BSGAL: Batched Streaming Active Learning for Generated Data
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
-
Related work
2.1. Generative Data Augmentation
2.2. Active Learning and Data Analysis
-
Preliminary
-
Our method
4.1. Estimation of Contribution in the Ideal Scenario
4.2. Batched Streaming Generative Active Learning
-
Experiments and 5.1. Offline Setting
5.2. Online Setting
-
Conclusion, Broader Impact, and References
\
A. Implementation Details
B. More ablations
C. Discussion
D. Visualization
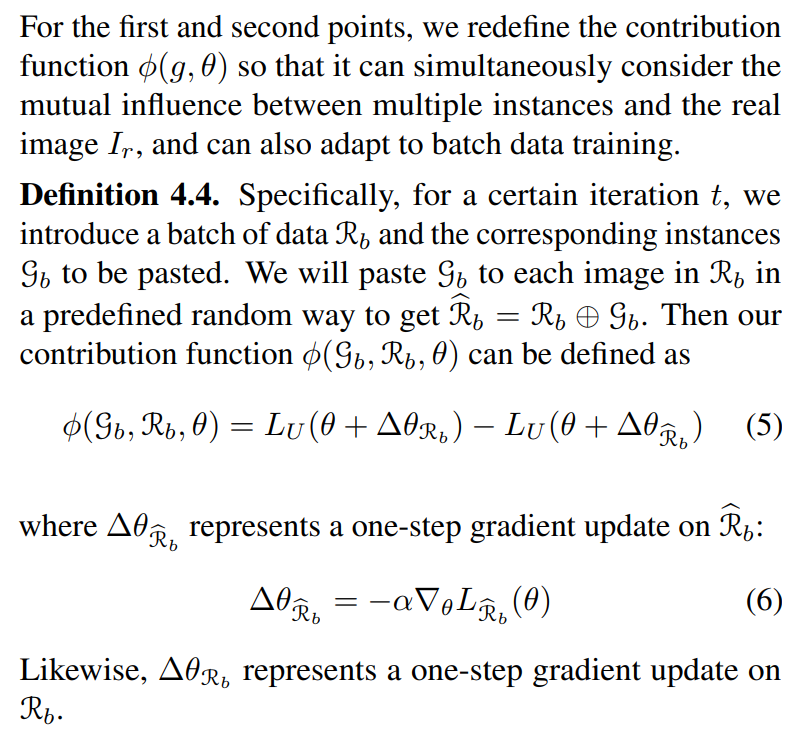
4.2. Batched Streaming Generative Active Learning
While we have proposed an ideal estimation of contribution in the preceding section, it is not directly transferable to a real segmentation training process. The specific reasons are as follows:
\ 
\
-
We conduct batch data training, eliminating the possibility of estimating each instance individually, as this would provoke excessive computation.
\
-
Our model undergoes constant updates. Therefore, even the same sample’s contribution to the model varies under different training stages. Furthermore, given the near-infinite data pool, the entire training process closely resembles a streaming process(Saran et al., 2023). After each data entry, we must decide whether to include this data in the present update.
\ 
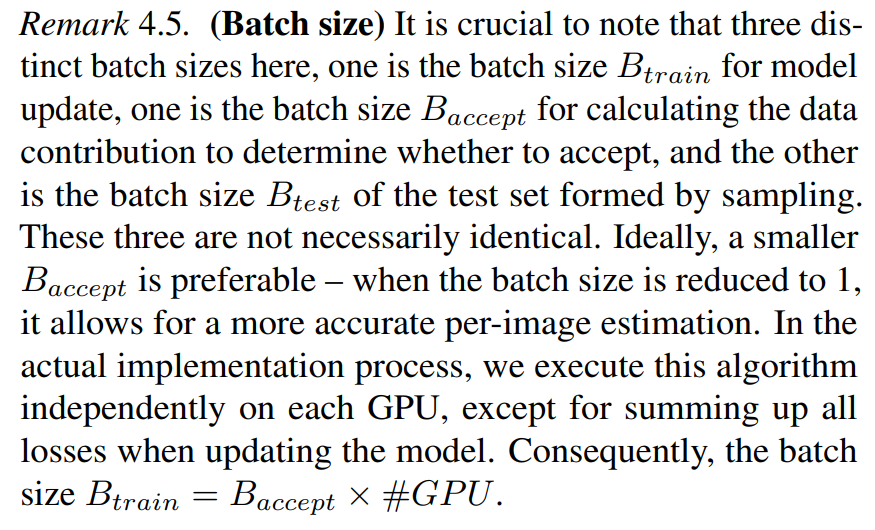
\ In response to the third point, based on Definition 4.4, we can propose an algorithm called Batched Streaming Generative Active Learning (BSGAL), as shown in Algorithm 2.
