Why Ethics Fail in Open Source Communities
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Background and Related Work
-
Study of Unethical Behavior in OSS
3.1 RQ1: Types of unethical behavior
3.2 RQ2: Affected software artifacts
-
Methodology
4.1 Modeling via SWRL rules
4.2 Automatic detection of unethical behavior
-
Evaluation
-
Discussion and Implications
-
Threats to Validity
-
Conclusion and References
2 BACKGROUND AND RELATED WORK
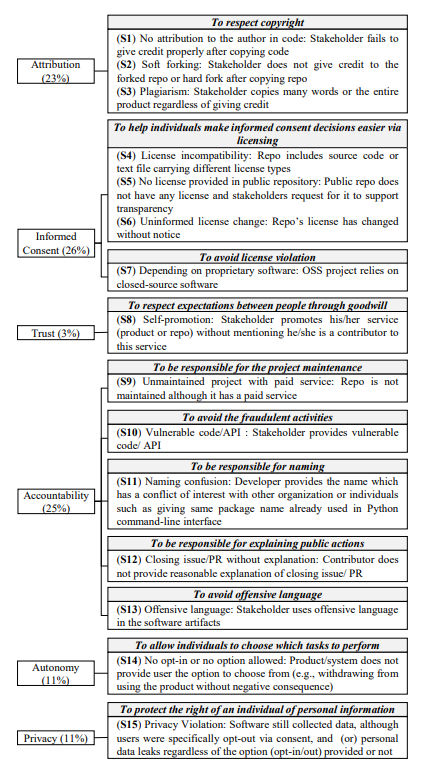
Ethical Principles. Prior work on ethical principles in OSS projects mainly studied six aspects: (1) accountability, (2) attribution, (3) autonomy, (4) informed consent, (5) privacy, and (6) trust [46, 51, 63, 77]. Accountability means that an individual is accountable for his/her actions. Attribution (e.g., copyright) means giving credit to authors when the credit is due. Autonomy allows an individual to decide, plan, and act to achieve their goals. In OSS projects, individuals inherently have autonomy because they can choose which tasks to perform but may gain or lose autonomy once they agree to participate. Informed Consent is an agreement between the individual and the institution maintaining ethical values, such as autonomy. Privacy is a right of a stakeholder on what information another stakeholder can obtain and communicate to others. Trust refers to expectations between people through goodwill.
\ Web Ontology Language (OWL) is a standard ontology language endorsed by the W3C to construct an OWL knowledge model [2, 38, 66]. It is a semantic web language designed to model rich and complex knowledge about things, groups of things, and relations between things. Knowledge expressed in OWL can be exploited by computer programs, e.g., to verify the consistency of that knowledge or to make implicit knowledge explicit. Thus, we design our tool based on ontology engineering.
\ Semantic Web Rule Language (SWRL) is a language that combines OWL and Rule Markup Language (RuleML), which can be used to express Horn-like rules and logic [3]. SWRL rules are used to infer new knowledge regarding the individual (instance) by chains of properties. We choose to model the unethical behavior in OSS projects using SWRL because (1) its expressiveness [80] is well-suited for modeling unethical behavior that involves different GitHub attributes and diverse types of software artifacts, and (2) it has been widely used to model concepts such as privacy for medical data [45] and access control policy [43, 62].
\ Related Work. Prior work studies focus on multiple aspects of ethical concerns for several domains.
\ Ethical concerns in Software Engineering research. Several studies focus on ethical concerns for empirical studies in software engineering. Badampudi conducted a study about the reports of the ethical considerations in Software Engineering publications [39]. Andrews et al. illustrated some of the common approaches to encourage ethical behavior and their limits for demanding ethical behavior between researchers’ duty and their publishing as well as the companies’ and individuals’ integrity [37]. Singer et al. introduced their work as a practical guide to ethical research involving humans in software engineering [75]. Our study is complementary to these studies as the types of unethical behavior discovered in our study points to potential violations of ethical principles that software engineering researchers should consider when their evaluations of automated tools use OSS projects.
