Building a Go Dependency Scanner From Scratch
When managing Go projects, you need to track dependencies, check for vulnerabilities, and ensure license compliance. Instead of relying on external tools, let's build our own dependency analyzer using Go's standard library.
\
The Core Structure
We'll work with Go modules, so we need structures to represent them:
package main import ( "bufio" "encoding/json" "fmt" "io" "net/http" "os" "regexp" "sort" "strings" "time" ) type Module struct { Path string Version string Indirect bool } type GoMod struct { Module Module Requires []Module } \ Our tool will handle three operations: listing dependencies, vulnerability scanning, and license checking.
\
Parsing go.mod Files
Understanding Module File Structure
The go.mod file uses a specific format that we need to parse correctly. Module declarations start with the module keyword followed by the module path. Dependencies are listed in require statements, which can be single-line or grouped in multi-line blocks.
\ The parsing logic handles both formats by tracking whether we're inside a multi-line require block. We use regular expressions to extract the module path and version from each line, and detect indirect dependencies by looking for the // indirect comment. This approach gives us the same information that go list would provide, but without spawning external processes.
\ Rather than shelling out to go list, we can parse the go.mod file directly:
func parseGoMod() (*GoMod, error) { file, err := os.Open("go.mod") if err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("go.mod not found: %v", err) } defer file.Close() goMod := &GoMod{ Requires: []Module{}, } scanner := bufio.NewScanner(file) inRequire := false requireRegex := regexp.MustCompile(`^\s*([^\s]+)\s+([^\s]+)(?:\s+//\s*indirect)?`) moduleRegex := regexp.MustCompile(`^module\s+(.+)`) for scanner.Scan() { line := strings.TrimSpace(scanner.Text()) if strings.HasPrefix(line, "module ") { if matches := moduleRegex.FindStringSubmatch(line); len(matches) > 1 { goMod.Module = Module{Path: matches[1]} } } if strings.HasPrefix(line, "require (") { inRequire = true continue } if inRequire && line == ")" { inRequire = false continue } if inRequire || strings.HasPrefix(line, "require ") { cleanLine := strings.TrimPrefix(line, "require ") if matches := requireRegex.FindStringSubmatch(cleanLine); len(matches) >= 3 { module := Module{ Path: matches[1], Version: matches[2], Indirect: strings.Contains(line, "indirect"), } goMod.Requires = append(goMod.Requires, module) } } } return goMod, scanner.Err() } \ The parser handles both single-line requires and multi-line require blocks. It extracts module paths, versions, and identifies indirect dependencies.
\
Vulnerability Database Queries
How Vulnerability Checking Works
Vulnerability databases maintain records of known security issues in software packages. Each vulnerability gets assigned identifiers like CVE numbers and includes details about affected versions. The process works like this: we send the package name and version to the database API, it checks if that specific version has any known vulnerabilities, then returns a list of issues if found.
\ The OSV database is particularly useful because it aggregates vulnerability data from multiple sources and provides a unified API. When we query it, we're essentially asking "does this exact version of this package have any reported security problems?" The database performs version matching and returns structured data about any findings.
