How SPIMs Tackle “Realistic” Spin Glass and Möbius Ladder Graphs
Table of Links
I. Introduction
II. Spim Performance, Advantages and Generality
III. Inherently Low Rank Problems
A. Properties of Low Rank Graphs
B. Weakly NP-Complete Problems and Hardware Precision Limitation
C. Limitation of Low Rank Matrix Mapping
IV. Low Rank Approximation
A. Decomposition of Target Coupling Matrix
B. How Fields Influence Ran
C. Low Rank Approximation of Coupling Matrices
D. Low-Rank Approximation of Random Coupling Matrices
E. Low Rank Approximation for Portfolio Optimization
F. Low-Rank Matrices in Restricted Boltzmann Machines
V. Constrained Number Partitioning Problem
A. Definition and Characteristics of the Constrained Number Partitioning Problem
B. Computational Hardness of Random CNP Instances
VI. Translation Invariant Problems
A. “Realistic” Spin Glass
B. Circulant Graphs
VII. Conclusions, Acknowledgements, and References
VI. TRANSLATION INVARIANT PROBLEMS
Beyond low-rank and constrained problems, translation invariant problems offer another interesting domain for SPIM applications. This section investigates how these problems can be effectively represented and solved using SPIMs.
A. “Realistic” Spin Glass
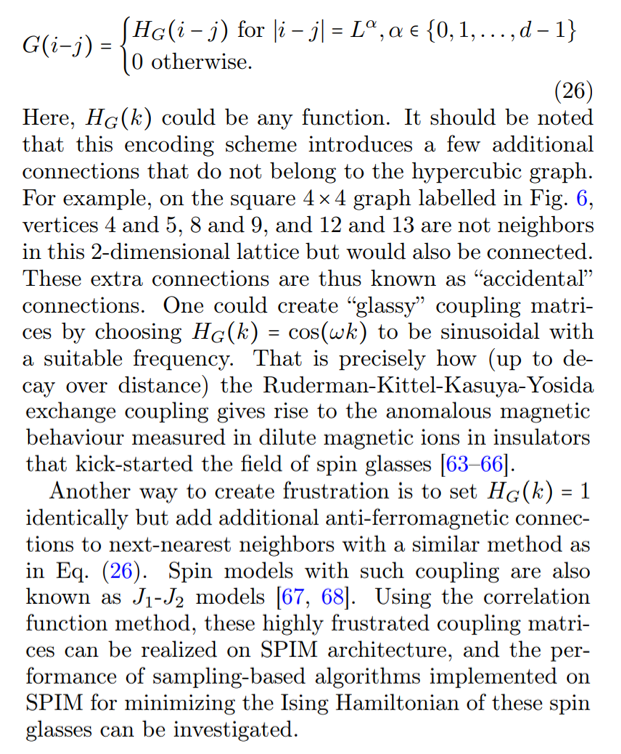
The correlation function method enables SPIM to encode translation invariant (or cyclic) coupling matrices. This type is important, and the hard problem is “realistic” spin glasses that live on an almost hypercubic lattice in d dimensions [62, 63]. The modified Mattis-type matrix encoding these problems is of the form given by Eq. (3), where
\ 
\ 
\
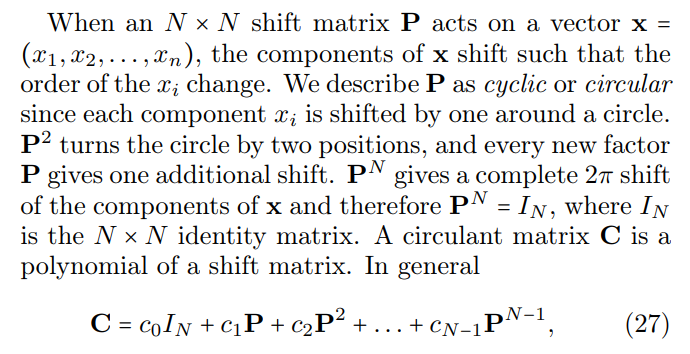
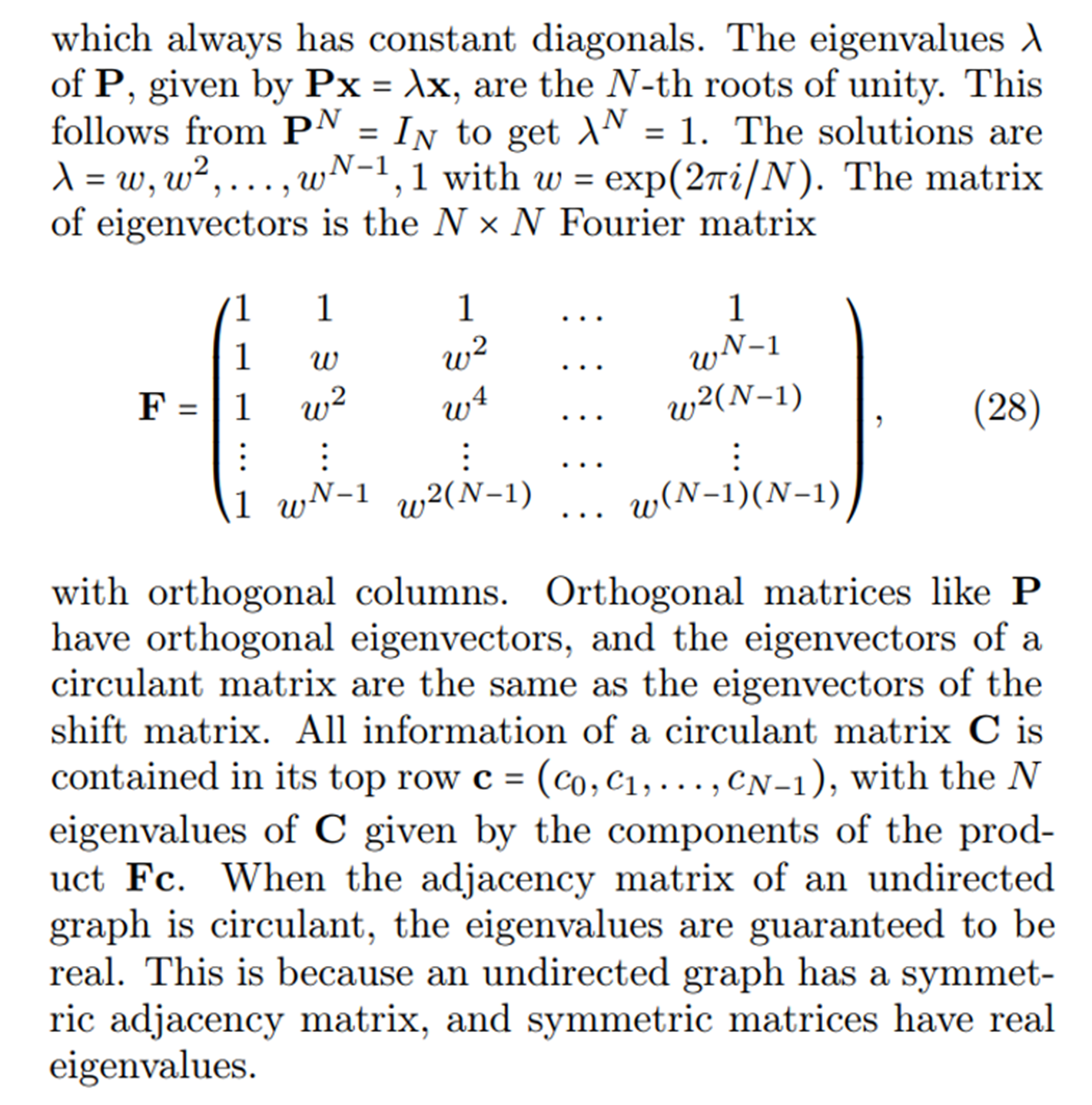
B. Circulant Graphs
\ 
\ \ \ 
\ \ \ 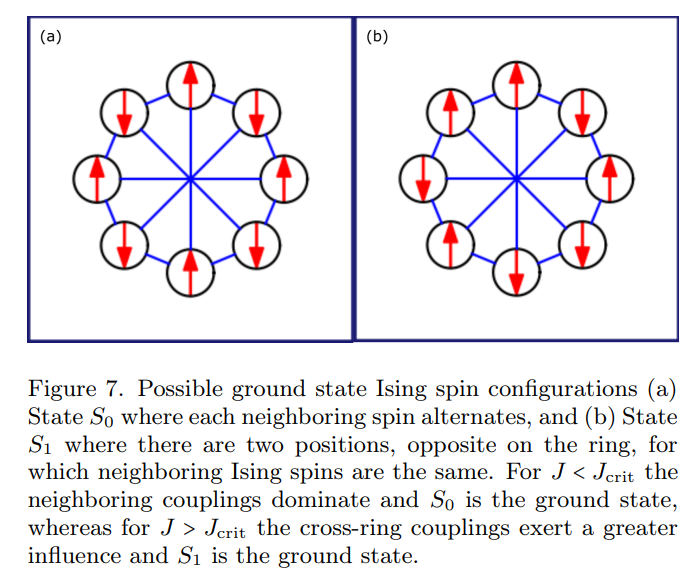
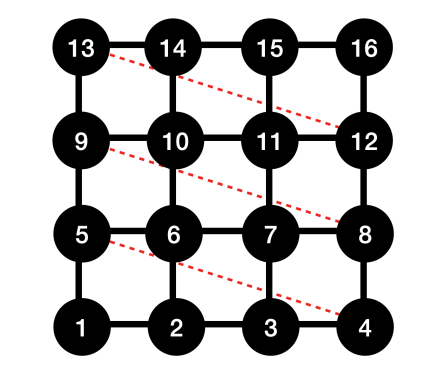
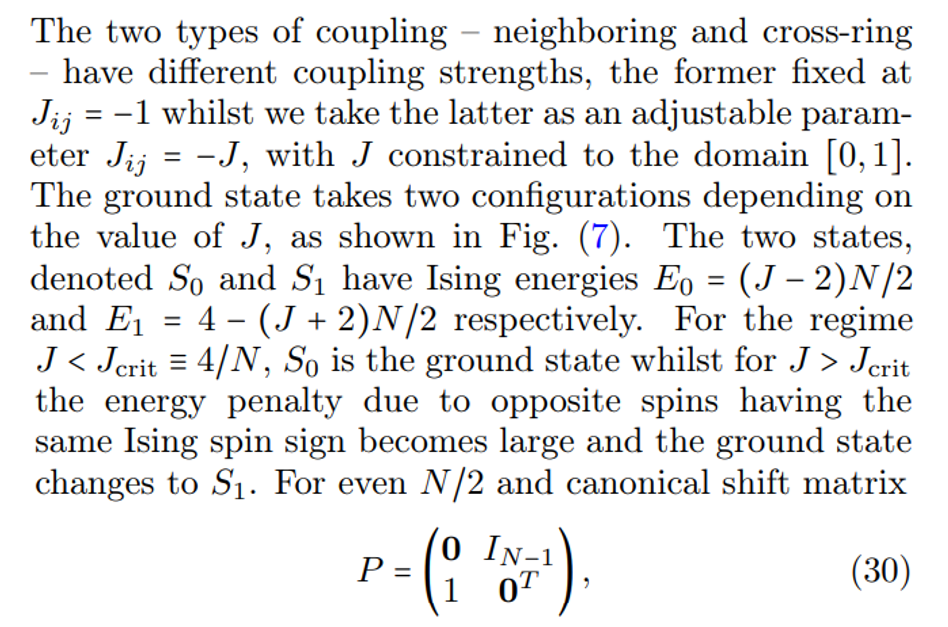
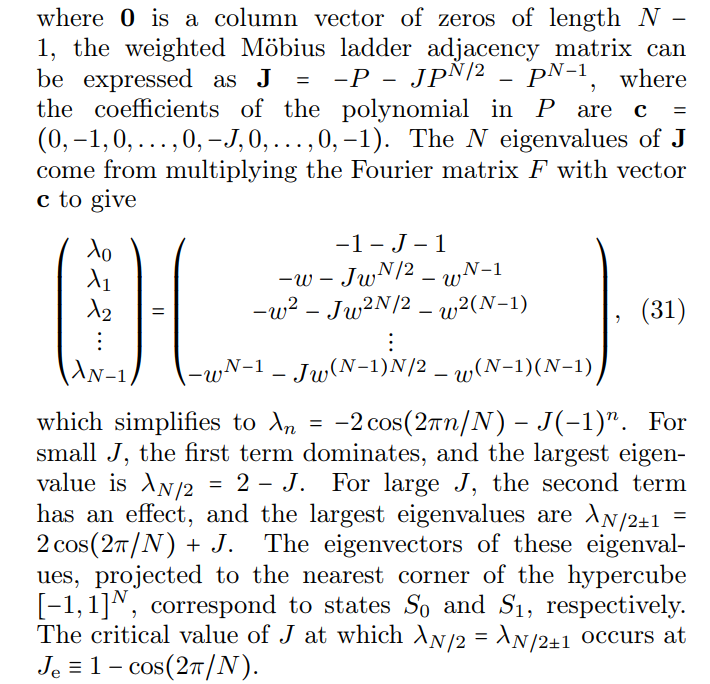
\ \ An example of a graph structure with a circulant adjacency matrix is a Möbius ladder graph. This 3-regular graph with even number of vertices N is invariant to cyclic permutations and can be implemented on SPIM hardware with each vertex of the Möbius ladder graph representing an Ising spin. The Ising spins are coupled antiferromagnetically according to the 3N/2 edges of the Möbius ladder graph. Each vertex is connected to two neighboring vertices arranged in a ring, and a cross-ring connection