Cracking the Constrained Number Partitioning Problem (CNP) with SPIMs
Table of Links
I. Introduction
II. Spim Performance, Advantages and Generality
III. Inherently Low Rank Problems
A. Properties of Low Rank Graphs
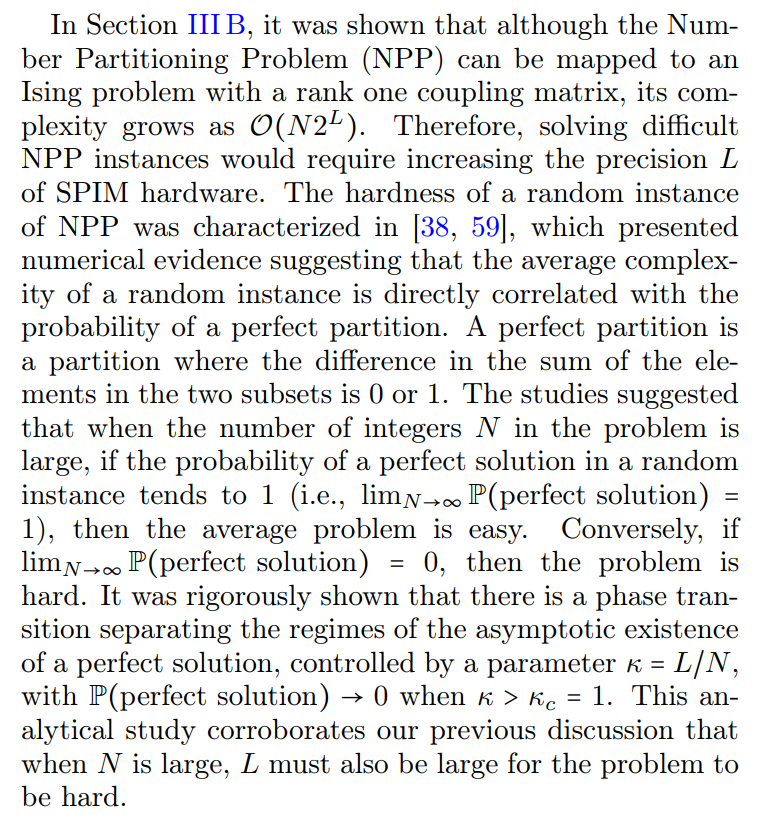
B. Weakly NP-Complete Problems and Hardware Precision Limitation
C. Limitation of Low Rank Matrix Mapping
IV. Low Rank Approximation
A. Decomposition of Target Coupling Matrix
B. How Fields Influence Ran
C. Low Rank Approximation of Coupling Matrices
D. Low-Rank Approximation of Random Coupling Matrices
E. Low Rank Approximation for Portfolio Optimization
F. Low-Rank Matrices in Restricted Boltzmann Machines
V. Constrained Number Partitioning Problem
A. Definition and Characteristics of the Constrained Number Partitioning Problem
B. Computational Hardness of Random CNP Instances
VI. Translation Invariant Problems
A. “Realistic” Spin Glass
B. Circulant Graphs
VII. Conclusions, Acknowledgements, and References
V. CONSTRAINED NUMBER PARTITIONING PROBLEM
To further illustrate the utility of SPIMs in tackling complex problems, we introduce the constrained number partitioning problem (CNP), examining its characteristics and computational challenges.
A. Definition and Characteristics of the Constrained Number Partitioning Problem
\ 
\ 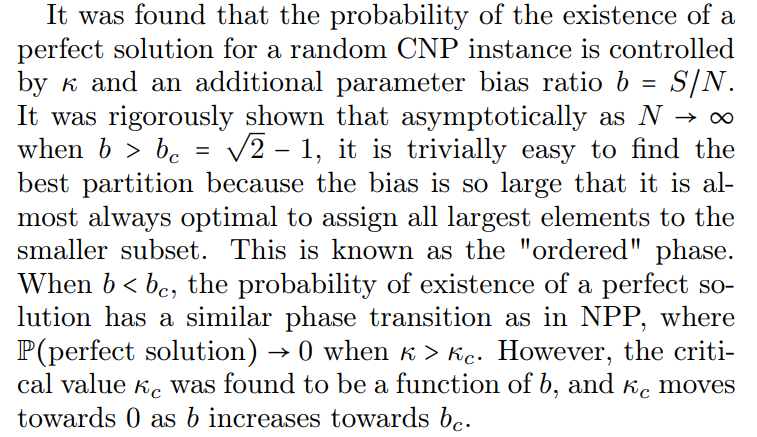
\ This suggests that CNP can be a perfect candidate for implementation on SPIM hardware because an average random CNP instance can be computationally hard even if L ≪ N (i.e. κ ≪ 1) as long as b is sufficiently close to bc. Two areas need to be explored to establish that this problem is computationally hard and suitable for implementation on SPIM. Firstly, the authors of [60] did not rigorously show that the existence of a perfect solution is correlated with the hardness of the CNP problem instance like it is in NPP. Secondly, in a system with finite size N, there will exist a non-zero value of κc,min which leads to the smallest number of precision L required for the average problem to be hard. This value is obtained when bias ratio b is as close as possible to bc given that S must be an even or odd integer depending on N. Finite-size effects are likely to make the transition between the easy and the hard phase gradual, with an intermediate region where the probability of having a perfect solution is close to neither 0 nor 1. In the following subsection, we will numerically investigate this phase transition with a finitely sized system and understand the precision requirement for a moderately sized CNP problem that is still computationally hard.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Richard Zhipeng Wang, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom;
(2) James S. Cummins, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom;
(3) Marvin Syed, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom;
(4) Nikita Stroev, Department of Physics of Complex Systems, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100, Israel;
(5) George Pastras, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece;
(6) Jason Sakellariou, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece;
(7) Symeon Tsintzos, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece and UBITECH ltd, 95B Archiepiskopou Makariou, CY 3020 Limassol, Cyprus;
(8) Alexis Askitopoulos, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece and UBITECH ltd, 95B Archiepiskopou Makariou, CY 3020 Limassol, Cyprus;
(9) Daniele Veraldi, Department of Physics, University Sapienza, Piazzale Aldo Moro 5, Rome 00185, Italy;
(10) Marcello Calvanese Strinati, Research Center Enrico Fermi, Via Panisperna 89A, 00185 Rome, Italy;
(11) Silvia Gentilini, Institute for Complex Systems, National Research Council (ISC-CNR), Via dei Taurini 19, 00185 Rome, Italy;
(12) Calvanese Strinati, Research Center Enrico Fermi, Via Panisperna 89A, 00185 Rome, Italy
(13) Davide Pierangeli, Institute for Complex Systems, National Research Council (ISC-CNR), Via dei Taurini 19, 00185 Rome, Italy;
(14) Claudio Conti, Department of Physics, University Sapienza, Piazzale Aldo Moro 5, Rome 00185, Italy;
(15) Natalia G. Berlof, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom (N.G.Berloff@damtp.cam.ac.uk).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like
FF Technical Analysis Mar 1

Buterin pushes Layer 2 interoperability as cornerstone of Ethereum’s future