\ We can check the OSV (Open Source Vulnerabilities) database for known issues:
func checkOSVDatabase(modulePath, version string) []string { url := "https://api.osv.dev/v1/query" payload := map[string]interface{}{ "package": map[string]string{ "name": modulePath, "ecosystem": "Go", }, "version": version, } jsonData, err := json.Marshal(payload) if err != nil { return []string{} } client := &http.Client{Timeout: 10 * time.Second} resp, err := client.Post(url, "application/json", strings.NewReader(string(jsonData))) if err != nil { return []string{} } defer resp.Body.Close() if resp.StatusCode != 200 { return []string{} } var result struct { Vulns []struct { ID string `json:"id"` Summary string `json:"summary"` } `json:"vulns"` } if err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&result); err != nil { return []string{} } var vulnerabilities []string for _, vuln := range result.Vulns { vulnStr := fmt.Sprintf("%s: %s", vuln.ID, vuln.Summary) vulnerabilities = append(vulnerabilities, vulnStr) } return vulnerabilities } func checkVulnerabilities() { goMod, err := parseGoMod() if err != nil { fmt.Printf("Error: %v\n", err) return } vulnerableModules := 0 for i, mod := range goMod.Requires { fmt.Printf("\rScanning %d/%d: %s", i+1, len(goMod.Requires), mod.Path) vulns := checkOSVDatabase(mod.Path, mod.Version) if len(vulns) > 0 { vulnerableModules++ fmt.Printf("\n🚨 %s@%s:\n", mod.Path, mod.Version) for _, vuln := range vulns { fmt.Printf(" - %s\n", vuln) } } } if vulnerableModules == 0 { fmt.Println("\n✅ No known vulnerabilities found") } else { fmt.Printf("\n⚠️ Found %d vulnerable modules\n", vulnerableModules) } } \ The vulnerability checker sends a JSON payload with the module name and version, then parses the response for any reported vulnerabilities.
\
License Information Fetching
How License Detection Works
License compliance checking involves identifying what legal terms govern each dependency in your project. Most open source projects include license files in their repositories, and platforms like GitHub parse these files to identify the license type using SPDX identifiers.
\ Our approach leverages GitHub's license detection API, which analyzes repository contents and returns standardized license identifiers. For modules hosted on GitHub, we extract the owner and repository name from the module path, then query GitHub's API endpoint that specifically provides license information. This gives us machine-readable license data without having to download and parse license files ourselves.
\ Different licenses have different requirements , some like MIT are very permissive, while others like GPL have copyleft requirements that might affect how you can distribute your software. Understanding these differences is crucial for legal compliance.
\ For GitHub-hosted modules, we can get license data from their API:
func fetchGitHubLicense(owner, repo string) string { url := fmt.Sprintf("https://api.github.com/repos/%s/%s/license", owner, repo) client := &http.Client{Timeout: 10 * time.Second} resp, err := client.Get(url) if err != nil { return "Unknown" } defer resp.Body.Close() if resp.StatusCode != 200 { return "Unknown" } var result struct { License struct { SPDXID string `json:"spdx_id"` } `json:"license"` } if err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&result); err != nil { return "Unknown" } if result.License.SPDXID != "" && result.License.SPDXID != "NOASSERTION" { return result.License.SPDXID } return "Unknown" } func fetchLicenseFromRepo(modulePath string) string { if strings.HasPrefix(modulePath, "golang.org/x/") { return "BSD-3-Clause" } if !strings.HasPrefix(modulePath, "github.com/") { return "Unknown" } parts := strings.Split(modulePath, "/") if len(parts) < 3 { return "Unknown" } return fetchGitHubLicense(parts[1], parts[2]) } func checkLicenses() { goMod, err := parseGoMod() if err != nil { fmt.Printf("Error: %v\n", err) return } licenseCount := make(map[string]int) for i, mod := range goMod.Requires { fmt.Printf("\rProcessing %d/%d...", i+1, len(goMod.Requires)) license := fetchLicenseFromRepo(mod.Path) licenseCount[license]++ fmt.Printf("\r %s: %s\n", mod.Path, license) } fmt.Println("\nLicense Distribution:") for license, count := range licenseCount { percentage := float64(count) / float64(len(goMod.Requires)) * 100 fmt.Printf(" %s: %d modules (%.1f%%)\n", license, count, percentage) } } \ The license checker recognizes that golang.org/x/ packages use BSD-3-Clause, then queries GitHub's API for other repositories.
