Storage Full? How to Free Up Storage on Android and iPhone Without Deleting A Single Photo

Running out of phone storage doesn’t always mean deleting your photos. In most cases, the real problem is hidden files – cached data, old downloads, and message attachments silently filling up your device.
In this guide, you’ll learn simple, safe, and effective ways to free up storage on Android and iPhone without deleting a single photo, using built-in tools and deep-clean techniques.
Primary storage fix: the fastest ways to get space back
Files downloaded online for offline use are mostly redundant after their initial use, yet they consume a lot of space. Targeting these high-volume media files is the most efficient first step for storage recovery on both iOS and Android devices.
Delete downloaded movies and music for instant free storage
Applications such as video streaming platforms (Netflix, Amazon Prime, etc.) and audio services (Podcasts, Spotify, Apple Music, etc.) tend to store content offline and often do not delete it automatically. The volume of temporary downloads adds up quickly and becomes a primary source of storage depletion.
For video streaming services like Netflix, users can delete all downloaded content. The process involves navigating to the app settings and selecting the Delete All Downloads option found under the download section, this could free between 2–10 GB, depending on the files occupying the storage space. Alternatively, users should consider streaming online to save space—similarly, audio streaming services reserve space for offline playlists.
To recover the storage:
- Open the app.
- Tap on the Profile icon.
- Go to Settings and Privacy.
- Locate Storage.
- Select Remove All Downloads.
Doing this will remove all locally stored music and free up storage immediately.
Clear your downloads folder and browser data
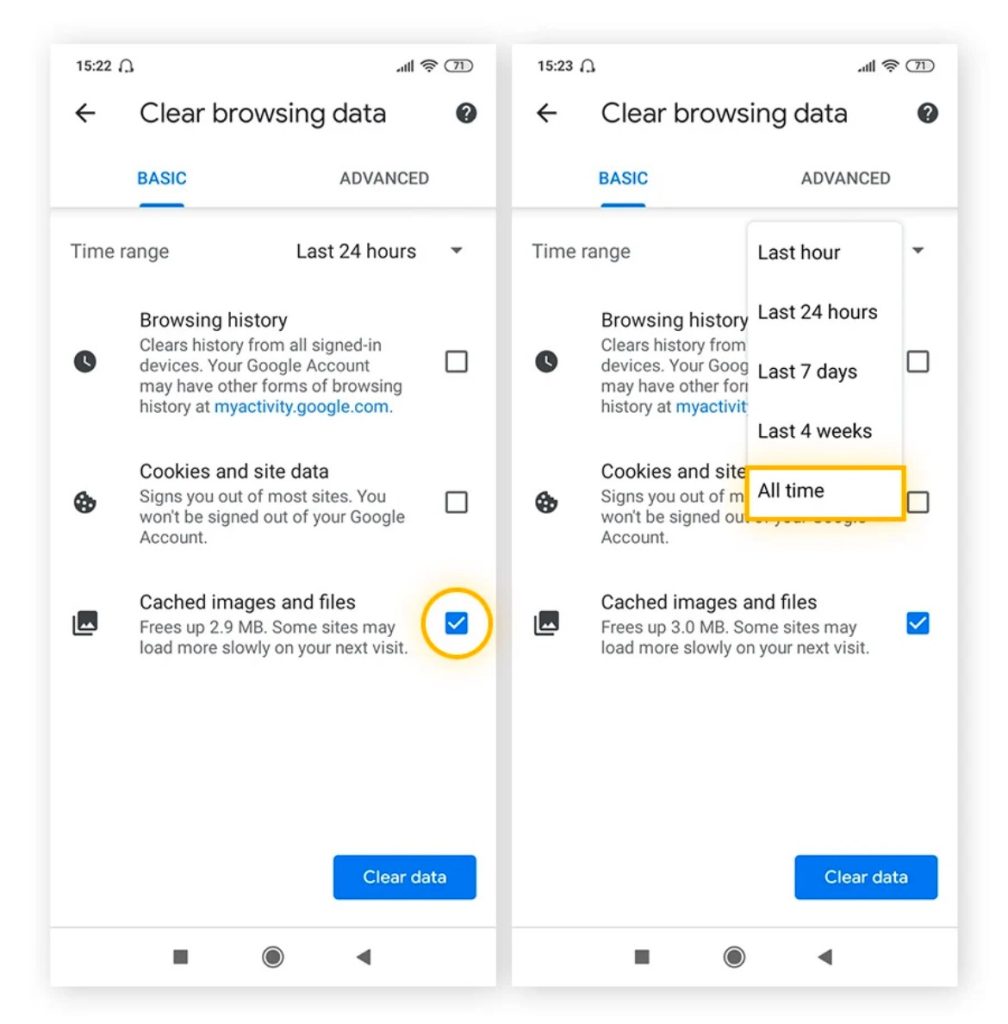
Smartphone download folders often harbour obsolete files, temporary documents, and large attachments inadvertently. Using a built-in file manager, such as Files by Google for Android devices or the Files app on iPhone or iPad, allows for easy identification and clearance of unnecessary documents.
