will perform a “heavy” operation, and we will run it with different priorities.
Tasks With the Same Priority Level
Let’s consider the following example:
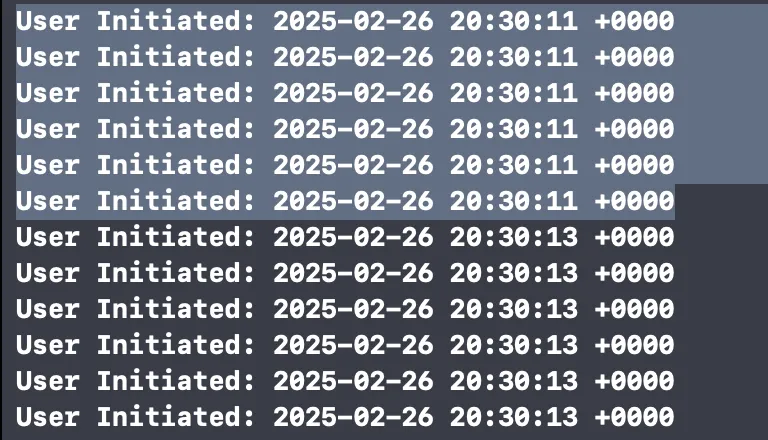
func runTask(seconds: UInt32) { Task(priority: .userInitiated) { print("User Initiated: \(Date())") sleep(seconds) } } for _ in 0...127 { runTask(seconds: 2) }
\ We can see that only 6 tasks are performed simultaneously, which is equal to the number of CPU cores on my device.
\
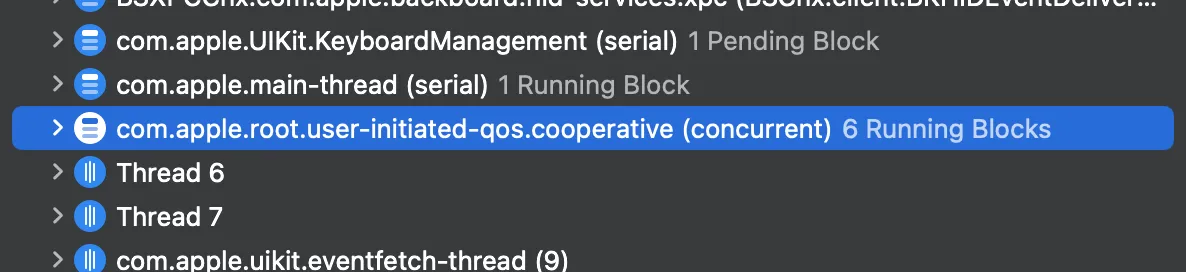
If you pause the execution, you may get a clearer picture of what happens behind the scenes.
\
\ We may notice that all of these operations are performed inside com.apple.root.user-initiated-qos.cooperative, which limits the number of threads so that it doesn’t exceed the number of CPU cores.
\ Based on this observation, it’s clear that Swift Concurrency prevents thread explosion and doesn’t create more threads than there are CPU cores on the device.
Tasks With All Priority Levels at Once.
Let’s look at another example. In this case, we’ll run tasks with different priorities and observe what happens.
func runUserInitiatedTask(seconds: UInt32) { Task(priority: .userInitiated) { print("User Initiated: \(Date())") sleep(seconds) } } func runUserUtilityTask(seconds: UInt32) { Task(priority: .utility) { print("Utility: \(Date())") sleep(seconds) } } func runUserBackgroundTask(seconds: UInt32) { Task(priority: .background) { print("Background: \(Date())") sleep(seconds) } } for _ in 0...127 { runUserInitiatedTask(seconds: 2) } for _ in 0...127 { runUserUtilityTask(seconds: 2) } for _ in 0...127 { runUserBackgroundTask(seconds: 2) }
\ As we can see, the .utility and .background queues are limited to 1 thread when there’s a higher-priority queue (.userInitiated).
\
In this specific scenario, the maximum number of threads is 8.
The Last Example
What if we add some delays before starting each group of tasks?
\ In this example, we demonstrate how introducing delays before starting each group of tasks can impact their execution. We have three types of tasks, each with a different priority: .background, .utility, and .userInitiated. Each task sleeps for a specified duration, and tasks are executed in three groups, with a 2-second delay between each group.
func runUserBackgroundTask(seconds: UInt32) { Task(priority: .background) { print("Background: \(Date())") sleep(seconds) } } func runUserUtilityTask(seconds: UInt32) { Task(priority: .utility) { print("Utility: \(Date())") sleep(seconds) } } func runUserInitiatedTask(seconds: UInt32) { Task(priority: .userInitiated) { print("User Initiated: \(Date())") sleep(seconds) } } for _ in 0...127 { runUserBackgroundTask(seconds: 2) } sleep(2) for _ in 0...127 { runUserUtilityTask(seconds: 2) } sleep(2) for _ in 0...127 { runUserInitiatedTask(seconds: 2) }
We can see that all three queues—background, utility, and user-initiated are processing multiple threads simultaneously. Interestingly, if the lower-priority queue is started first and given some time to run, the higher-priority queue doesn’t seem to negatively impact the performance of the lower-priority queue.
\ This suggests that the system is capable of handling tasks with different priorities efficiently, maintaining a balance even when tasks run concurrently.
Conclusion
While GCD doesn’t inherently prevent thread explosion, it offers tools for managing concurrency, such as task queues and dispatch groups. However, thread explosion can occur if tasks are dispatched incorrectly or in excess. In contrast, Swift Concurrency improves upon this by offering a more structured and efficient approach to concurrency management.
\ By prioritizing tasks and limiting concurrency based on available resources, Swift Concurrency reduces the risk of thread explosion and optimizes performance, ensuring that multiple tasks can run concurrently without overwhelming the system.
You May Also Like
XRP Crowned South Korea’s Most-Traded Crypto of 2025

DeFi Development Corp. expands Solana treasury accelerator