The WormHole Algorithm for Approximate Shortest Paths in Large Graphs
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
1.1 Our Contribution
1.2 Setting
1.3 The algorithm
-
Related Work
-
Algorithm
3.1 The Structural Decomposition Phase
3.2 The Routing Phase
3.3 Variants of WormHole
-
Theoretical Analysis
4.1 Preliminaries
4.2 Sublinearity of Inner Ring
4.3 Approximation Error
4.4 Query Complexity
-
Experimental Results
5.1 WormHole𝐸, WormHole𝐻 and BiBFS
5.2 Comparison with index-based methods
5.3 WormHole as a primitive: WormHole𝑀
References
3 ALGORITHM
WormHole utilizes insights about the structure of real world networks to cleverly decompose the graph and calculate approximate shortest paths. We discuss the algorithm and various steps in detail in this section; our two main components are a sublinear decomposition procedure, adapted from the recent work of Ben-Eliezer et al [10], and a routing algorithm that takes advantage of this decomposition to find highly accurate approximate shortest paths.
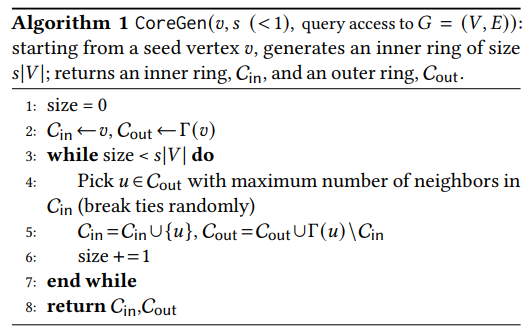
3.1 The Structural Decomposition Phase

\ We emphasize that the decomposition is performed only once, and all subsequent operations are done using this precomputed decomposition.
\ 
\
3.2 The Routing Phase
The approach is simple: assume the preprocessing phase acquires the inner ring. Upon an inquiry (𝑠,𝑡), the algorithm
\ \ 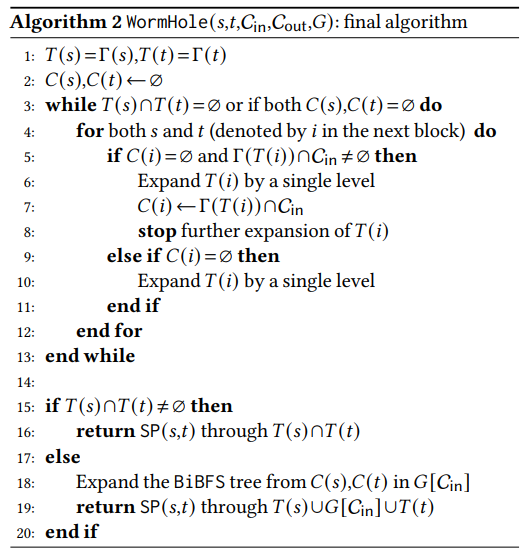
\ \ starts two BFS trees from both 𝑠 and 𝑡. It then expands the tree at each step till one of the followings happens:
\ (1) the two trees intersect, or
\ (2) the trees reach the outer ring.
\ If the search trees in the former do not intersect, WormHole mandatorily routes shortest paths through the inner ring. Once in the inner ring, it computes the exact shortest path through it.
\
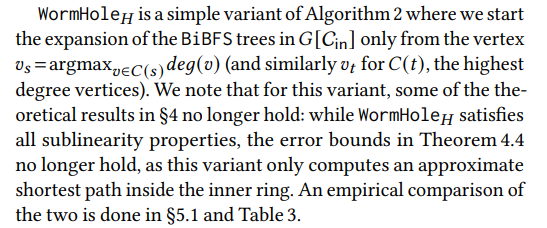
3.3 Variants of WormHole
In the default variant of Algorithm 2, WormHole𝐸, we use the bidirectional breadth-first BiBFS shortest path algorithm as a primitive in order to compute the shortest path between two inner ring vertices; see [46] for a full description of BiBFS. The theoretical analysis in §4 considers this variant.
\ \ 
\ \ In WormHole𝑀 we combine WormHole with an index-based algorithm restricted to the core. While indexing-based algorithms are quite expensive, in terms of both preprocessing and space cost, they lead to much lower times per inquiry. Therefore this variant is suitable when faster inquiry times are preferable to low space requirements. WormHole𝑀 makes the index creation cost substantially lower(compared to generating it for the entire graph) while providing speedups for answering shortest path inquiries compared to the BiBFS implementation. We discuss this briefly in §5.3 but leave a complete systematic exploration of these options for future research.
\ \ ![Figure 4: Construction of the inner and outer rings of the core; figure taken from [10]. At any point, the outer ring is the set of vertices adjacent to the inner ring. The algorithm expands the inner ring by adding to it a vertex from the outer ring that has the most neighbors in the inner ring. The image looks at two successive steps: the numbers labelling vertices in the outer ring refer to how many inner ring vertices it is adjacent to. Thus, in the second step, the vertex labelled 2 is added to the inner ring.](https://cdn.hackernoon.com/images/null-xb1347x.png)
\ \ \
:::info Authors:
(1) Talya Eden, Bar-Ilan University (talyaa01@gmail.com);
(2) Omri Ben-Eliezer, MIT (omrib@mit.edu);
(3) C. Seshadhri, UC Santa Cruz (sesh@ucsc.edu).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

US SEC approves options tied to Grayscale Digital Large Cap Fund and Cboe Bitcoin US ETF Index

Kast Stablecoin Firm Hits $600M Valuation after $80M Raise: Report