Browser maintenance also contributes to storage recovery by deleting cached files and cookies. This option involves accessing history settings and selecting the option to clear browsing data.
On iOS, clearing Safari data offers a significant opportunity for freeing space:
- Navigate to Settings > Safari > Advanced > Website Data > Remove All Website Data.
This action clears cookies, tracking data, and deletes temporary internet files without erasing the user’s browsing history. However, note that it will require users to log back into previously saved services.
How to clear app cache on Android and iPhone to free up space
Temporary files generated by applications (cache) are created to improve performance. While useful in the short term, this data can silently accumulate into gigabytes, robbing users of valuable space.
How to wipe Android cache (step-by-step)
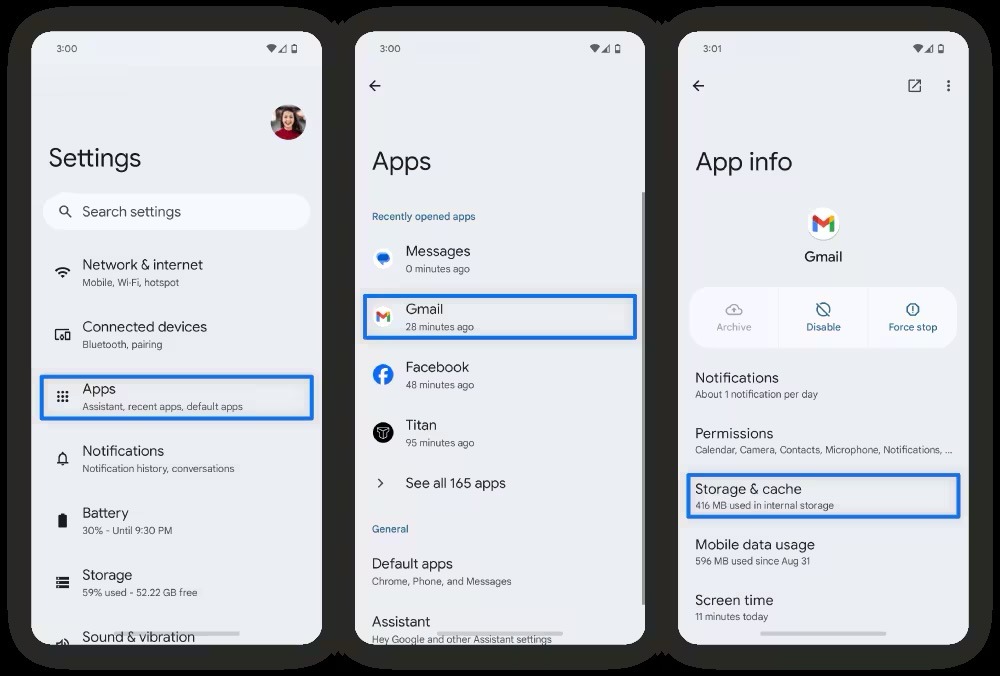
Android provides manual control over temporary app files. The system allows control over cache or temporary files in two ways:
- Individual app management: The system allows users to clear the cache for individual applications through a simple process. Open the Settings app > navigate to Apps (or Applications) > select the specific app > tap Storage> and then tap the Clear Cache button. This removes non-essential files while preserving your personal information.
