End-to-End Deep Learning Improves CT Material Decomposition
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
- Dual-Energy CT Forward Model
- [Model-based Optimization Problem]()
- End-to-End Model-based Deep Learning for Material Decomposition (E2E-Decomp)
- Numerical Results
- Conclusion
- Compliance with Ethical Standards and References
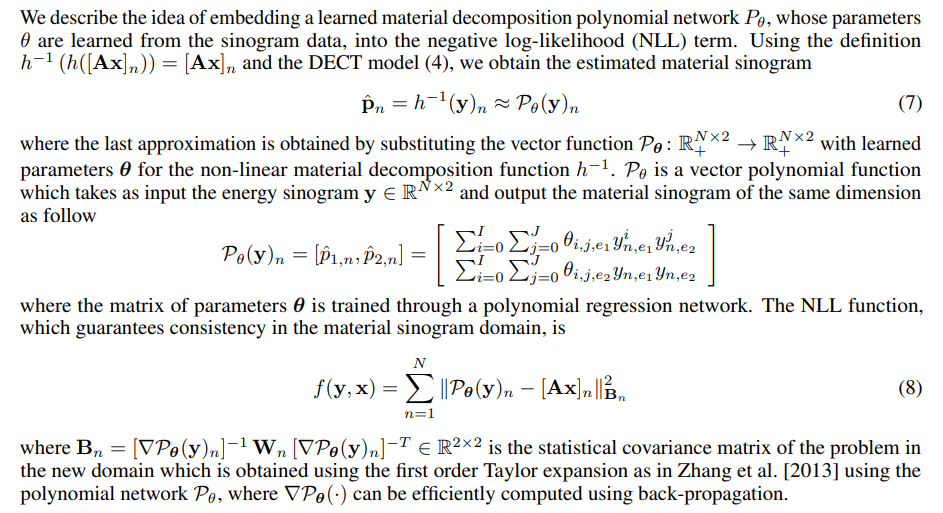
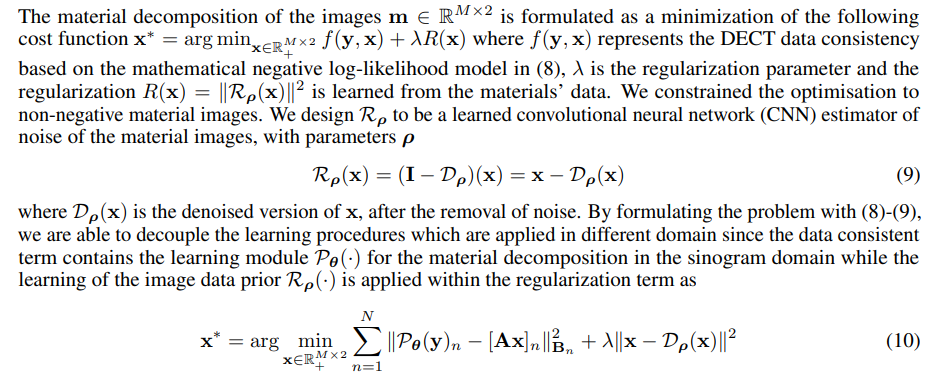
4 End-to-End Model-based Deep Learning for Material Decomposition (E2E-Decomp)
\ 
\ 
\ 
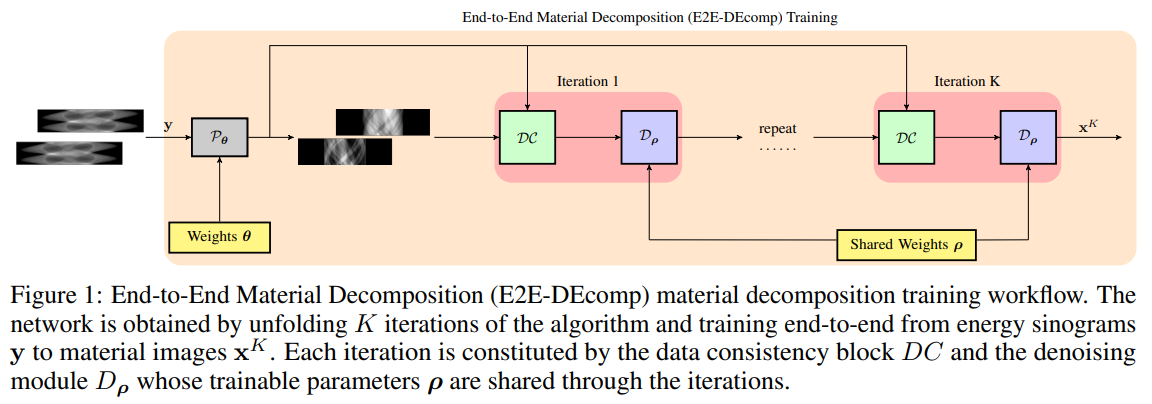
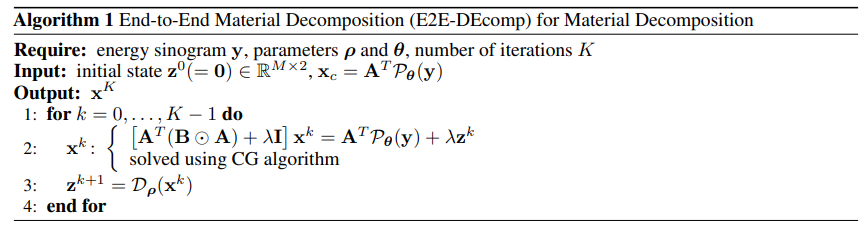
\ The workflow of the E2E-DEcomp algorithm at inference is shown in Fig. 1, and the structure of the E2EDEcomp algorithm for inference is reported in Table 1.
