Why Predictive AI Might Be the Future of Disk Hygiene
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Motivation and design goals
-
Related Work
-
Conformal prediction
4.1. Mondrian conformal prediction (MCP)
4.2. Evaluation metrics
-
Mondrian conformal prediction for Disk Scrubbing: our approach
5.1. System and Storage statistics
5.2. Which disk to scrub: Drive health predictor
5.3. When to scrub: Workload predictor
-
Experimental setting and 6.1. Open-source Baidu dataset
6.2. Experimental results
-
Discussion
7.1. Optimal scheduling aspect
7.2. Performance metrics and 7.3. Power saving from selective scrubbing
-
Conclusion and References
5. Mondrian conformal prediction for Disk Scrubbing: our approach
In contrast to the conventional studies mentioned above, we propose a novel approach for disk drive scrubbing based on Mondrian conformal prediction to quantitatively assess the health status of disk drives and use it as a metric for selecting drives for scrubbing. Figure 1 shows a high-level overview of the proposed method.
\ 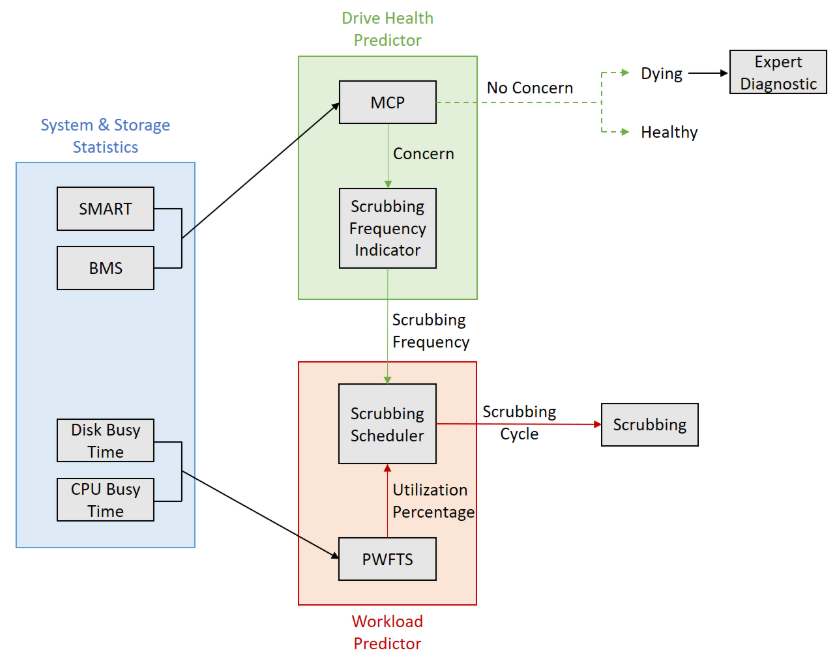
\ The proposed architecture consists of three subsystems. The first subsystem is responsible for collecting storage and system statistics, which includes retrieving disk drive data from the storage array, as well as capturing CPU and disk busy statuses. The second subsystem, referred to as the drive health predictor engine, predicts the health status of the drives. It uses MCP to output a set of ”No concern” drive disks, i.e. unhealthy/dying drives that can be flagged for manual diagnostics by experts (not discussed in this paper) or completely healthy drives that do not need any scrubbing, as well as a set of ”Concern” disks with assigned health scores based on the predictor’s confidence, which then are turned into scrubbing frequencies with the scrubbing frequency indicator. The underlying non-conformity score used is margin error function. The third subsystem is the workload predictor engine, which first predicts the resources’ utilization percentage by taking into account SAR logs[2], and then combine this result with the scrubbing frequencies in order to schedule when and how frequently disk drive scrubbing is performed. Finally, the scrubbing operation is triggered on the storage array based on the scrubbing cycle. In the following subsections, each component of the overall architecture is described in detail.
5.1. System and Storage statistics
The main components of this subsystem are:
\ • SMART: stands for Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology, and refers to a set of predefined parameters provided by device manufacturers that offer insights into various aspects of a storage device’s performance, including temperature, error rates, reallocated sectors, and more. Each attribute has a threshold value assigned by the manufacturer, indicating the acceptable limit for that parameter. When a parameter exceeds its threshold value, it may indicate a potential issue with the storage device. We use SMART parameters as input features for the drive health predictor engine.
\ • BMS: stands for Background Media Scanning, and is a passive process that differs from disk scrubbing, which actively scans the disk for errors during idle periods without reading or writing data. BMS involves scanning the disk for errors in the background without interrupting normal operations. In our proposed architecture, we also extract this BMS feature, which is a numerical value for the number of times it encounters errors while performing a scan on the same drive, and feed it to the drive health predictor engine.
\ • Disk and CPU busy time: The performance of a drive is heavily dependent on its critical processes, such as data access and write speed. The numeric values range between 1 to 100 in terms of percentage and change over time with a sampling period of 1 hour. These system statistics are extracted from the SAR logs (standard logs for system utilization) and converted into time series data, which can then be used by the workload predictor engine.
\ \
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Noncommercial-Noderivs 4.0 International) license.
:::
[2] The System Activity Report is a command that provides information about different aspects of system performance. For example, data on CPU usage, memory and paging, interrupts, device workload, network activity, and swap space utilization
:::info Authors:
(1) Rahul Vishwakarma, California State University Long Beach, 1250 Bellflower Blvd, Long Beach, CA 90840, United States (rahuldeo.vishwakarma01@student.csullb.edu);
(2) Jinha Hwang, California State University Long Beach, 1250 Bellflower Blvd, Long Beach, CA 90840, United States (jinha.hwang01@student.csulb.edu);
(3) Soundouss Messoudi, HEUDIASYC - UMR CNRS 7253, Universit´e de Technologie de Compiegne, 57 avenue de Landshut, 60203 Compiegne Cedex - France (soundouss.messoudi@hds.utc.fr);
(4) Ava Hedayatipour, California State University Long Beach, 1250 Bellflower Blvd, Long Beach, CA 90840, United States (ava.hedayatipour@csulb.edu).
:::
\
You May Also Like

‘Love Island Games’ Season 2 Release Schedule—When Do New Episodes Come Out?

Tesla, Inc. (TSLA) Stock: Rises as Battery Cell Investment Expands at German Gigafactory
