What Investors and AI Researchers Can Learn from Low-Rank Optimization
Table of Links
I. Introduction
II. Spim Performance, Advantages and Generality
III. Inherently Low Rank Problems
A. Properties of Low Rank Graphs
B. Weakly NP-Complete Problems and Hardware Precision Limitation
C. Limitation of Low Rank Matrix Mapping
IV. Low Rank Approximation
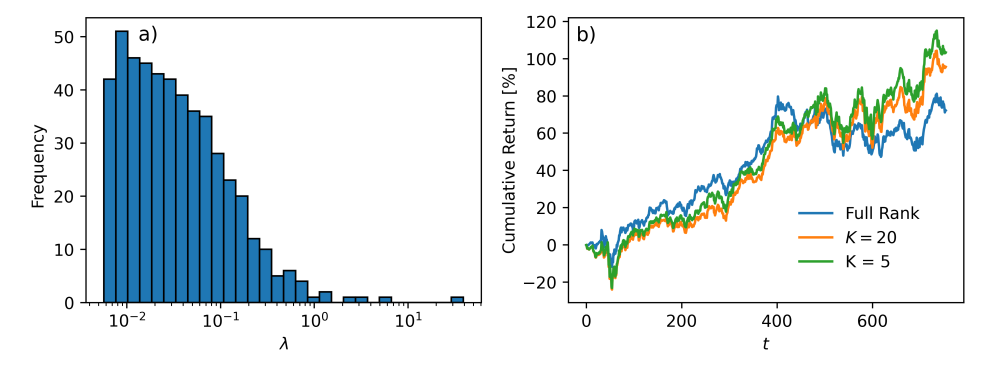
A. Decomposition of Target Coupling Matrix
B. How Fields Influence Ran
C. Low Rank Approximation of Coupling Matrices
D. Low-Rank Approximation of Random Coupling Matrices
E. Low Rank Approximation for Portfolio Optimization
F. Low-Rank Matrices in Restricted Boltzmann Machines
V. Constrained Number Partitioning Problem
A. Definition and Characteristics of the Constrained Number Partitioning Problem
B. Computational Hardness of Random CNP Instances
VI. Translation Invariant Problems
A. “Realistic” Spin Glass
B. Circulant Graphs
VII. Conclusions, Acknowledgements, and References
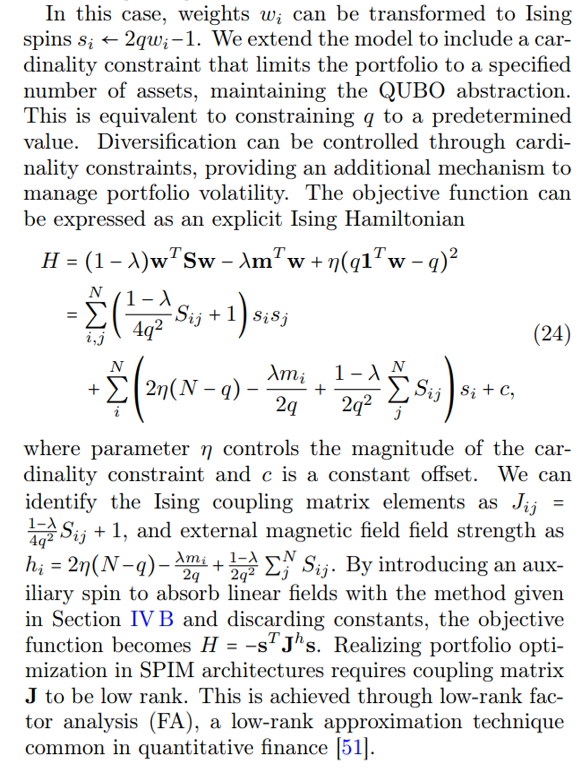
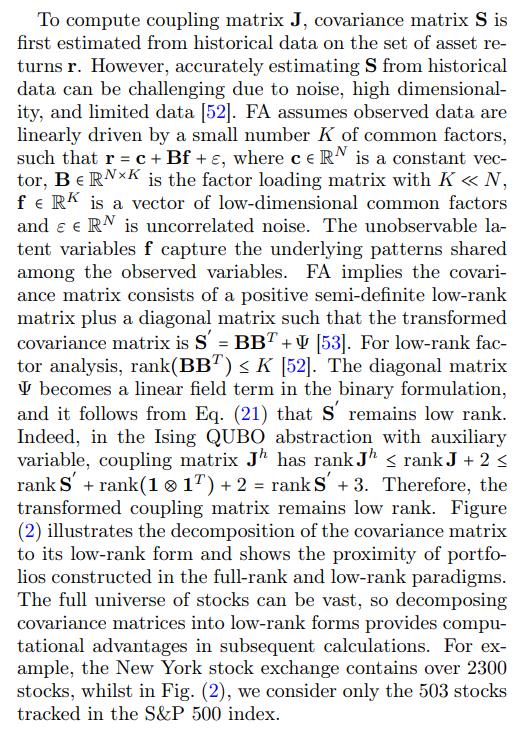
E. Low Rank Approximation for Portfolio Optimization
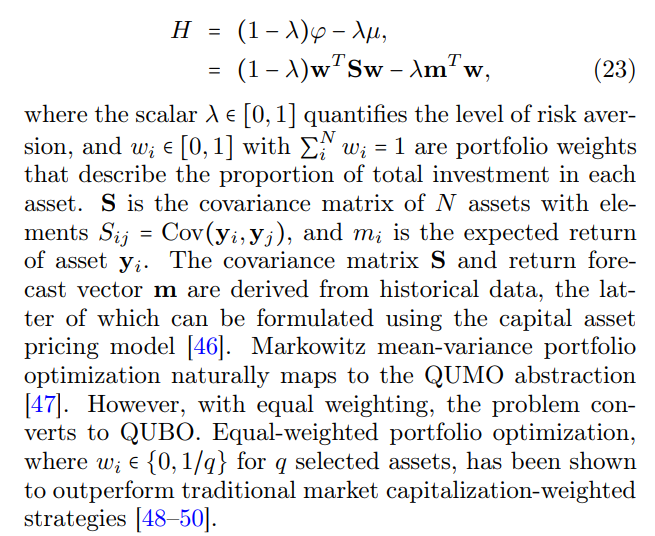
Low-rank matrices can arise during the construction of securities portfolios in financial analytics. Specifically, the optimal portfolio is the solution to a model-dependent quadratic unconstrained mixed optimization (QUMO) problem. Under an equal-weighting constraint, which we will explain below, this transforms into a quadratic unconstrained binary optimization (QUBO) problem that SPIMs can solve. Portfolio optimization involves creating an investment portfolio that balances risk and return. The objective is to allocate assets yi optimally to maximize expected returns µ while minimizing risk φ. In modern portfolio theory, this problem is formulated in the Markowitz mean-variance optimization model [43– 45] with the objective function:
\ 
\ 
\ 
\ For a quadratic unconstrained continuous optimization problem, if the coupling matrix is positive semi-definite as the covariance matrix is, then the problem is convex for any linear field term. However, for QUBO problems, even if S and hence J is positive semi-definitive, the problem is not necessarily easy to solve. The reason is that the binary constraint makes the feasible region discrete, not convex, which is why QUBO problems are generally NP-hard. SPIMs derive a temporal advantage over classical computing due to optical hardware implementing fast and energy-efficient computation. This is particularly crucial in high-frequency trading, where optimal portfolios must be calculated over microseconds to minimize latency in placing orders [54, 55].
\ 
\
F. Low-Rank Matrices in Restricted Boltzmann Machines
In Section III A, we mentioned that the minimum rank of a weighted complete bipartite graph is 2. The restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) [56, 57] is a computational model naturally defined on complete bipartite graphs. Thus, it is sensible to consider encoding low-rank approximations of RBMs within the SPIM paradigm.
\ Previous studies have shown that RBMs can provide good results when trained with low-rank approximations for collaborative filtering [58]. Recent advancements have explored low-rank approximations in unrestricted Boltzmann machines (UBMs). Notably, UBMs trained on Spatial Photonic Ising Machine (SPIM) based optical hardware have demonstrated promising results. This novel approach leverages the computational power of optical systems for machine learning tasks, offering significant performance improvements [25].
