Smarter Fine-Tuning for NLU and NLG Tasks
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Background
2.1 Mixture-of-Experts
2.2 Adapters
-
Mixture-of-Adaptations
3.1 Routing Policy
3.2 Consistency regularization
3.3 Adaptation module merging and 3.4 Adaptation module sharing
3.5 Connection to Bayesian Neural Networks and Model Ensembling
-
Experiments
4.1 Experimental Setup
4.2 Key Results
4.3 Ablation Study
-
Related Work
-
Conclusions
-
Limitations
-
Acknowledgment and References
Appendix
A. Few-shot NLU Datasets B. Ablation Study C. Detailed Results on NLU Tasks D. Hyper-parameter
4 Experiments
4.1 Experimental Setup
Dataset. We perform experiments on a wide range of tasks including eight natural language understanding (NLU) tasks in the General Language Understanding Evaluation (GLUE) benchmark (Wang et al., 2019) and three natural language generation (NLG) tasks, namely, E2E (Novikova et al., 2017), WebNLG (Gardent et al., 2017) and DART (Nan et al., 2020). For the NLU and NLG tasks, we follow the same setup as (Houlsby et al., 2019) and (Li and Liang, 2021; Hu et al., 2021), respectively.
\ Baselines. We compare AdaMix to full model fine-tuning and several state-of-the-art parameterefficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods, namely, Pfeiffer Adapter (Pfeiffer et al., 2021), Houlsby Adapter (Houlsby et al., 2019), BitFit (Zaken et al., 2021), Prefix-tuning (Li and Liang, 2021), UNIPELT (Mao et al., 2021) and LoRA (Hu et al., 2021). We use BERT-base (Devlin et al., 2019) and RoBERTa-large (Liu et al., 2019) as encoders for NLU tasks (results in Table 1 and Table 2), and GPT-2 (Brown et al., 2020) for NLG tasks (results in Table 3).
\ AdaMix implementation details. We implement AdaMix in Pytorch and use Tesla V100 gpus for experiments with detailed hyper-parameter configurations presented in Section D in Appendix. AdaMix with adapters uses a dimension of 16 and 48 using BERT-base and RoBERTa-large encoders following the setup of (Hu et al., 2021; Mao et al., 2021) for fair comparison. AdaMix with LoRA uses rank r = 4 following the setup of (Hu et al., 2021) to keep the same number of adaptation parameters during inference. The number of adaptation modules in AdaMix is set to 4 for all the tasks and encoders unless otherwise specified. The impact of adapter dimension and number of adaptation modules for NLU tasks are investigated in Table 9 and 10. For most of the experiments and ablation analysis, we report results from AdaMix with adapters for NLU tasks. For demonstrating the generalizability of our framework, we report results from AdaMix with LoRA (Hu et al., 2021) as the underlying PEFT mechanism for NLG tasks.
