Estimating Bitcoin Transaction Fees Based on Confirmation Time
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
- Preliminaries
- Problem definition
- BtcFlow
- Bitcoin Core (BCore)
- Mempool state and linear perceptron machine learning (MSLP)
- Fee estimation based on neural network (FENN)
- Experiments
- Conclusion, Acknowledgements, and References
2 Preliminaries
Proposed in 2008, the Bitcoin blockchain system as a decentralized digital currency payment system operates on a worldwide basis [24]. Even though different cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum (ETH) [34], Dash[7], Ripple (XRP) [27], Litecoin[8] (LTC), have been designed, a recent study shows that Bitcoin remains the dominant cryptocurrency in terms of market capitalisation and it is the most widely supported cryptocurrency among participating exchanges, wallets and payment companies [15, 23]. Blockchain revolutionizes the way we interact, automate payments, trace and track transactions. Fundamentally, it uses an immutable linked chain of blocks to record and track transactions. [24, 26, 38].
\ Transactions in the Bitcoin system record the digital asset transfer between clients. In a transaction, the output describes the amount of digital assets to be transferred to the new owner(s), while the input identifies the digital assets to be consumed [24]. One transaction can have several inputs and outputs. Transaction fee is set with the difference between the total of input and output assets, which will be collected by miners once the transaction is confirmed. Consequently, miners often choose transactions with larger transaction fees to maximise their mining profits. As a result, the transaction fee has to be increased to help with transaction confirmation by increasing the processing priority. Transaction feerate measures the fee density of a transaction or the transaction fee per size unit. In fact, each time only a limited number of transactions can be confirmed, hence miners would prioritise transactions with higher feeratess in order to increase mining profits.
\ Transactions can be submitted to the blockchain network via the Bitcoin wallets (desktop wallet, mobile wallet, web wallet, paper wallet, etc.) [24]. The submitted pending transactions are then broadcast across various nodes. If they meet the transactions’ validity criteria [2], Bitcoin nodes will add them to their mempools (memory pools), where transactions wait until they can be included (mined) into a block. Miners are the nodes responsible for the verification and block construction. Specifically, miners first select unconfirmed transactions from the mempool to construct their own candidate blocks, and then compete to determine a computational solution (Proof of Work (Pow)) to attach their candidature block to the blockchain (referred to as ‘mining a block’). Among all the miners, only the first miner who solves this computational issue will be rewarded with a fixed Bitcoin reward from the blockchain system plus transaction fees from the chosen transactions. Once a new block is added to the blockchain, these transactions are confirmed and will then be removed from the miner’s mempool.
\ A transaction is complete when it is recorded in a blockchain block. The block stores information about the selected transactions, as well as information about the mining complexity, block size, etc. In the meantime, the Bitcoin blockchain system keeps track of the generation time of each block.
3 Problem definition
The paper targets on estimating the transaction fee for a transaction with a given expected confirmation time (time between entering mempool and confirmed in the blockchain). As for the starting timestamp of confirmation time, a more realistic and meaningful choice could be the submission time for a transaction. We make our decision on using the entering mempool time mainly for two reasons. The first one is that the submission timestamp is unavailable. The second one is that the entering time is more reasonable. In the blockchain system, there can be different kinds of time delays between transaction submission and transaction entering the mempool, such as the propagation routine among network nodes, network traffic, etc. However, once the transactions enter the mempool, it means that they will start to compete to be included in the next block.
\ \ 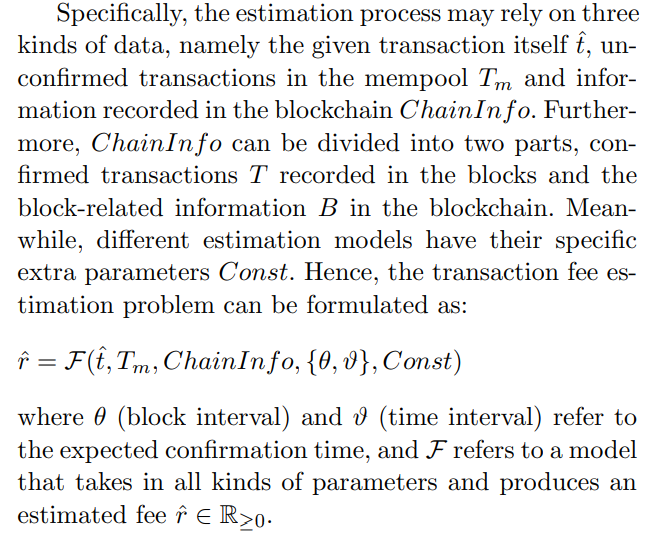
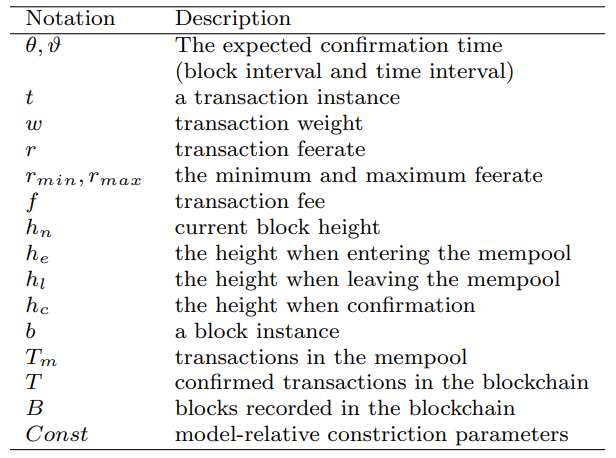
\ \ Table 1 summarizes the parameters of the three categories information used in different transactions fee models presented in this paper. In Section 8, we will compare the performance of these models with their respective features. The main notations used in this paper can be found in Table 2.
\ \ 
\ \ \
:::info Authors:
(1) Limeng Zhang, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne, Australia (limengzhang@swin.edu.au);
(2) Rui Zhou Swinburne, University of Technology, Melbourne, Australia (rzhou@swin.edu.au);
(3) Qing Liu, Data61, CSIRO, Hobart, Australia (q.liu@data61.csiro.au);
(4) Chengfei Liu, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne, Australia (cliu@swin.edu.au);
(5) M.Ali Babar, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia (ali.babar@adelaide.edu.au).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC0 1.0 UNIVERSAL license.
:::
[7] https://www.dash.org/
\ [8] https://litecoin.org/
Ayrıca Şunları da Beğenebilirsiniz

The Channel Factories We’ve Been Waiting For

SOLANA NETWORK Withstands 6 Tbps DDoS Without Downtime
