Securing Java Microservices with Zero Trust Architecture
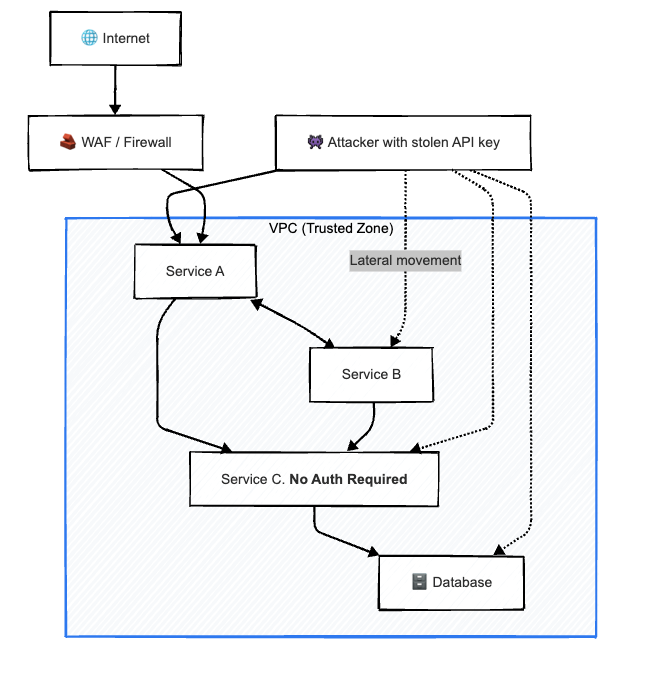
\ Suppose someone gets hold of your API key. Suddenly, they have access to everything inside your internal microservices — free roaming, no questions asked. By the time you even realize something’s wrong, they’ve already siphoned off data, exercised every permission you never meant to grant, and left you with a hefty bill and an even heavier task: rebuilding customer trust.
So how does this kind of breach even happen? In large part, it’s because most microservices assume they can trust each other simply because they sit on the same network. Not because it’s real security — but because we treat proximity like protection.
In simple terms:
In the past, with a single application and a single data store, as well as a single network perimeter, security was much simpler, as everything was running on-premises with a local data center.
However, once you switched to microservices, all of this changed. Now you have many (dozens) of applications/services, hundreds of APIs, and many different teams are releasing code each and every day. In addition, most services will communicate with other services and assume that since they are communicating across a common network, they should be able to trust each service.
Your architectural design has grown and evolved; however, your "security" thinking has not. Your home now looks like it is wide open. Anyone who can get a key for the front door can go into every room, open every drawer, and unlock every safe locker in the building.
\ 
The Philosophy That Changed The Way Of Thinking About Architecture: Zero Trust
Zero Trust is a change in the way you think about trust, not an improvement in security trends.
It used to be, "Trust but Verify." It isn't anymore. This principle can be summarized simply as, "Don't ever trust; always verify."
All connections (user, service & internal network) must identify themselves, state what they can do, and say if the connection is safe. No exceptions.
Basically, it looked like this for the microservices Mutual TLS all the way: All of a service connection's communication is confirmed by the use of mutual TLS (mTLS) before any of the parties can communicate with each other.
API-based permissions are replacing firewall-based permissions. Each call/transaction is being verified login.
We’ve had to rethink how we build and how we trust anything inside our architecture to meet Zero Trust principles — but in doing so, we’ve ended up with a far safer system.
\
\ \
Zero Trust: Not Optional — Not Anymore
Are you running microservices without Zero Trust? If you wait too long, your business won’t just fall behind — it may hit a wall. Now is the time to start, long before your systems stall out. Our own rollout wasn’t flawless. We dealt with outages, pushed through developer resistance, and learned a few hard lessons along the way. But after six months, we shipped it — and proved that security isn’t something you stumble into. It’s something you design for, deliberately, from day one.
Solution/Tools
Here are some of the technologies we used to transition our trust model, which is based on networks, to an identity-based trust model:
- For Service Identity: SPIFFE/SPIRE
- service mesh/service-to-service encrypted communications: Istio mTLS
- Code of policies: Open Policy Agent (openpolicyagent.org)
- Active secrets management, Dynamic secrets management: HashiCorp Vault
- Dynamic threat analysis: Falco.
- Rate-Limiting, Audit Logging, OAuth2: Kong API Gateway
Optimization
- Decisions made by OPA are cached (Redis/Caffeine).