to the vertex that is diametrically opposite, as illustrated in Fig. (7). When N/2 is even, and for large cross-ring coupling, no configuration exists where all coupled Ising spins have opposite signs, and thus, frustrations must arise. The Ising Hamiltonian we seek to minimize is given by Eq. (1) with no external magnetic field and a coupling matrix J given by the Möbius ladder weighted adjacency matrix. The correlation function method can encode the weights of any circulant graph, which for Möbius ladders is given by
\ \ 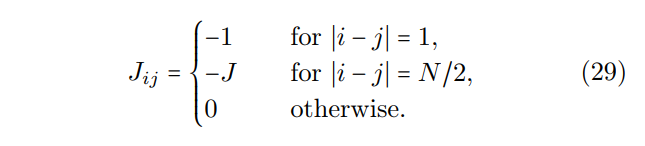
\ \ \ 
\ \ \ 
\ \ \ 
\ \ \
:::info Authors:
(1) Richard Zhipeng Wang, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom;
(2) James S. Cummins, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom;
(3) Marvin Syed, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom;
(4) Nikita Stroev, Department of Physics of Complex Systems, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100, Israel;
(5) George Pastras, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece;
(6) Jason Sakellariou, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece;
(7) Symeon Tsintzos, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece and UBITECH ltd, 95B Archiepiskopou Makariou, CY 3020 Limassol, Cyprus;
(8) Alexis Askitopoulos, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece and UBITECH ltd, 95B Archiepiskopou Makariou, CY 3020 Limassol, Cyprus;
(9) Daniele Veraldi, Department of Physics, University Sapienza, Piazzale Aldo Moro 5, Rome 00185, Italy;
(10) Marcello Calvanese Strinati, Research Center Enrico Fermi, Via Panisperna 89A, 00185 Rome, Italy;
(11) Silvia Gentilini, Institute for Complex Systems, National Research Council (ISC-CNR), Via dei Taurini 19, 00185 Rome, Italy;
(12) Calvanese Strinati, Research Center Enrico Fermi, Via Panisperna 89A, 00185 Rome, Italy
(13) Davide Pierangeli, Institute for Complex Systems, National Research Council (ISC-CNR), Via dei Taurini 19, 00185 Rome, Italy;
(14) Claudio Conti, Department of Physics, University Sapienza, Piazzale Aldo Moro 5, Rome 00185, Italy;
(15) Natalia G. Berlof, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom (N.G.Berloff@damtp.cam.ac.uk).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Shocking OpenVPP Partnership Claim Draws Urgent Scrutiny

Ethereum Price Closer to $4,000 Breakout as ETH Whales go on Buying Spree
