Candidate Stars and Proper Motions: Uncovering the Origin of the Galactic Tadpole's Tail
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
-
Faraday Rotation and Faraday Synthesis
-
Dara & Instruments
3.1. CHIME and GMIMS surveys and 3.2. CHIME/GMIMS Low Band North
3.3. DRAO Synthesis Telescope Observations
3.4. Ancillary Data Sources
-
Features of the Tadpole
4.1. Morphology in single-frequency images
4.2. Faraday depths
4.3. Faraday complexity
4.4. QU fitting
4.5. Artifacts
-
The Origin of the Tadpole
5.1. Neutral Hydrogen Structure
5.2. Ionized Hydrogen Structure
5.3. Proper Motions of Candidate Stars
5.4. Faraday depth and electron column
-
Summary and Future Prospects
\ APPENDIX
A. RESOLVED AND UNRESOLVED FARADAY COMPONENTS IN FARADAY SYNTHESIS
B. QU FITTING RESULTS
\ REFERENCES
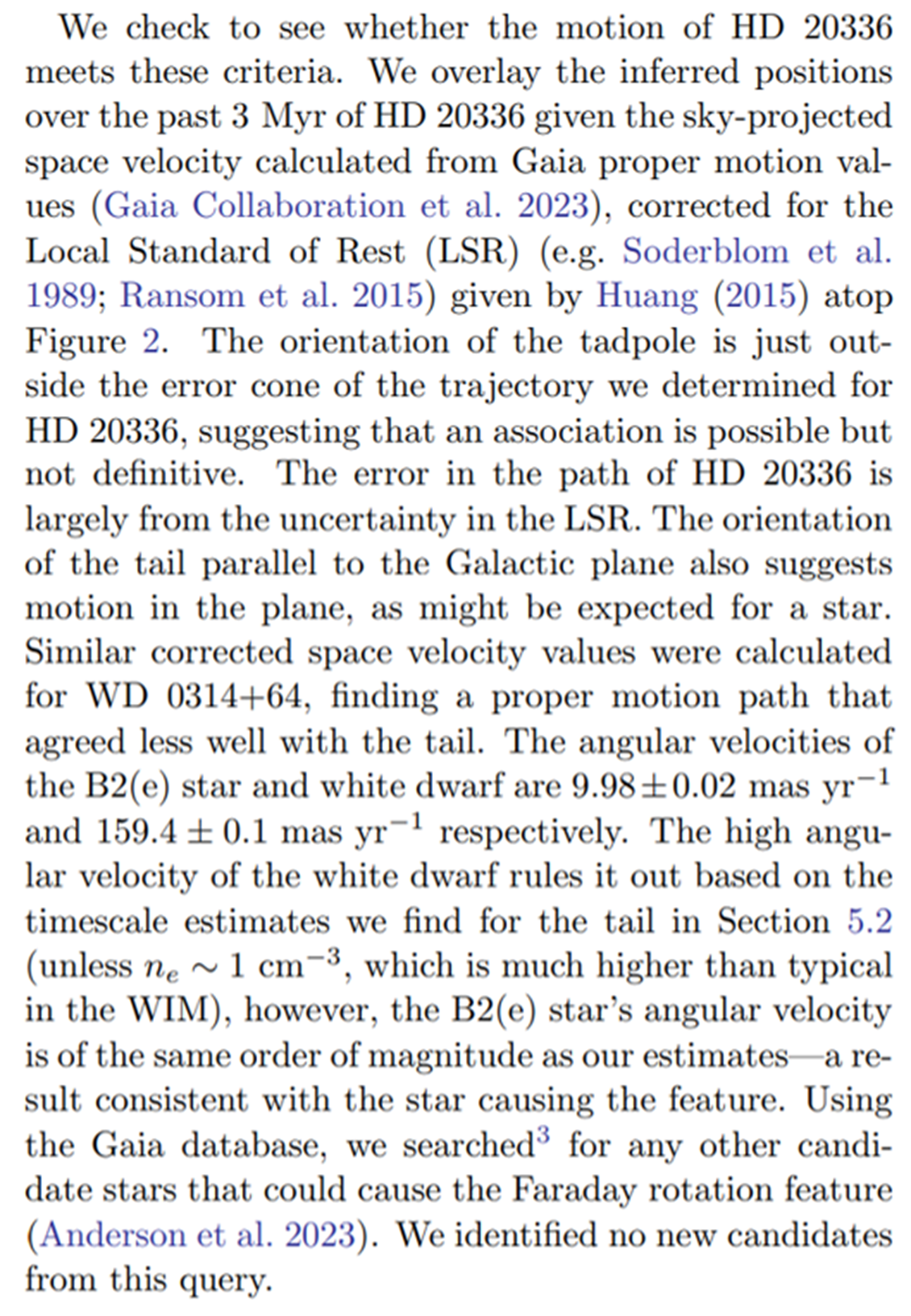
5.3. Proper Motions of Candidate Stars
Previous studies of feature G137+7 considered the circular region to be a result of a Str¨omgren sphere of the B2(e) star HD 20336, or alternatively, a relic Str¨omgren sphere from the white dwarf WD 0314+64, both of which lay within the head of the tadpole (Verschuur 1968; Iacobelli et al. 2013).