\ Although UBMs might offer greater modeling flexibility due to their unrestricted connectivity, they suffer significant computational downsides. Each step in the UBM training algorithm involves navigating a complex energy landscape, leading to inefficient convergence. This inefficiency is particularly problematic for large-dimensional datasets, where training time and computational resources can become prohibitively high [25].
\ In contrast, RBMs can be framed as minimal rank problems. Their bipartite nature simplifies the training process and reduces computational complexity, making them more practical for SPIM applications. The training efficiency of RBMs was significantly enhanced by Hinton’s method of minimizing contrastive divergence, which simplified the optimization of these models [57]. This minimal rank framework suggests that RBMs can be trained more efficiently, so they are often preferred for collaborative filtering and feature learning tasks. The theoretical foundations of harmony theory, laid out by Smolensky in 1986 [56], underpin the information processing capabilities of both RBMs and UBMs.
\ In general, RBMs, exhibiting lower computational demands, are valuable tools in machine learning. Recent research demonstrating the efficacy of low-rank UBMs on SPIM hardware [25] indicates that low-rank RBMs could be a promising direction for future applications of SPIM devices.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Richard Zhipeng Wang, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom;
(2) James S. Cummins, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom;
(3) Marvin Syed, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom;
(4) Nikita Stroev, Department of Physics of Complex Systems, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100, Israel;
(5) George Pastras, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece;
(6) Jason Sakellariou, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece;
(7) Symeon Tsintzos, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece and UBITECH ltd, 95B Archiepiskopou Makariou, CY 3020 Limassol, Cyprus;
(8) Alexis Askitopoulos, QUBITECH, Thessalias 8, Chalandri, GR 15231 Athens, Greece and UBITECH ltd, 95B Archiepiskopou Makariou, CY 3020 Limassol, Cyprus;
(9) Daniele Veraldi, Department of Physics, University Sapienza, Piazzale Aldo Moro 5, Rome 00185, Italy;
(10) Marcello Calvanese Strinati, Research Center Enrico Fermi, Via Panisperna 89A, 00185 Rome, Italy;
(11) Silvia Gentilini, Institute for Complex Systems, National Research Council (ISC-CNR), Via dei Taurini 19, 00185 Rome, Italy;
(12) Calvanese Strinati, Research Center Enrico Fermi, Via Panisperna 89A, 00185 Rome, Italy
(13) Davide Pierangeli, Institute for Complex Systems, National Research Council (ISC-CNR), Via dei Taurini 19, 00185 Rome, Italy;
(14) Claudio Conti, Department of Physics, University Sapienza, Piazzale Aldo Moro 5, Rome 00185, Italy;
(15) Natalia G. Berlof, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, United Kingdom (N.G.Berloff@damtp.cam.ac.uk).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
x
You May Also Like

Mitosis Price Flashes a Massive Breakout Hope; Cup-And-Handle Pattern Signals MITO Targeting 50% Rally To $0.115305 Level

Spot ETH ETFs Surge: Remarkable $48M Inflow Streak Continues

