KC-EMA Mechanism: Theoretical Analysis and Derivation for IIL
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
-
Related works
-
Problem setting
-
Methodology
4.1. Decision boundary-aware distillation
4.2. Knowledge consolidation
-
Experimental results and 5.1. Experiment Setup
5.2. Comparison with SOTA methods
5.3. Ablation study
-
Conclusion and future work and References
\
Supplementary Material
- Details of the theoretical analysis on KCEMA mechanism in IIL
- Algorithm overview
- Dataset details
- Implementation details
- Visualization of dusted input images
- More experimental results
7. Details of the theoretical analysis on KCEMA mechanism in IIL
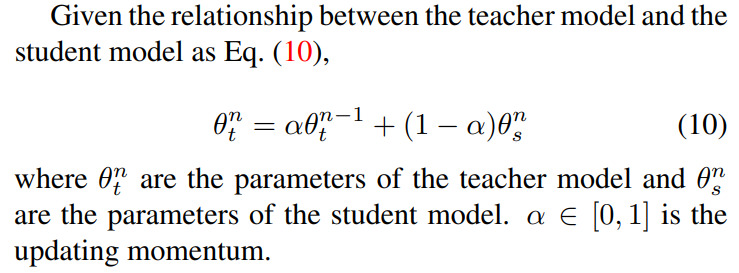
In Sec. 4.3 of the manuscript, we theoretically analyze the feasibility of applying a model EMA-like mechanism in the IIL. Here, gives more derivation details of the Eq. 7.
\ 
\ 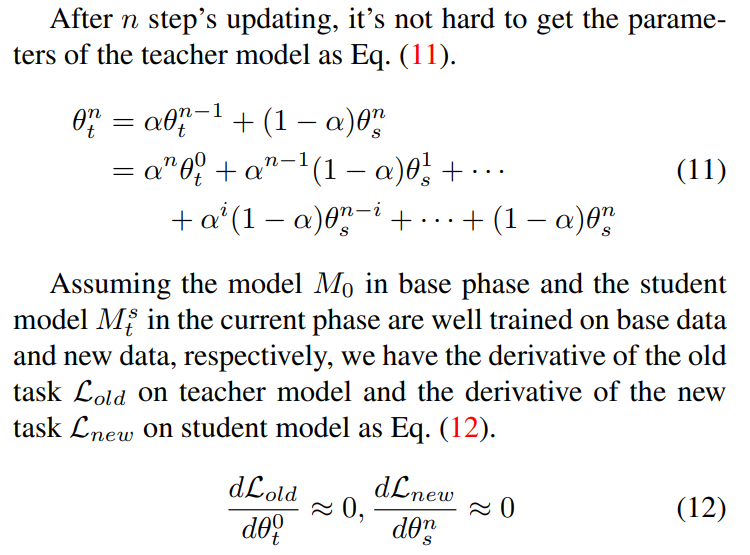
\ The derivative of the old task(s) and the new task on the teacher model in current IIL phase is
\ 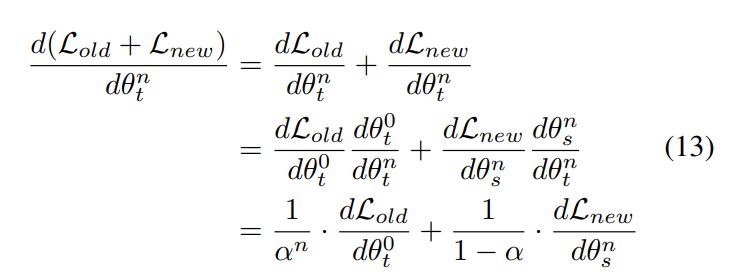
\ Therefore, we get Eq. (7) and many conclusions can be drawn based on it as we present in the manuscript. Notably, as we assume the student is fully trained on new data, we set a freezing period during which we only train the student without implementing KC-EMA. In the manuscript, we empirically set the freezing period to 10 epochs.
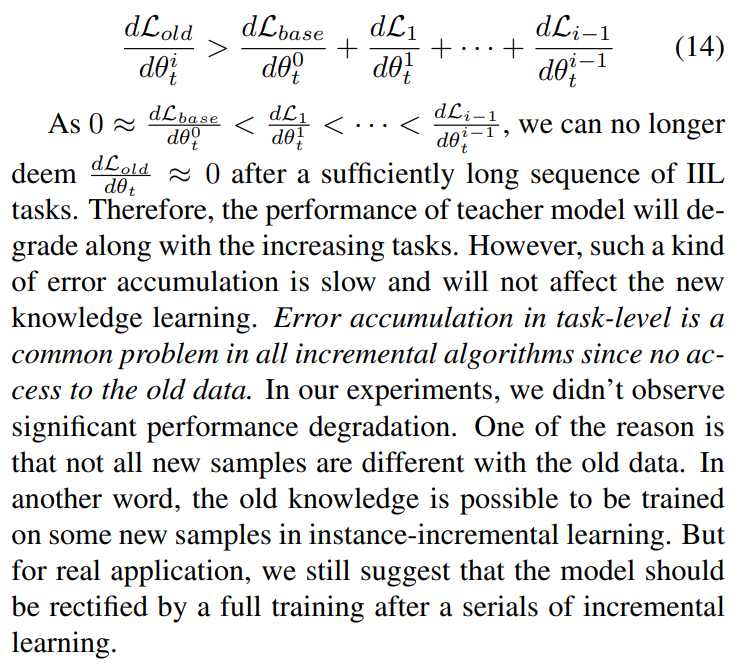
\ Limitation. Our method may accumulate errors after a long consecutive IIL tasks. For example, in the ith IIL task, the old model should consider the base task and the previous i − 1 IIL task. The old task’s derivative on the parameters of teacher becomes
\ 
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Qiang Nie, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou);
(2) Weifu Fu, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(3) Yuhuan Lin, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(4) Jialin Li, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(5) Yifeng Zhou, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(6) Yong Liu, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(7) Qiang Nie, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou);
(8) Chengjie Wang, Tencent Youtu Lab.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Noncommercial-Noderivs 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Golden surge in practical shooting propels PH past Malaysia in SEA Games medal tally

Here are Two Major Milestones for Saylor as Strategy Acquires 10K+ Bitcoin in Latest Scoop