\ We hypothesize that the tail of the tadpole is a trail of ionized gas behind a suitable star, and should indicate motion related to the feature, potentially in the fashion suggested by Haverkorn et al. (2003) with an elongated Str¨omgren sphere. The tail may be similar to tails associated with planetary nebulae (Ransom et al. 2010, 2015), yielding estimates of the timescales for the interactions of planetary nebulae and the ISM. For a star to be considered a strong candidate for the tadpole, the characteristics we observe require it to be a hot star (Type O or B) with a proper motion comparable to our calculations based on the recombination time (see section 5.2) and direction aligned with the orientation of the tail.
\ 
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Nasser Mohammed, Department of Computer Science, Math, Physics, & Statistics, University of British Columbia, Okanagan Campus, Kelowna, BC V1V 1V7, Canada and Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Research Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, National Research Council Canada, PO Box 248, Penticton, BC V2A 6J9, Canada;
(2) Anna Ordog, Department of Computer Science, Math, Physics, & Statistics, University of British Columbia, Okanagan Campus, Kelowna, BC V1V 1V7, Canada and Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Research Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, National Research Council Canada, PO Box 248, Penticton, BC V2A 6J9, Canada;
(3) Rebecca A. Booth, Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW, Calgary, Alberta, T2N 1N4, Canada;
(4) Andrea Bracco, INAF – Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi 5, 50125 Firenze, Italy and Laboratoire de Physique de l’Ecole Normale Superieure, ENS, Universit´e PSL, CNRS, Sorbonne Universite, Universite de Paris, F-75005 Paris, France;
(5) Jo-Anne C. Brown, Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW, Calgary, Alberta, T2N 1N4, Canada;
(6) Ettore Carretti, INAF-Istituto di Radioastronomia, Via Gobetti 101, 40129 Bologna, Italy;
(7) John M. Dickey, School of Natural Sciences, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Tas 7000 Australia;
(8) Simon Foreman, Department of Physics, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287, USA;
(9) Mark Halpern, Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, 6224 Agricultural Road, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z1 Canada;
(10) Marijke Haverkorn, Department of Astrophysics/IMAPP, Radboud University, PO Box 9010, 6500 GL Nijmegen, The Netherlands;
(11) Alex S. Hill, Department of Computer Science, Math, Physics, & Statistics, University of British Columbia, Okanagan Campus, Kelowna, BC V1V 1V7, Canada and Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Research Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, National Research Council Canada, PO Box 248, Penticton, BC V2A 6J9, Canada;
(12) Gary Hinshaw, Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, 6224 Agricultural Road, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z1 Canada;
(13) Joseph W. Kania, Department of Physics and Astronomy, West Virginia University, P.O. Box 6315, Morgantown, WV 26506, USA and Center for Gravitational Waves and Cosmology, West Virginia University, Chestnut Ridge Research Building, Morgantown, WV 26505, USA;
(14) Roland Kothes, Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Research Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, National Research Council Canada, PO Box 248, Penticton, BC V2A 6J9, Canada;
(15) T.L. Landecker, Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Research Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, National Research Council Canada, PO Box 248, Penticton, BC V2A 6J9, Canada;
(16) Joshua MacEachern, Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, 6224 Agricultural Road, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z1 Canada;
(17) Kiyoshi W. Masui, MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA and Department of Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA;
(18) Aimee Menard, Department of Computer Science, Math, Physics, & Statistics, University of British Columbia, Okanagan Campus, Kelowna, BC V1V 1V7, Canada and Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Research Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, National Research Council Canada, PO Box 248, Penticton, BC V2A 6J9, Canada;
(19) Ryan R. Ransom, Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Research Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, National Research Council Canada, PO Box 248, Penticton, BC V2A 6J9, Canada and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Okanagan College, Kelowna, BC V1Y 4X8, Canada;
(20) Wolfgang Reich, Max-Planck-Institut fur Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hugel 69, 53121 Bonn, Germany;(21) Patricia Reich, 16
(22) J. Richard Shaw, Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, 6224 Agricultural Road, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z1 Canada
(23) Seth R. Siegel, Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, 31 Caroline Street N, Waterloo, ON N25 2YL, Canada, Department of Physics, McGill University, 3600 rue University, Montreal, QC H3A 2T8, Canada, and Trottier Space Institute, McGill University, 3550 rue University, Montreal, QC H3A 2A7, Canada;
(24) Mehrnoosh Tahani, Banting and KIPAC Fellowships: Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology (KIPAC), Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA;
(25) Alec J. M. Thomson, ATNF, CSIRO Space & Astronomy, Bentley, WA, Australia;
(26) Tristan Pinsonneault-Marotte, Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, 6224 Agricultural Road, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z1 Canada;
(27) Haochen Wang, MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA and Department of Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA;
(28) Jennifer L. West, Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Research Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, National Research Council Canada, PO Box 248, Penticton, BC V2A 6J9, Canada;
(29) Maik Wolleben, Skaha Remote Sensing Ltd., 3165 Juniper Drive, Naramata, BC V0H 1N0, Canada.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
[3] We used the capabilities of a natural language model to construct ADQL search queries of the Gaia archive (OpenAI 2023).
You May Also Like

Shocking OpenVPP Partnership Claim Draws Urgent Scrutiny

Bitcoin Has Taken Gold’s Role In Today’s World, Eric Trump Says