\
Dependency Analysis with Checksum Verification
The dependency analyzer lists modules and verifies their integrity using go.sum:
func parseGoSum() map[string]string { checksums := make(map[string]string) file, err := os.Open("go.sum") if err != nil { return checksums } defer file.Close() scanner := bufio.NewScanner(file) for scanner.Scan() { parts := strings.Fields(scanner.Text()) if len(parts) >= 3 { module := parts[0] + "@" + parts[1] checksums[module] = parts[2] } } return checksums } func analyzeDependencies() { goMod, err := parseGoMod() if err != nil { fmt.Printf("Error: %v\n", err) return } checksums := parseGoSum() fmt.Printf("Module: %s\n", goMod.Module.Path) fmt.Printf("Found %d dependencies:\n\n", len(goMod.Requires)) direct, indirect := 0, 0 sort.Slice(goMod.Requires, func(i, j int) bool { return goMod.Requires[i].Path < goMod.Requires[j].Path }) for _, mod := range goMod.Requires { status := "direct" if mod.Indirect { status = "indirect" indirect++ } else { direct++ } checksumKey := mod.Path + "@" + mod.Version hasChecksum := "❌" if _, exists := checksums[checksumKey]; exists { hasChecksum = "✅" } fmt.Printf(" %s %s@%s (%s)\n", hasChecksum, mod.Path, mod.Version, status) } fmt.Printf("\nSummary: %d direct, %d indirect dependencies\n", direct, indirect) } \
Command Interface
The main function routes commands to the appropriate handlers:
func main() { if len(os.Args) < 2 { fmt.Println("Usage: go run main.go <command>") fmt.Println("Commands:") fmt.Println(" deps List all dependencies") fmt.Println(" vulns Check for vulnerabilities") fmt.Println(" licenses Check license compliance") os.Exit(1) } switch os.Args[1] { case "deps": analyzeDependencies() case "vulns": checkVulnerabilities() case "licenses": checkLicenses() default: fmt.Println("Unknown command") os.Exit(1) } } \