\
4.2 Key Results
4.2.1 NLU Tasks
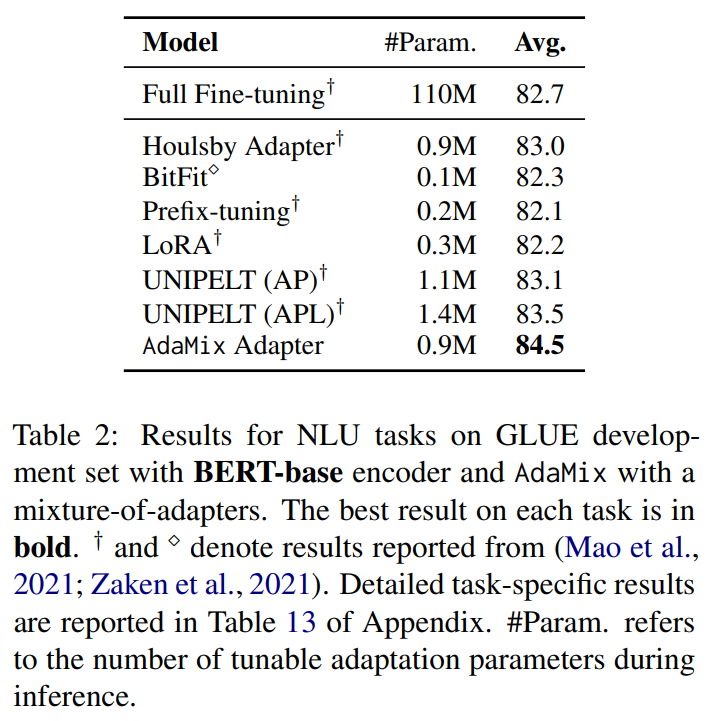
\ Tables 1 and 2 show the performance comparison among PEFT models with RoBERTa-large and BERT-base encoders respectively. Fully fine-tuned
\ \ 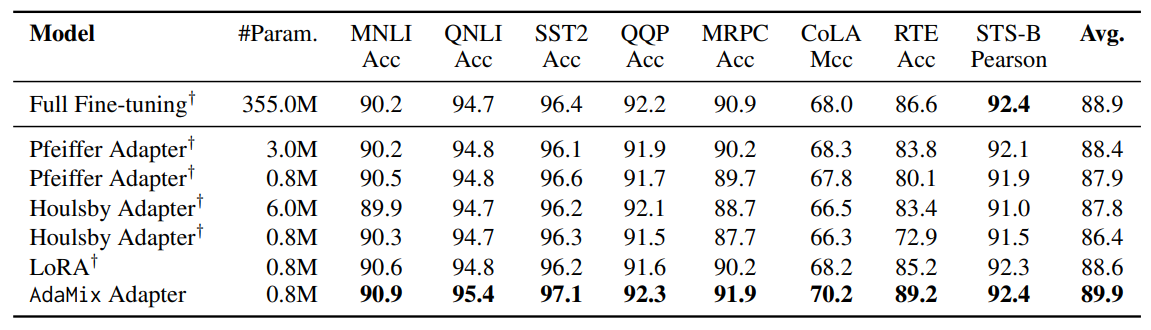
\ \ RoBERTa-large and BERT-base provide the ceiling performance. We observe AdaMix with a mixture-of-adapters to significantly outperform other state-of-the-art baselines on most tasks with different encoders. AdaMix with adapters is the only PEFT method which outperforms full model fine-tuning on all the tasks and on average score.
\ \ 
\ \ 4.2.2 NLG Tasks
\ AdaMix leverages mixture of adaptations to improve over underlying PEFT method as demonstrated in Table 3 for E2E NLG i.e. AdaMix with LoRA and AdaMix with adapters outperform LoRA (Hu et al., 2021) and adapters (Houlsby et al., 2019) respectively. We report results on DART and WebNLG in Tables 4 and 5 in Appendix.
\ 4.2.3 Few-shot NLU
\ In contrast to the fully supervised setting in the above experiments, we also perform few-shot experiments on six GLUE tasks following the same setup (e.g., shots, train and test splits) and evaluation as in (Wang et al., 2021). Detailed experimental configuration presented in Section A of Appendix. AdaMix uses a mixture-of-adapters with prompt-based fine-tuning (Gao et al., 2021).
\ Table 6 shows the performance comparison among different PEFT methods with |K| = 30 labeled examples with RoBERTa-large as frozen encoder. We observe significant performance gap for most PEFT methods with full model promptbased fine-tuning i.e. with all model parameters being updated. AdaMix with adapters outperforms full model tuning performance for few-shot NLU similar to that in the fully supervised setting. Note that AdaMix and LiST (Wang et al., 2021) use similar adapter design with prompt-based fine-tuning.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Yaqing Wang, Purdue University (wang5075@purdue.edu);
(2) Sahaj Agarwal, Microsoft (sahagar@microsoft.com);
(3) Subhabrata Mukherjee, Microsoft Research (submukhe@microsoft.com);
(4) Xiaodong Liu, Microsoft Research (xiaodl@microsoft.com);
(5) Jing Gao, Purdue University (jinggao@purdue.edu);
(6) Ahmed Hassan Awadallah, Microsoft Research (hassanam@microsoft.com);
(7) Jianfeng Gao, Microsoft Research (jfgao@microsoft.com).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

The Channel Factories We’ve Been Waiting For

XRP Price Prediction: Can Ripple Rally Past $2 Before the End of 2025?