\ Studies on ethical concerns in OSS. Existing studies of OSS projects focus on issues related to gender bias [59, 76], fairness of the code review process [53], similar code in Stack Overflow and GitHub [41, 83], and software licensing [64] [78] [79]. Studies relating to gender bias in GitHub [59, 76] aims to address the obstacles in improving gender diversity. Meanwhile, a study of a large industrial open source ecosystem (OpenStack) shows that unfairness is “starting to be perceived as an issue” in OSS [53]. Several studies investigated code clones between code snippets from Stack Overflow and projects on GitHub and found a considerable number of non-trivial clones [41, 83]. Although these studies also explored how GitHub stakeholder’s reference code was copied or adapted from Stack Overflow answers without giving proper credits to the authors (who wrote the code), they did not consider the scenario where the stakeholder of the code snippets used in GitHub is the same as the owner of the code in Stack Overflow (in this case, a credit is not needed). Several techniques have been proposed for the automated detection of license incompatibility [52, 60, 82]. While our study identifies license incompatibility as an unethical behavior, it includes more diverse types of issues related to licensing (e.g., missing license, and uninformed license change). Nevertheless, all existing studies on ethical concerns in OSS projects only focus on a few aspects of ethical principles, and they did not conduct analysis of the diverse types of ethical violations in OSS projects in GitHub.
3 STUDY OF UNETHICAL BEHAVIOR IN OSS
To address the two research questions introduced in Section 1, we conducted a study of unethical behavior in OSS projects. Although using a mixed-method research methodology (e.g., adding a survey that asks developers for their opinions on each unethical behavior) would provide stronger empirical evidences, we choose to observe unethical behavior passively by reading developers’ discussions to avoid spamming developers [40].
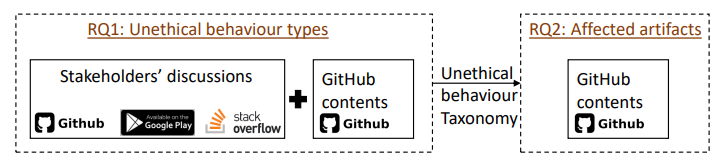
Study methodology. Figure 1 gives an overview of our study. We built a crawler that crawls GitHub issues by searching using the keyword “ethic”, concepts related to unethics, and synonyms for “un/ethical” (i.e., “unprofessional”, “unfair”, “right”, “proper”, and “principle”) via the GitHub API. We then manually checked the results to exclude issues that do not have a clear description or are unrelated to ethical behavior. After getting the relevant issues, we manually analyzed the stakeholders’ discussions using thematic analysis [48], an approach for identifying patterns (or “themes”) within data. Specifically, the first two authors of the paper followed five steps: (1) we carefully read and analyzed all discussions in the issue to understand what stakeholders discussed about and how they described unethical behavior, identifying the key sentences and phrases which represent unethical behavior. (2) We coded the key sentences and phrases in each issue by highlighting sections of text, and coming up with shorthand labels or “codes” to describe their content. We reread the related key sentences, phrases, and their surrounding context discussions to generate initial codes. New codes can be added as we go through the discussions. After we have been through the discussions, we collate together all the key sentences and phrases into groups identified by codes. These codes allow us to gain a condensed overview of the main points and common meanings that recur throughout the discussions. (3) After generating initial codes, we looked over the created codes, aggregated codes with similar meaning into groups, and started coming up with themes for those groups. Themes are generally broader than codes. (4) With the initial set of themes in the previous step, we reviewed all themes to look for chances to merge similar themes or sub-theme. (5) We finalized the themes by providing clear definitions. To reduce research bias, steps (1) to (4) were conducted independently by the first two authors of the paper. Then, a sequence of meetings was held to resolve conflicts and define the final themes in step (5). Both authors are PhD students with more than two years of research experience. The first author had taken a computer ethics course, while the second author had experience in OSS development. For RQ1, we develop a taxonomy of the types of unethical behavior in OSS projects and its underlying principles. Before following the steps of thematic analysis, we reviewed ethical principles from prior studies [46, 51, 63, 77], and identified six ethical principles guiding the action of stakeholders in OSS projects, including: (1) accountability, (2) attribution, (3) autonomy, (4) informed consent, (5) privacy, and (6) trust (i.e., we exclude “welfare” because it is related to fair wages which is generally not discussed in our studied issues). We use these six underlying ethical principles and their corresponding ethical guidelines as guidance for merging relevant themes. For RQ2, we first obtained the initial “themes” (i.e., software artifacts) based on prior work [58, 74]. Then, via an iterative process of (1) reading 316 issues with their corresponding types of unethical behavior, and (2) refining the themes via thematic analysis, we derived 18 types of affected software artifacts.
\ 
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Hsu Myat Win, Southern University of Science and Technology, China (11960003@mail.sustech.edu.cn);
(2) Haibo Wang, Southern University of Science and Technology, China (wanghb2020@mail.sustech.edu.cn);
(3) Shin Hwei Tan, a corresponding author from Southern University of Science and Technology, China (tansh3@sustech.edu.cn).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Adoption Leads Traders to Snorter Token

Lovable AI’s Astonishing Rise: Anton Osika Reveals Startup Secrets at Bitcoin World Disrupt 2025