Running the Tool
Save the code as main.go and run it in any Go project:
# List dependencies with checksum verification go run main.go deps 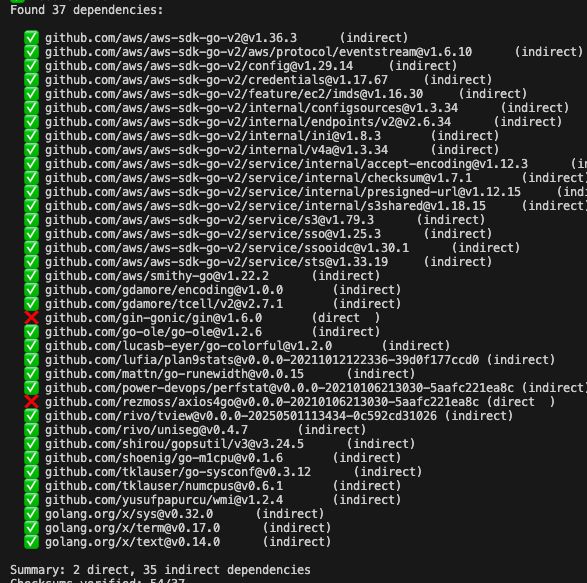
\
# Scan for vulnerabilities go run main.go vulns \ 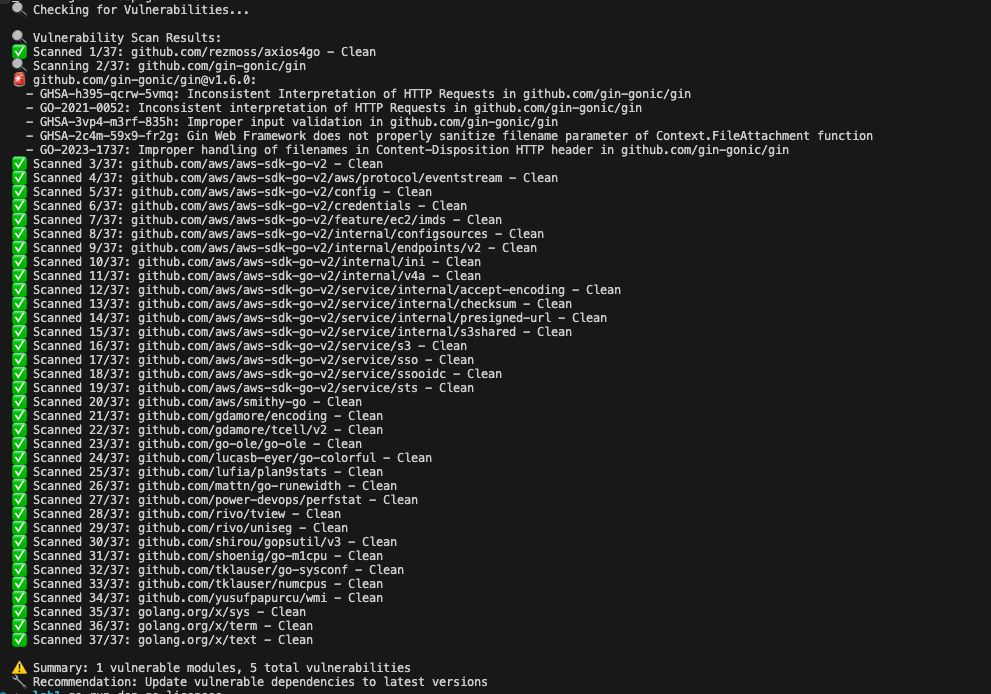
\
# Analyze licenses go run main.go licenses \ 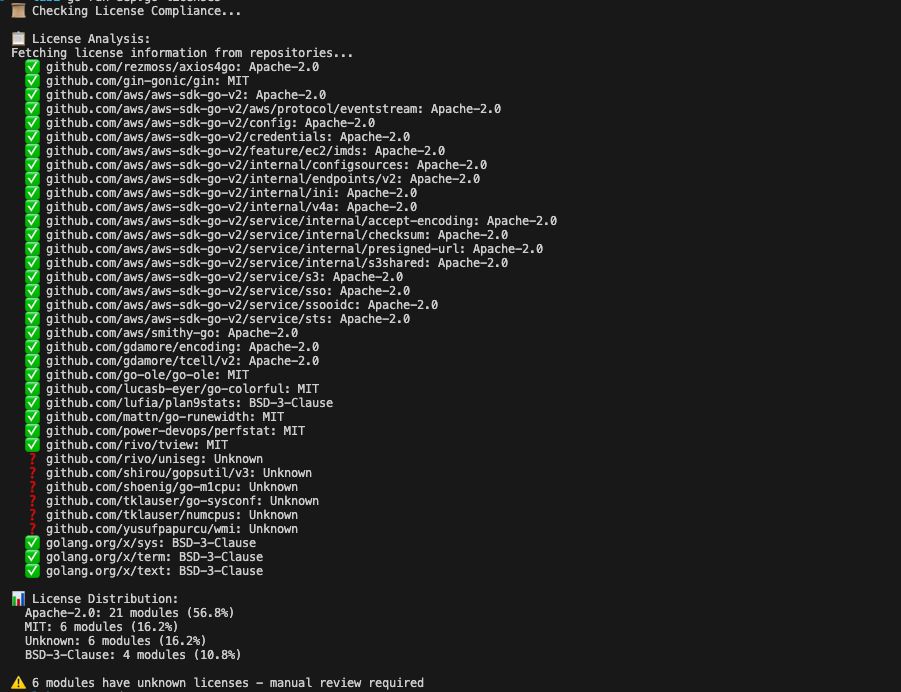
\ The output shows dependency information, vulnerability reports, and license distribution across your project's dependencies. The tool demonstrates how dependency analysis works behind the scenes, parsing module files, querying public APIs, and cross-referencing data sources.
\ This implementation covers the basic concepts but is just a starting point. Real vulnerability scanning requires comprehensive databases, sophisticated version range matching, false positive filtering, and robust error handling. License compliance tools need legal policy engines, compatibility matrices, and custom license detection beyond what GitHub's API provides. For production use, you'd want multiple data sources, caching, rate limiting, and much more thorough validation logic.
\ Happy coding ;)
\ You can find source code here https://github.com/rezmoss/go-dependency-scanner
You May Also Like

Liquid crypto funds have a DeFi problem nobody talks about

HBAR Eyes Breakout Above $0.105 With Bullish Momentum and Trend Reversal Signals

