Solving 3D Segmentation’s Biggest Bottleneck
:::info Authors:
(1) George Tang, Massachusetts Institute of Technology;
(2) Krishna Murthy Jatavallabhula, Massachusetts Institute of Technology;
(3) Antonio Torralba, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
:::
Table of Links
Abstract and I. Introduction
II. Background
III. Method
IV. Experiments
V. Conclusion and References
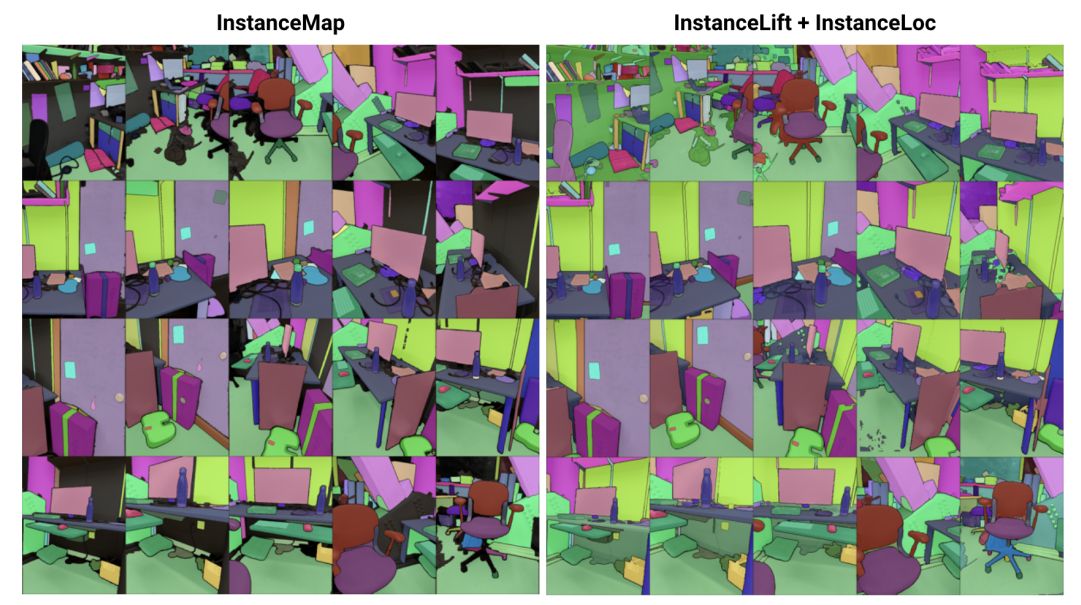
\ 
\ Abstract— We tackle the problem of learning an implicit scene representation for 3D instance segmentation from a sequence of posed RGB images. Towards this, we introduce 3DIML, a novel framework that efficiently learns a label field that may be rendered from novel viewpoints to produce view-consistent instance segmentation masks. 3DIML significantly improves upon training and inference runtimes of existing implicit scene representation based methods. Opposed to prior art that optimizes a neural field in a self-supervised manner, requiring complicated training procedures and loss function design, 3DIML leverages a two-phase process. The first phase, InstanceMap, takes as input 2D segmentation masks of the image sequence generated by a frontend instance segmentation model, and associates corresponding masks across images to 3D labels. These almost view-consistent pseudolabel masks are then used in the second phase, InstanceLift, to supervise the training of a neural label field, which interpolates regions missed by InstanceMap and resolves ambiguities. Additionally, we introduce InstanceLoc, which enables near realtime localization of instance masks given a trained label field and an offthe-shelf image segmentation model by fusing outputs from both. We evaluate 3DIML on sequences from the Replica and ScanNet datasets and demonstrate 3DIML’s effectiveness under mild assumptions for the image sequences. We achieve a large practical speedup over existing implicit scene representation methods with comparable quality, showcasing its potential to facilitate faster and more effective 3D scene understanding.
I. INTRODUCTION
Intelligent agents require scene understanding at the object level to effectively carry out context-specific actions such as navigation and manipulation. While segmenting objects from images has seen remarkable progress with scalable models trained on internet-scale datasets [1], [2], extending such capabilites to the 3D setting remains challenging.
\ In this work, we tackle the problem of learning a 3D scene representation from posed 2D images that factorizes the underlying scene into its set of constituent objects. Existing approaches to tackle this problem have focused on training class-agnostic 3D segmentation models [3], [4], requiring large amounts of annotated 3D data, and operating directly over explicit 3D scene representations (e.g., pointclouds). An alternate class of approaches [5], [6] has instead proposed to directly lift segmentation masks from off-the-shelf instance segmentation models into implicit 3D representations, such as neural radiance fields (NeRF) [7], enabling them to render 3D-consistent instance masks from novel viewpoints.