- Using Files by Google for a system-wide clean: Android users should utilise the Files by Google application. This tool analyses the device’s storage to identify junk files—temporary logs, app residue, and cache that can be safely removed. To use this, open the Files app > tap the Clean tab at the bottom left > locate the Junk files card > and tap Clean.
How iPhone users can offload apps to free space without losing data
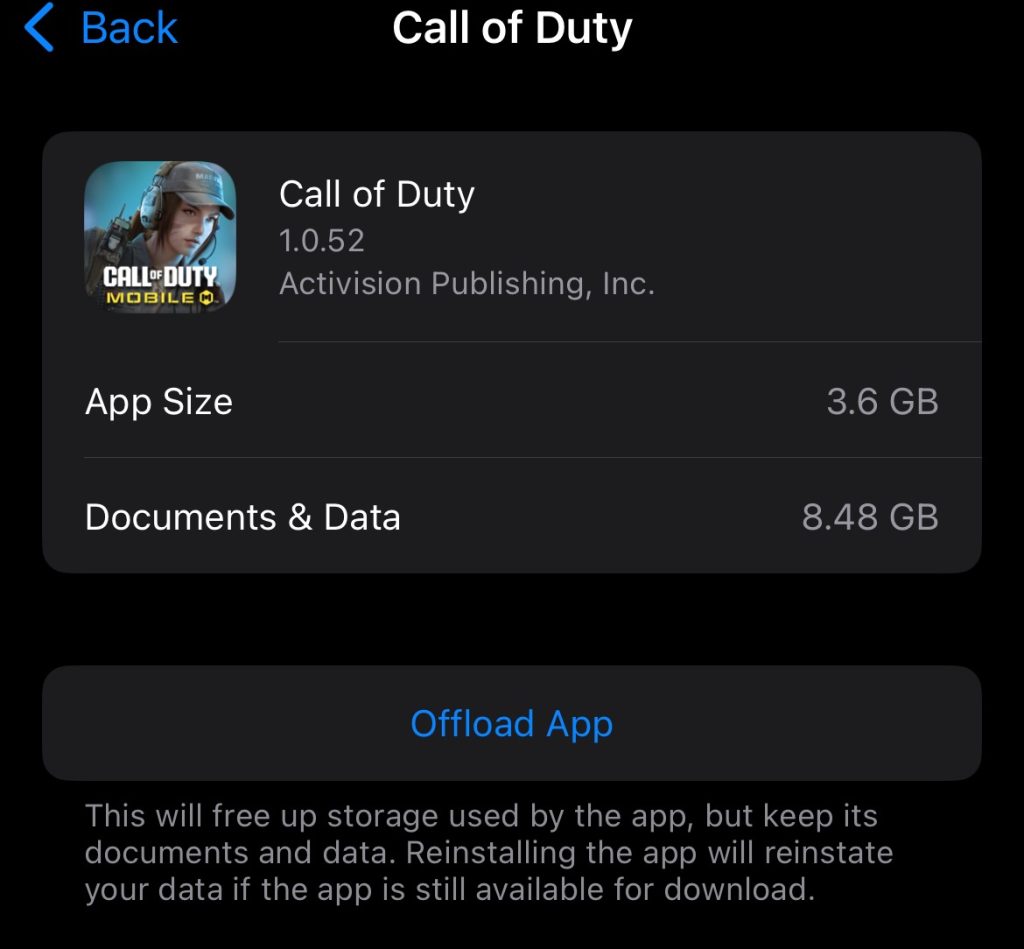
For iPhone users, the system restricts access to individual app caches, meaning there is no “Clear Cache” button within the app’s settings. To clear an iPhone cache, users have two options:
- Offload apps: The primary solution for cache management in iOS is to offload apps. The process removes the core application from the device but preserves all associated documents, data, and user settings.
