Performance Analysis of Optimization Methods on Hyperbolic Embeddings
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Related Works
-
Convex Relaxation Techniques for Hyperbolic SVMs
3.1 Preliminaries
3.2 Original Formulation of the HSVM
3.3 Semidefinite Formulation
3.4 Moment-Sum-of-Squares Relaxation
-
Experiments
4.1 Synthetic Dataset
4.2 Real Dataset
-
Discussions, Acknowledgements, and References
\
A. Proofs
B. Solution Extraction in Relaxed Formulation
C. On Moment Sum-of-Squares Relaxation Hierarchy
D. Platt Scaling [31]
E. Detailed Experimental Results
F. Robust Hyperbolic Support Vector Machine
4 Experiments
We validate the performances of semidefinite relaxation (SDP) and sparse moment-sum-of-squares relaxations (Moment) by comparing various metrics with that of projected gradient descent (PGD) on a combination of synthetic and real datasets. The PGD implementation follows from adapting the MATLAB code in Cho et al. [4], with learning rate 0.001 and 2000 epochs for synthetic and 4000 epochs for real dataset and warm-started with a Euclidean SVM solution.
\ Datasets. For synthetic datasets, we construct Gaussian and tree embedding datasets following Cho et al. [4], Mishne et al. [6], Weber et al. [7]. Regarding real datasets, our experiments include two machine learning benchmark datasets, CIFAR-10 [34] and Fashion-MNIST [35] with their hyperbolic embeddings obtained through standard hyperbolic embedding procedure [1, 3, 5] to assess image classification performance. Additionally, we incorporate three graph embedding datasets—football, karate, and polbooks obtained from Chien et al. [5]—to evaluate the effectiveness of our methods on graph-structured data. We also explore cell embedding datasets, including Paul Myeloid Progenitors developmental dataset [36], Olsson Single-Cell RNA sequencing dataset [37], Krumsiek Simulated Myeloid Progenitors dataset[38], and Moignard blood cell developmental trace dataset from single-cell gene expression [39], where the inherent geometry structures well fit into our methods.
\ We emphasize that all features are on the Lorentz manifold, but visualized in Poincaré manifold through stereographic projection if the dimension is 2.
\ Evaluation Metrics. The primary metrics for assessing model performance are average training and testing loss, accuracy, and weighted F1 score under a stratified 5-fold train-test split scheme. Furthermore, to assess the tightness of the relaxations, we examine the relative suboptimality gap, defined as
\ 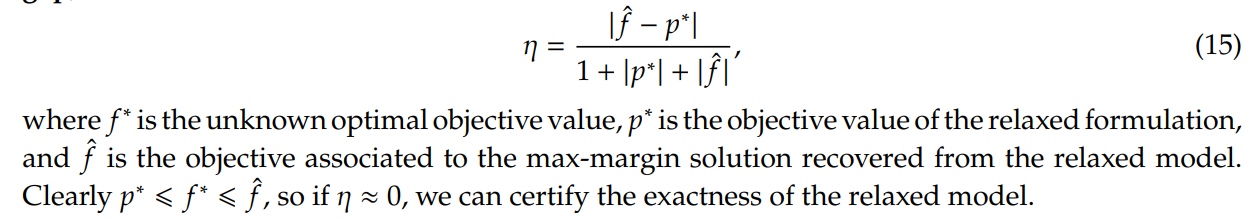
\ Implementations Details. We use MOSEK [40] in Python as our optimization solver without any intermediate parser, since directly interacting with solvers save substantial runtime in parsing the problem. MOSEK uses interior point method to update parameters inside the feasible region without projections. All experiments are run and timed on a machine with 8 Intel Broadwell/Ice Lake CPUs and 40GB of memory. Results over multiple random seeds have been gathered and reported.
\ We first present the results on synthetic Gaussian and tree embedding datasets in Section 4.1, followed by results on various real datasets in Section 4.2. Code to reproduce all experiments is available on GitHub.[1]
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Sheng Yang, John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA (shengyang@g.harvard.edu);
(2) Peihan Liu, John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA (peihanliu@fas.harvard.edu);
(3) Cengiz Pehlevan, John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, Center for Brain Science, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, and Kempner Institute for the Study of Natural and Artificial Intelligence, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA (cpehlevan@seas.harvard.edu).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC by-SA 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Sharealike 4.0 International) license.
:::
[1] https://github.com/yangshengaa/hsvm-relax
You May Also Like

The Federal Reserve cut interest rates by 25 basis points, and Powell said this was a risk management cut

Zero Knowledge Proof Kicks Off 2026 With Presale Auction Plus $5M Reward – Could This Spark Major Movement?