\ However, the neural field-based approaches have remained notoriously difficult to optimize, with [5] and [6] taking several hours to optimize for low-to-mid resolution images (e.g., 300 × 640). In particular, Panoptic Lifting [5] scales cubicly with the number of objects in the scene preventing it from being applied to scenes with hundreds of objects, while Contrastively Lifting [6] requires a complicated, multi-stage training procedure, hindering practicality for use in robotics applications.
\ To this end, we propose 3DIML, an efficient technique to learn 3D-consistent instance segmentation from posed RGB images. 3DIML comprises two phases: InstanceMap and InstanceLift. Given view-inconsistent 2D instance masks extracted from the RGB sequence using a frontend instance segmentation model [2], InstanceMap produces a sequence of view-consistent instance masks. To do so, we first associate masks across frames using keypoint matches between similar pairs of images. We then use these potentially noisy associations to supervise a neural label field, InstanceLift, which exploits 3D structure to interpolate missing labels and resolve ambiguities. Unlike prior work, which requires multistage training and additional loss function engineering, we use a single rendering loss for instance label supervision, enabling the training process to converge significantly faster. The total runtime of 3DIML, including InstanceMap, takes 10-20 minutes, as opposed to 3-6 hours for prior art.
\ In addition, we devise InstaLoc, a fast localization pipeline that takes in a novel view and localizes all instances segmented in that image (using a fast instance segmentation model [8]) by sparsely querying the label field and fusing the label predictions with extracted image regions. Finally, 3DIML is extremely modular, and we can easily swap components of our method for more performant ones as they become available.
\ To summarize, our contributions are:
\ • An efficient neural field learning approach that factorizes a 3D scene into its constituent objects
\ • A fast instance localization algorithm that fuses sparse queries to the trained label field with performant image instance segmentation models to generate 3D-consistent instance segmentation masks
\ • An overall practical runtime improvement of 14-24× over prior art benchmarked on a single GPU (NVIDIA RTX 3090)
II. BACKGROUND
2D segmentation: The prevalence of vision transformer architecture and the increasing scale of image datasets have resulted in a series of state-of-the-art image segmentation models. Panoptic and Contrastive Lifting both lift panoptic segmentation masks produced by Mask2Former [1] to 3D by learning a neural field. Towards open-set segmentation, segment anything (SAM) [2] achieves unprecedented performance by training on a billion masks over 11 million images. HQ-SAM [9] improves upon SAM for fine-grained masks. FastSAM [8] distills SAM into a CNN architecture and achieves similar performance while being orders of magnitude faster. In this work, we use GroundedSAM [10], [11], which refines SAM to produce object-level, as opposed to part-level segmentation masks.
\ Neural fields for 3D instance segmentation: NeRFs are implicit scene representations that can accurately encode complex geometry, semantics, and other modalities, as well as resolve viewpoint inconsistent supervision [12]. Panoptic lifting [5] constructs semantics and instances branches on an efficient variant of NeRF, TensoRF [13], utilizing a Hungarian matching loss function to assign learned instance masks to surrogate object IDs given reference view-inconsistent masks. This scales poorly with increasing number of objects (owing to the cubic complexity of Hungarian matching). Contrastive lifting [6] addresses this by instead employing contrastive learning on scene features, with positive and negative relations determined by whether or not they project onto the same mask. In addition, contrastive lifting requires a slow-fast clustering-based loss for stable training, leading to faster performance than panoptic lifting but requires multiple stages of training, leading to slow convergence. Concurrently to us, Instance-NeRF [14] directly learn a label field, but they based their mask association on utilizing NeRF-RPN [15] to detect objects in a NeRF. Our approach, on the contrary, allows scaling to very high image resolutions while requiring only a small number (40-60) of neural field queries to render segmentation masks.
\ Structure from Motion: During mask association in InstanceMap, we take inspiration from scalable 3D reconstruction pipelines such as hLoc [16], including the use of visual descriptors for matching image viewpoints first, then applying keypoint matching as a preliminary for mask association. We utilize LoFTR [17] for keypoint extraction and matching.
\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed (Attribution 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Stephen Gregory named binance us ceo as exchange targets expansion in US crypto market

The Growing World of Medical Aesthetics: Enhancing Beauty Through Science and Innovation