- Users can enable automatic offloading by navigating to Settings > App Store, scrolling to the bottom, and toggling on Offload Unused Apps.
- Alternatively, specific apps can be manually offloaded by going to Settings > General > iPhone Storage, selecting the app from the list, and pressing Offload App. Offloaded apps remain visible on the home screen (usually with a cloud icon) and can be instantly re-downloaded when needed without any data loss.
Messaging apps: hidden files that fill up your storage
Messaging applications are often hidden storage drains, especially for users who exchange videos, photos, and other large files. These media files get saved locally, even if you never open them again.
iPhone: how to delete large iMessage attachments
iOS provides tools to visualise and manage media within texts. Users can free substantial storage by targeting and removing large attachments. This can be done by navigating to Settings > General > iPhone Storage, selecting Messages, and then tapping on the listed categories, such as Videos or Photos.
For long-term maintenance, users can implement proactive retention limits. Configure the device to automatically delete old messages and their attachments by going to Settings > Messages, scrolling to Message History, tapping Keep Messages, and selecting an option (e.g., 30 Days or 1 Year). This prevents messages from accumulating indefinitely.
Android: How to remove large messaging files
Android users can employ manual cleanup available in the retention settings. Conversation threads that contain large attachments can be manually selected and deleted in bulk. Also, users can clear residual messaging files by clearing the cache and temporary data of the messaging application itself. Navigate to Settings > Apps > [Messaging App] > Storage.
WhatsApp cleanup: how to remove media without losing chats
For many users, the “Storage Full” warning is not caused by the photos they took, but by the photos and videos sent to them. WhatsApp media auto-download is a notorious storage consumer, often saving gigabytes of viral videos, voice notes, and memes from group chats directly to the device’s internal memory.
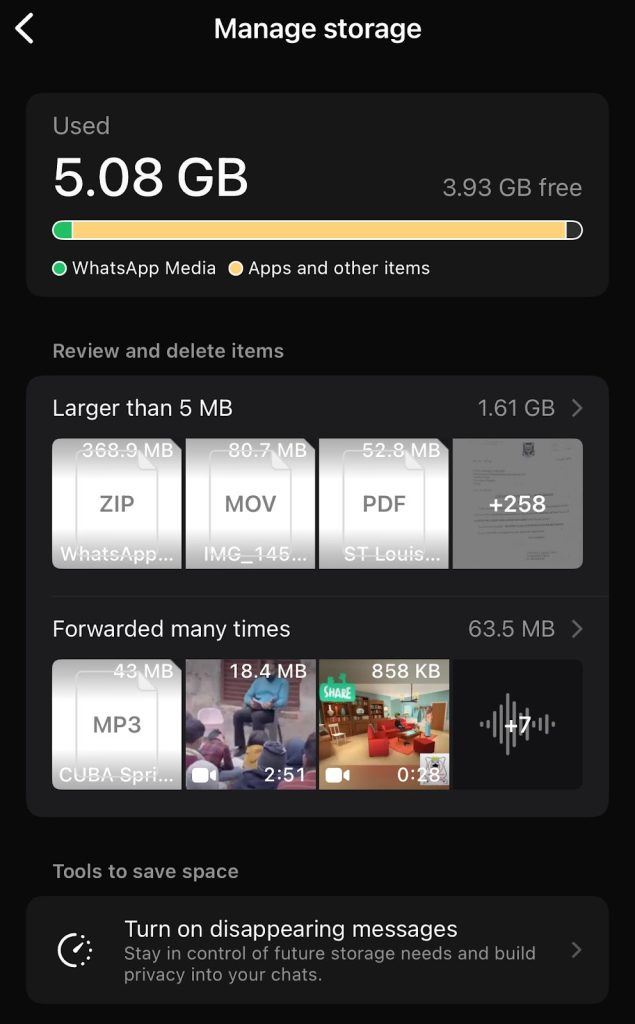
How to use the WhatsApp storage manager to free up space
WhatsApp has a built-in tool that specifically identifies and deletes these redundant files without affecting your personal chat history.