\ 
5 Numerical Results

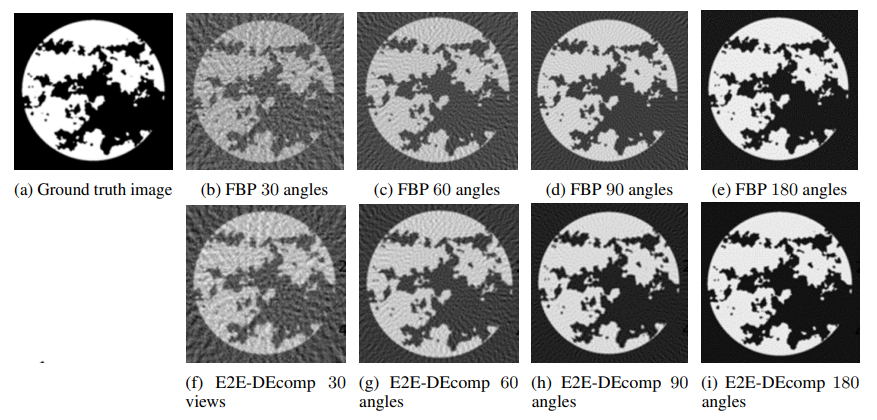
\ In order to reduce the number of learnable parameters we utilise the same architecture for the denoising module D at each iteration k with shared parameters ρ. In Fig. 2 it is shown the qualitative comparison on a test material image of the adipose tissue using filtered back projection (FBP) and E2E-DEcomp while in Fig. 3 is is reported the PSNR error for a set of 10 testing images for the 2 material decomposition.
\ 
\ 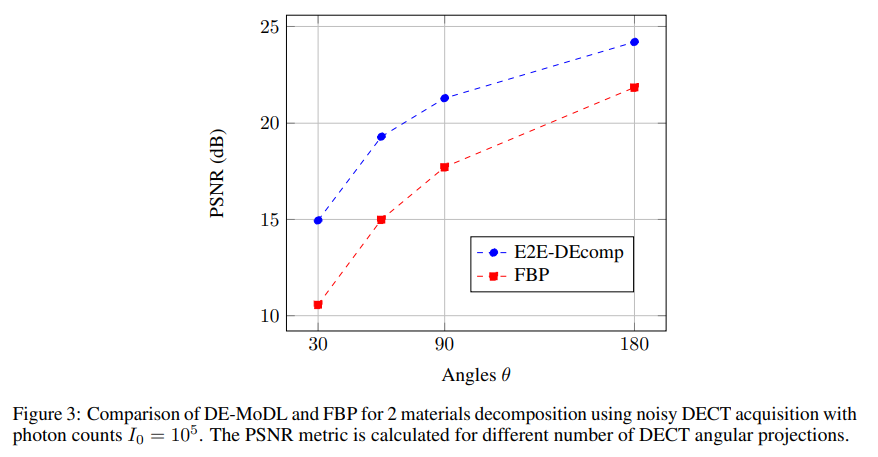
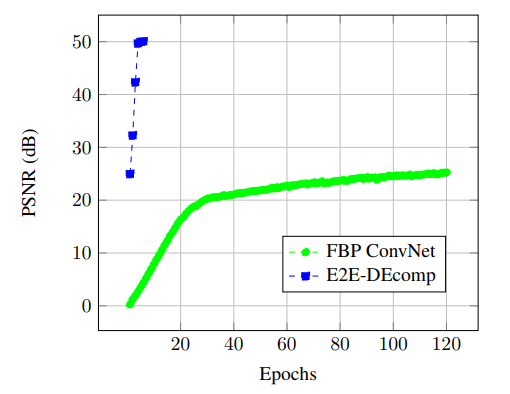
\ It is worth noting that the improvement in the decomposition accuracy are consistent, around 5 dB, across different levels of dose, i.e. from sparse views to higher number of projections. We have also compared the E2E-DEcomp framework with the FBP ConvNet method Jin et al. [2017] and Fig. 4 shows how E2E-DEcomp can achieve a faster convergence in training using fewer epochs.
6 Conclusion
This work proposed a direct method for DECT material decomposition using a model-based optimization able to decouple the learning in the measurement and image domain. Numerical results show the effectiveness
\ 
\ of the proposed E2E-DEcomp compared to other supervised approaches since it has fast convergence and excellent performance on low-dose DECT which can lead to further study with clinical dataset.