- Connection Pooling for mTLS
- Audit logs of Kafka are asynchronously rewritten.
Next, I will describe the implementation of a Zero Trust model for my Java-based microservice applications, including how identities are verified, mTLS is used, and secrets are rotated within the application, as well as provide real-world examples of code and configurations used.
JWT Using Identity Service
Each service acquires its identity. We generate and sign a JWT using RSA-256 keys.
```
java package com.zero.trust.common; import com.auth0.jwt.JWT; import com.auth0.jwt.algorithms.Algorithm; import java.security.; import java.security.interfaces.; import java.util.*; public class IdentityServiceManager {
private final String serviceName; private final Algorithm algorithm; public IdentityServiceManager(String serviceName) { this.serviceName = serviceName; try { KeyPairGenerator gen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); gen.initialize(2048); KeyPair pair = gen.generateKeyPair(); this.algorithm = Algorithm.RSA256( (RSAPublicKey) pair.getPublic(), (RSAPrivateKey) pair.getPrivate()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException("KeyPair creation failed", e); } } public String generateTokenData() { return JWT.create() .withIssuer(serviceName) .withClaim("service", serviceName) .withExpiresAt(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + 3600_000)) .sign(algorithm); } public boolean verifyTokenData(String token) { try { JWT.require(algorithm).build().verify(token); return true; } catch (Exception e) { return false; } }
}
java
\ ## Service Auth using SpringSecuirty Filter Every request is validated to check whether the token is valid or not. \n No token/Invalid token: it's 401. Only valid JWTs proceed.
java
java package com.zero.trust.demo.config;
java import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter;
java import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder; import org.springframework.security.web.*; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
java //few importing missing refer git hub as i am getting error to copy the all imports
javascript
@Configuration public class ZeroTrustSecurityConfig {
@Bean public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable) .authorizeHttpRequests(req -> req .requestMatchers("/health").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated()) .addFilterBefore((Filter) new TokenFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class); return http.build(); } static class TokenFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter { @Override protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws ServletException, IOException { String auth = req.getHeader("Authorization"); if (auth == null || !auth.startsWith("Bearer ")) { res.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED, "Missing token"); return; } String jwt = auth.substring(7); IdentityServiceManager manager = new IdentityServiceManager("user-service"); if (!manager.verifyTokenData(jwt)) { res.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED, "Invalid token"); return; } Authentication a = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken("service", null, List.of()); SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(a); chain.doFilter(req, res); } }
}
## Dynamic Secrets using Vault Simulator In the real world, we will use HashiCorp Vault. But locally, we simulate rotating DB credentials in-memory every minute.
java
javascript package com.zero.trust.valut;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.UUID;
@Component public class VaultServ { private String username = "dbuser"; private String password = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000) public void rotate() { password = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); System.out.println("[VaultSim] Rotated password -> " + password); } public String getUsername() { return username; } public String getPassword() { return password; }
}
java
\ ## Gateway Code The Gateway generates a JWT with its own identity and connects to the User Service over mutual TLS. The User Service then authenticates both the token and the certificate — ensuring that only trusted, verified services can communicate.
java
javascript package com.damu;
import com.zero.trust.common.IdentityServiceManager; import org.springframework.boot.; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; import org.springframework.http.*;
@SpringBootApplication @RestController public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args); } @Bean public RestTemplate restTemplate() { return new RestTemplate(); } private final IdentityServiceManager identity = new IdentityServiceManager("gateway-service"); private final RestTemplate rest = new RestTemplate(); @GetMapping("/gatewaytest") public String test() { String token = identity.generateTokenData(); HttpHeaders h = new HttpHeaders(); h.set("Authorization","Bearer "+token); HttpEntity<Void> entity = new HttpEntity<>(h); ResponseEntity<String> res = rest.exchange( "https://localhost:8443/api/users/1", HttpMethod.GET, entity, String.class); return "Gateway → " + res.getBody(); }
}
java ```
Check out our GitHub for a more detailed flow.
\
You May Also Like

Japan-Based Bitcoin Treasury Company Metaplanet Completes $1.4 Billion IPO! Will It Buy Bitcoin? Here Are the Details

InvestCapitalWorld Updates Platform Features to Support Broader Multi-Asset Market Access