- Access the app: Open WhatsApp > go to Settings > Storage and Data > Manage Storage.
- Review and delete: The bar at the top shows exactly how much space WhatsApp occupies. Below that, look for the section labelled “Larger than 5 MB.” This folder contains heavy video files and forwarded media. Users can open this, select all, and delete them in bulk.
- Chat-specific cleaning: Scroll down to see a list of chats arranged by size. If a specific group chat is occupying 2GB of space, you can tap on it and delete just the media from that specific conversation while keeping the text messages intact.
How to stop WhatsApp media from filling up your space
To stop this from happening again, users must disable media auto-download.
- Navigate to Settings > Storage and Data > Media Auto-Download.
- Set “Photos,” “Audio,” and “Video” to Never or Wi-Fi only, depending on preference.
This ensures that media is only downloaded when you specifically tap on it, keeping your storage control in your hands.
Storage optimisation: how to keep your photos safe while freeing space
To be fair, not deleting photos while freeing space requires using cloud services. By utilising an external cloud service, users can maintain access to their full-quality media while keeping local storage clean. This approach shifts storage management from reactive to proactive defence.
iPhone users: turn on optimise iPhone storage
The most effective strategy without deleting photos for iOS is to enable optimising iPhone storage settings within iCloud Photos. To optimise iPhone storage, navigate to Settings > [Your Name] > iCloud > Photos.
With this feature enabled, when local storage runs low, the operating system automatically replaces high-resolution images stored locally on the device with compressed thumbnails. The original copies remain stored on iCloud and are accessible on demand. The only downside is iCloud’s limited 5GB of free storage, with options to pay for additional space.
Android users: How to use cloud storage
For Android users, open the Google Photos app, tap your Profile icon, and select Free up space. This feature safely deletes photos from your device that have already been backed up to the cloud, instantly reclaiming gigabytes of space while keeping your memories safe online.
Android users managing files using services such as Google Drive or Dropbox must review and control local sync settings. If the cloud apps are set to automatically sync for offline access, unnecessary duplication of backed-up files will accumulate on the device, making optimisation impossible. Disabling automatic sync settings prevents unwanted file duplication.
Routine cache clearing for cloud storage applications is also advised. Although the main files reside on the cloud, these apps accumulate temporary data locally. Clearing the cache refreshes the data without affecting saved files.
Disable background app refresh to reduce hidden storage use
This is a simple but overlooked step in managing background storage usage. By disabling background app refresh for applications that don’t require constant, real-time updates, users can limit the ability of these applications to regularly download and cache data in the background.
Long-term storage strategy: Keep your phone from getting full
Storage management must be viewed as an ongoing maintenance cycle—there’s a need to maintain storage regularly and not just in emergencies. By adopting this multi-platform approach, users can reclaim control over their device’s memory and ensure stability.
To stay ahead of the curve and manage your storage before getting a “Storage Full” message, follow these steps:
Weekly
- Restart your phone.
- Clear cache for heavy-use apps (Android).
- Reinstall apps with huge sizes (iPhone, only if needed).
Monthly
- Delete Netflix/Spotify/YouTube downloads.
- Clean your downloads folder.
- Clear the browser website data.
Quarterly
- Clear message attachments.
- Check iPhone Storage or Files by Google for unusual spikes.
You May Also Like

How ZKP’s Daily Presale Auction Is Creating a New Standard for 1,000x Returns

Little Pepe (LILPEPE) koers, nu investeren in de lopende presale?
