Ethereum Bug Nearly Triggers Network Crisis After Fusaka Upgrade
Ethereum’s Fusaka upgrade executed flawlessly on December 4, 2025, marking a historic milestone as the network achieved zero downtime while implementing its most significant expansion of data availability since EIP-4844.
However, within hours of activation, a critical bug in the Prysm consensus client threatened network stability, causing validation issues that slowed block finalization before client diversity safeguards prevented a potential crisis.
The incident unfolded as Prysm nodes experienced denial-of-service-like conditions triggered by excessive historical state generation.
Prysm core developer Terence Tsao explained that “historical state generation is compute and memory heavy, and a node can be dos’ed by a large number heavy, and a node can be dos’ed by a large number of state replays happening in parallel.”
Over two hours, a spike in stale attestations targeting checkpoint roots from off-slots forced affected nodes to reconstruct historical states, pushing systems into compromised operating conditions.
The Ethereum Foundation quickly issued emergency guidance, while ten other consensus clients maintained network operations, preventing any service disruption.
Client Diversity Proves Its Value During Crisis
While Prysm operators scrambled to implement the emergency workaround flag –disable-last-epoch-targets, alternative clients, including Lighthouse, Teku, Nimbus, and Lodestar, continued validating blocks without interruption.
The network maintained consensus throughout the incident, with finalization continuing despite affected validators experiencing participation issues.
Lido Finance reported minimal impact compared to other staking solutions, attributing its resilience to distributed validator operations where Prysm powers approximately 15% of node operators.
The protocol’s Q3 2025 metrics demonstrate balanced client usage as a deliberate strategy to mitigate single-client failure risks.
Most Lido-operated Prysm setups recovered within hours after applying the recommended configuration changes or temporarily switching to alternative clients.
The incident reinforced long-standing arguments for client diversity as Ethereum’s primary defense against consensus failures.
Developer Kydo captured the significance, noting that the upgrade simultaneously reinforced four critical narratives:
- Zero-downtime operations
- Layer-2 scaling capability through PeerDAS activation
- Client diversity protection
- Revenue-generating potential.
Ethereum briefly hit $3.2 billion annual run rate during the incident as blob fee mechanisms adjusted to new pricing parameters.
PeerDAS and Blob Scaling Transform Data Availability
Beyond the Prysm incident, Fusaka delivered transformative upgrades to Ethereum’s data layer through the PeerDAS implementation and the Blob Parameter Only (BPO) fork mechanism.
PeerDAS introduced data availability sampling, enabling nodes to store only 1/8 of the blob data while maintaining security guarantees.
This architectural shift enables throughput increases up to 8x current capacity while keeping hardware requirements manageable for independent operators.
Vitalik Buterin emphasized the upgrade’s historical significance, stating, “PeerDAS in Fusaka is significant because it literally is sharding.“
He celebrated the achievement as a dream dating back to 2015, noting “Ethereum is coming to consensus on blocks without requiring any single node to see more than a tiny fraction of the data.“
The implementation represents a breakthrough first proposed in 2017, though Buterin acknowledged remaining challenges, including distributed block building and sharded mempool development.
The BPO mechanism enables Ethereum to increase blob capacity between major upgrades rather than waiting for coordinated hard forks.
Fusaka maintains the current 6-blob target initially, but scheduled adjustments will raise limits to 10/15 on December 9, 2025, and 14/21 on January 7, 2026.
This addresses mounting pressure as layer-2 demand pushed Ethereum’s blob capacity toward saturation throughout 2024.
EIP-7918 ties blob base fees to execution costs, preventing market collapse. Blob fees jumped 1,500x immediately after activation, rising from 1 wei to 1,500 wei.
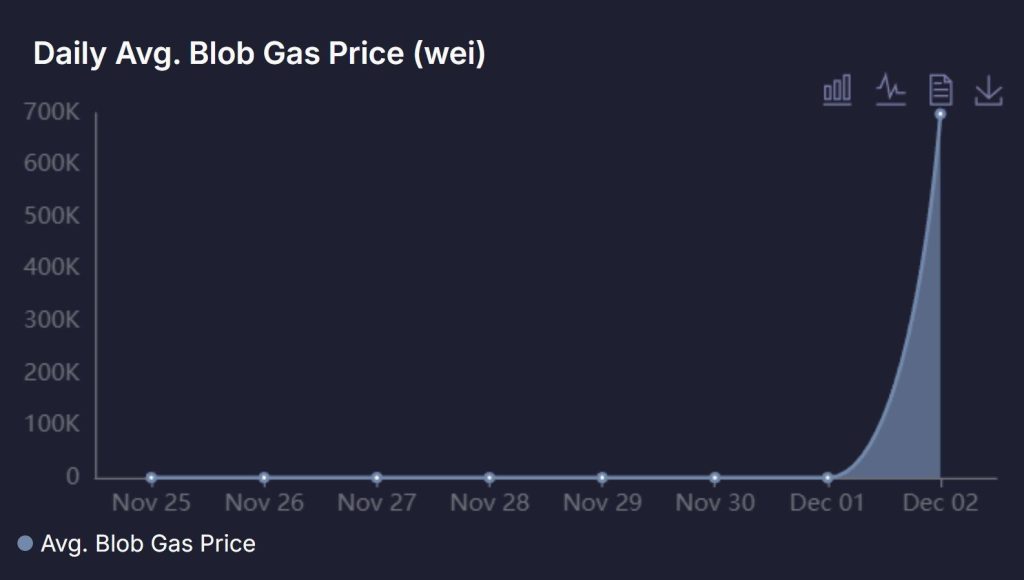 Source: X/@jarrodwatts
Source: X/@jarrodwatts
Developer Kydo explained this increase “restores a functioning fee market for blobs, so the protocol can actually use price to steer blob demand instead of being stuck at 1 wei.“
The change ensures that layer-2 operators pay meaningful costs for the computational resources their operations impose on network nodes.
Notably, Matt Hougan, CIO at Bitwise, also praised the momentum, noting, “Ethereum delivering two major upgrades in one year is impressive. The giant is awake and doing the right things.“
Among major L2s, according to information shared with Cryptonews, Optimism has announced plans to adopt Fusaka features into the OP Stack in early 2026, with Base, Soneium, and other layer-2 teams contributing to testing throughout development.
You May Also Like

Community Banks, Crypto Industry ‘Are Allies’ In CLARITY Act Clash: Exec

Liquidity shock? LIT drops 16% after Justin Sun pulls funds from Lighter