\ 
\ 
\ 
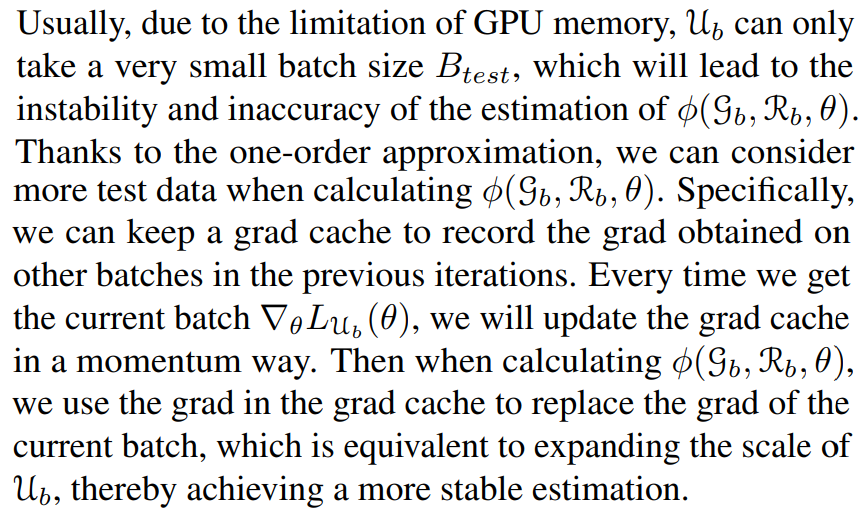
\ So the Algorithm 2 can be further simplified by using Equation (7) in Line 10.
\ 
\ 
\ 
\ 
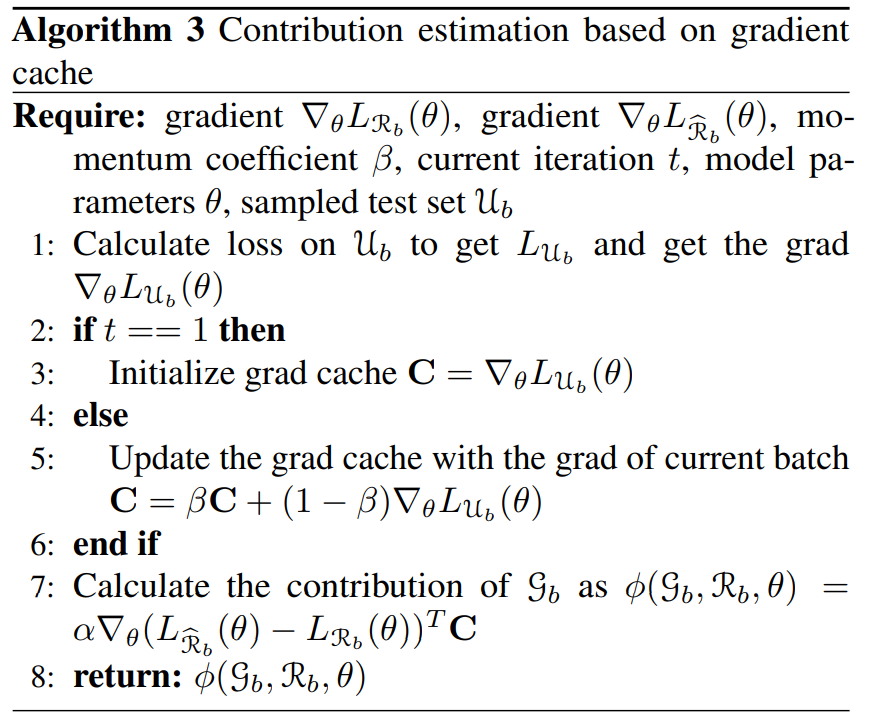
\ The modified contribution estimation algorithm for the final BSGAL is shown in Algorithm 3.
\ 
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Muzhi Zhu, with equal contribution from Zhejiang University, China;
(2) Chengxiang Fan, with equal contribution from Zhejiang University, China;
(3) Hao Chen, Zhejiang University, China (haochen.cad@zju.edu.cn);
(4) Yang Liu, Zhejiang University, China;
(5) Weian Mao, Zhejiang University, China and The University of Adelaide, Australia;
(6) Xiaogang Xu, Zhejiang University, China;
(7) Chunhua Shen, Zhejiang University, China (chunhuashen@zju.edu.cn).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Noncommercial-Noderivs 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
You May Also Like
![[Tambay] Tres niños na bagitos](https://www.rappler.com/tachyon/2026/01/TL-TRES-NINOS-NA-BAGITOS-JAN-17-2026.jpg)
[Tambay] Tres niños na bagitos

Massive Whale Buying Spree Could Trigger XRP Supply Shock as Exchange Balances Drop to Lowest Since 2023 ⋆ ZyCrypto