\
7 Compliance with Ethical Standards
This is a numerical simulation study for which no ethical approval was required.
References
Hemant K Aggarwal, Merry P Mani, and Mathews Jacob. Modl: Model-based deep learning architecture for inverse problems. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 38(2):394–405, 2018.
\ Robert E Alvarez and Albert Macovski. Energy-selective reconstructions in x-ray computerised tomography. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 21(5):733, 1976.
\ Caifang Cai, Thomas Rodet, Samuel Legoupil, and Ali Mohammad-Djafari. A full-spectral bayesian reconstruction approach based on the material decomposition model applied in dual-energy computed tomography. Medical physics, 40(11):111916, 2013.
\ A. Eguizabal, O. Öktem, and M. Persson. A deep learning one-step solution to material image reconstruction in photon counting spectral CT. In Wei Zhao and Lifeng Yu, editors, Medical Imaging 2022: Physics of Medical Imaging, volume 12031, page 120310Y. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2022. doi:10.1117/12.2612426.
\ W. Fang, D. Wu, K. Kim, M.K. Kalra, R. Singh, L. Li, and Q. Li. Iterative material decomposition for spectral CT using self-supervised Noise2Noise prior. Phys Med Biol, 66(15):155013, July 2021. doi:10.1088/1361- 6560/ac0afd.
\ Kyong Hwan Jin, Michael T McCann, Emmanuel Froustey, and Michael Unser. Deep convolutional neural network for inverse problems in imaging. IEEE transactions on image processing, 26(9):4509–4522, 2017.
\ Thorsten RC Johnson, Bernhard Krauss, Martin Sedlmair, Michael Grasruck, Herbert Bruder, Dominik Morhard, Christian Fink, Sabine Weckbach, Miriam Lenhard, Bernhard Schmidt, et al. Material differentiation by dual energy ct: initial experience. European radiology, 17:1510–1517, 2007.
\ Yong Long and Jeffrey A Fessler. Multi-material decomposition using statistical image reconstruction for spectral ct. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 33(8):1614–1626, 2014.
\ Clemens Maaß, Matthias Baer, and Marc Kachelrieß. Image-based dual energy ct using optimized precorrection functions: A practical new approach of material decomposition in image domain. Medical physics, 36(8): 3818–3829, 2009.
\ Korbinian Mechlem, Thorsten Sellerer, Sebastian Ehn, Daniela Münzel, Eva Braig, Julia Herzen, Peter B Noël, and Franz Pfeiffer. Spectral angiography material decomposition using an empirical forward model and a dictionary-based regularization. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 37(10):2298–2309, 2018.
\ Paulo RS Mendonça, Peter Lamb, and Dushyant V Sahani. A flexible method for multi-material decomposition of dual-energy ct images. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 33(1):99–116, 2013.
\ Rohan Nadkarni, Alex Allphin, Darin P Clark, and Cristian T Badea. Material decomposition from photoncounting ct using a convolutional neural network and energy-integrating ct training labels. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 67(15):155003, 2022.
\ John L Nazareth. Conjugate gradient method. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics, 1(3): 348–353, 2009.
\ A. Perelli and M.S. Andersen. Regularization by denoising sub-sampled newton method for spectral CT multi-material decomposition. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 379(2200):20200191, 2021. doi:10.1098/rsta.2020.0191.
\ Zaifeng Shi, Huilong Li, Qingjie Cao, Zhongqi Wang, and Ming Cheng. A material decomposition method for dual-energy ct via dual interactive wasserstein generative adversarial networks. Medical Physics, 48(6): 2891–2905, 2021.
\ Emil Y Sidky and Xiaochuan Pan. Report on the AAPM deep-learning spectral CT grand challenge. Medical Physics, 2023.
\ Wim Van Aarle, Willem Jan Palenstijn, Jeroen Cant, Eline Janssens, Folkert Bleichrodt, Andrei Dabravolski, Jan De Beenhouwer, K Joost Batenburg, and Jan Sijbers. Fast and flexible x-ray tomography using the astra toolbox. Optics express, 24(22):25129–25147, 2016.
\ Ruoqiao Zhang, Jean-Baptiste Thibault, Charles A Bouman, Ken D Sauer, and Jiang Hsieh. Model-based iterative reconstruction for dual-energy x-ray ct using a joint quadratic likelihood model. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 33(1):117–134, 2013.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Jiandong Wang, Shenzhen Xilaiheng Medical Electronics, (HORRON), China and Centre for Medical Engineering and Technology, University of Dundee, DD1 4HN, UK (jack@horron.com);
(2) Alessandro Perelli, Centre for Medical Engineering and Technology, University of Dundee, DD1 4HN, UK (aperelli001@dundee.ac.uk).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

SEC urges caution on crypto wallets in latest investor guide

Crucial Fed Rate Cut: October Probability Surges to 94%
