The Algorithmic Evolution of Blockchain Fee Design
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
1.1 Our Approach
1.2 Our Results & Roadmap
1.3 Related Work
-
Model and Warmup and 2.1 Blockchain Model
2.2 The Miner
2.3 Game Model
2.4 Warm Up: The Greedy Allocation Function
-
The Deterministic Case and 3.1 Deterministic Upper Bound
3.2 The Immediacy-Biased Class Of Allocation Function
-
The Randomized Case
-
Discussion and References
- A. Missing Proofs for Sections 2, 3
- B. Missing Proofs for Section 4
- C. Glossary
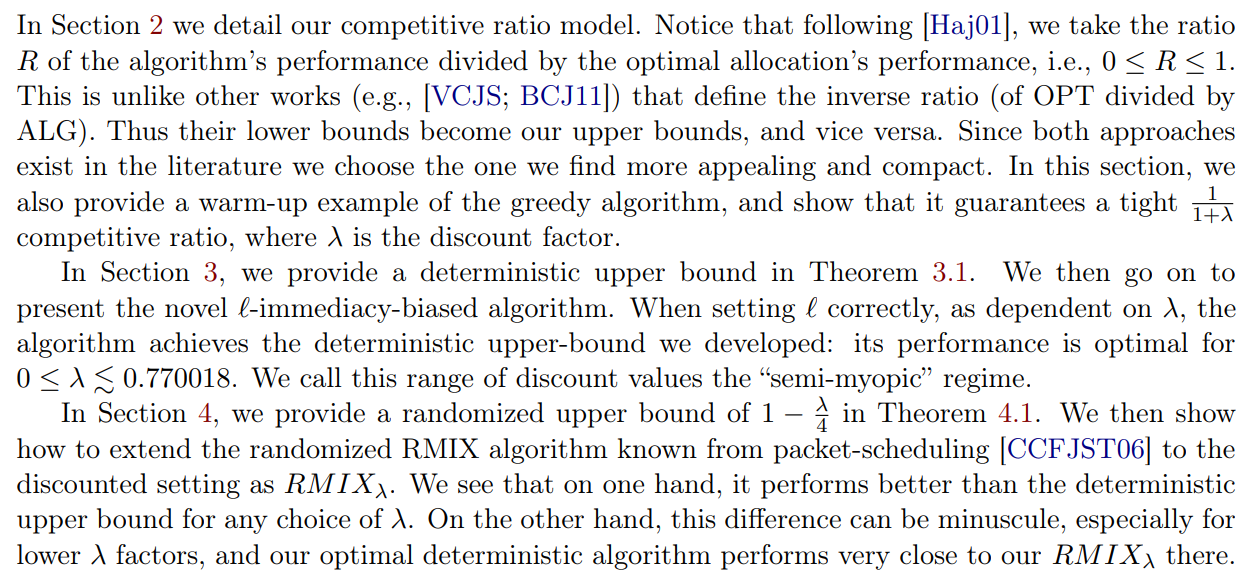
1.2 Our Results & Roadmap
1.3 Related Work
The application of auction theory to the design of TFMs was explored by a line of works [LSZ22; Yao18; BEOS19; Rou21; CS23], that focused primarily on the axiomatic aspects of the blockchain setting when considering myopic miners.
\ Considerations such as transactions with a finite time to live and non-myopic miners are outside the scope of all the above literature and is a recognized important gap in our understanding of TFMs. Although we focus on the TFM of Blockchain systems, the addition of a predefined expiry date for transactions means that the setting is related to other resource allocation under time-constraints problems. Some examples are deadline-aware job scheduling [SC16] and ride-sharing [DSSX21]. The closest model to ours is perhaps that of Fiat et al. [FGKK16], who analyze a similar framework that considers single-minded users who assign both a fee and some urgency to their requests.
\ \ 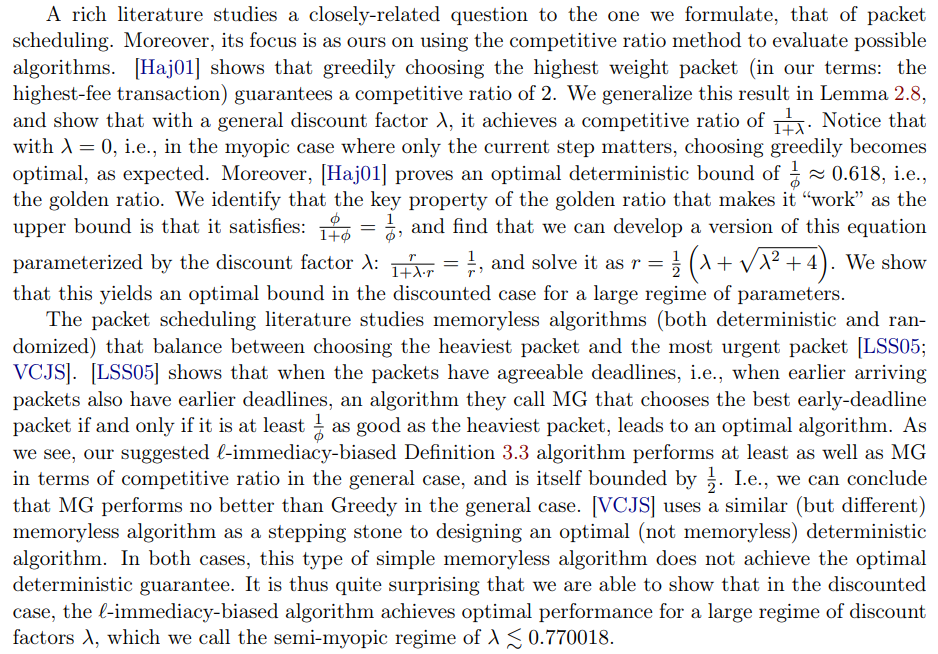
\ \ The literature of packet scheduling also considered randomized algorithms and upper bounds. [CCFJST06] suggested a randomized algorithm that works, similarly to MG, by considering the heaviest packet vs. the best early-deadline packet, but uses a randomized coefficient to determine which of them to choose. We show that [CCFJST06] can be generalized to depend on the discount factor. Our generalization is the same as RMIX when λ = 1, and the same as the greedy algorithm when λ = 0, where it achieves the optimal competitive ratio of 1. [BCJ11] extended RMIX analysis from the oblivious to the adaptive adversary, and also provided an upper bound for any randomized algorithm against the adaptive adversary. We show how to extend their construction to depend on the discount factor. An overview of the packet scheduling literature, including open problems in the field, can be found in [Ves21]. While we do not attempt to give a conclusive overview, we note that there is an alternative literature to that of packet scheduling with deadlines, that considers analysis of whether or not to accept packets to a FIFO queue, and there, a latency sensitive model was previously considered [FMN08].
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Yotam Gafni, Weizmann Institute (yotam.gafni@gmail.com);
(2) Aviv Yaish, The Hebrew University, Jerusalem (aviv.yaish@mail.huji.ac.il).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

The Channel Factories We’ve Been Waiting For

American Bitcoin’s $5B Nasdaq Debut Puts Trump-Backed Miner in Crypto Spotlight

