What You Should Know About the Next Generation of Encryption
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Contribution
-
Related Work
-
Brief of Homomorphic Polynomial Public Key Cryptography and 4.1 DPPK
4.2 MPPK Key Encapsulation Mechanism
4.3 HPPK KEM
4.4 MPPK DS
-
HPPK Digital Signature Scheme
5.1 HPPK DS Algorithm
5.2 Signing
5.3 Verify
5.4 A Variant of the Barrett Reduction Algorithm
5.5 A Toy Example
-
HPPK DS Security Analysis
-
Conclusion, References, Acknowledgements, and Author contributions statement
4 Brief of Homomorphic Polynomial Public Key Cryptography
In this section, we are going to briefly describe the motivation behind and development of the HPPK scheme: the path from the original deterministic polynomial public key or DPPK, proposed by Kuang in 2021[1], then multivariate polynomial public key or MPPK, proposed by Kuang, Perepechaenko, and Barbeau in 2022[5], to the homomorphic polynomial public key over a single hidden ring in 2023[6], and over a dual hidden ring scheme[7]. MPPK schemes for digital signature or MPPK/DS have been proposed by Kuang, Perepechaenko, and Barbeau in 2022[8], then an optimized version was proposed by Kuang and Perepechaenko in 2023[9]. A forged signature attack was reported by Guo in 2023[10].
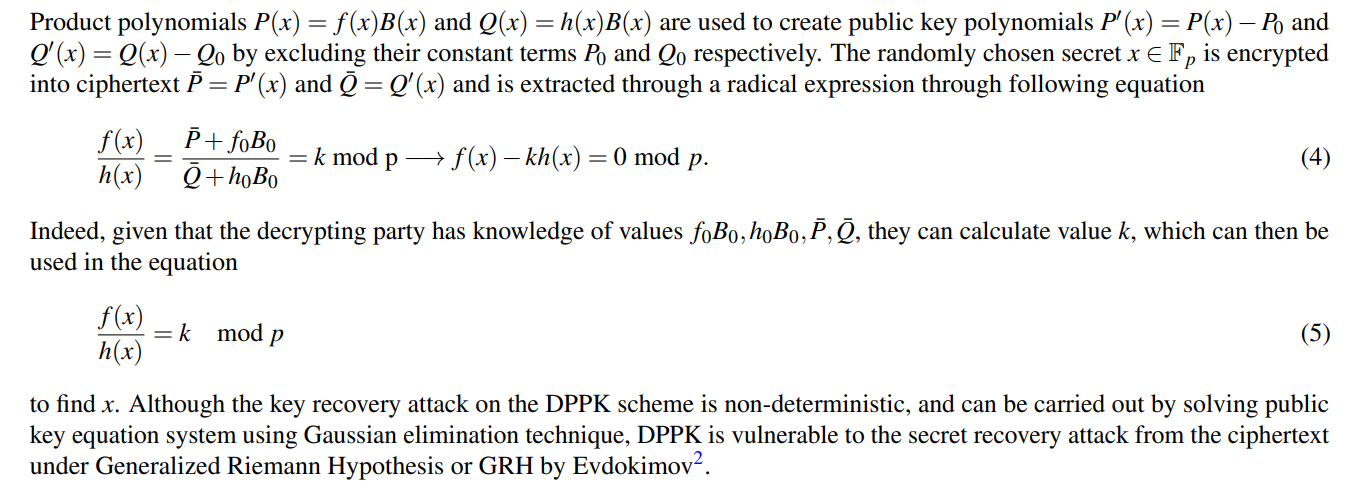
4.1 DPPK

\ 
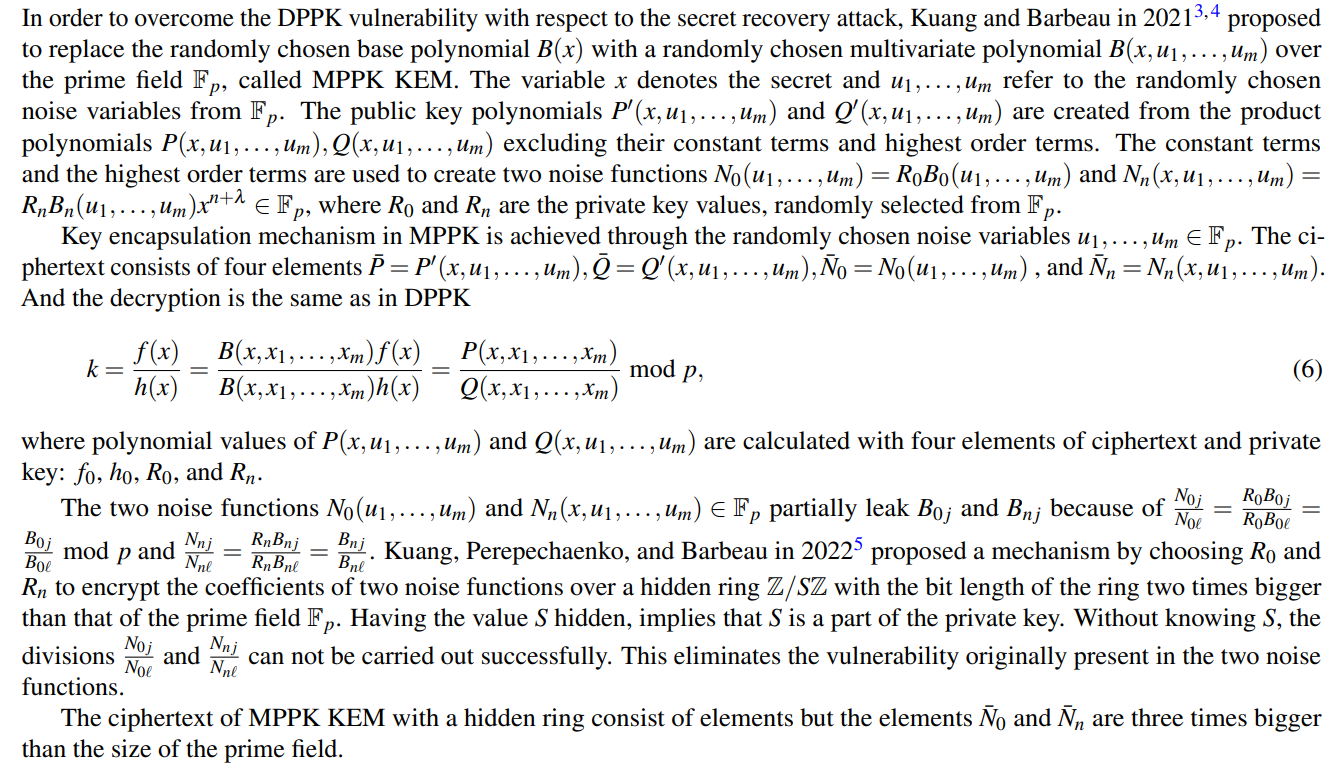
4.2 MPPK Key Encapsulation Mechanism
\ 
\
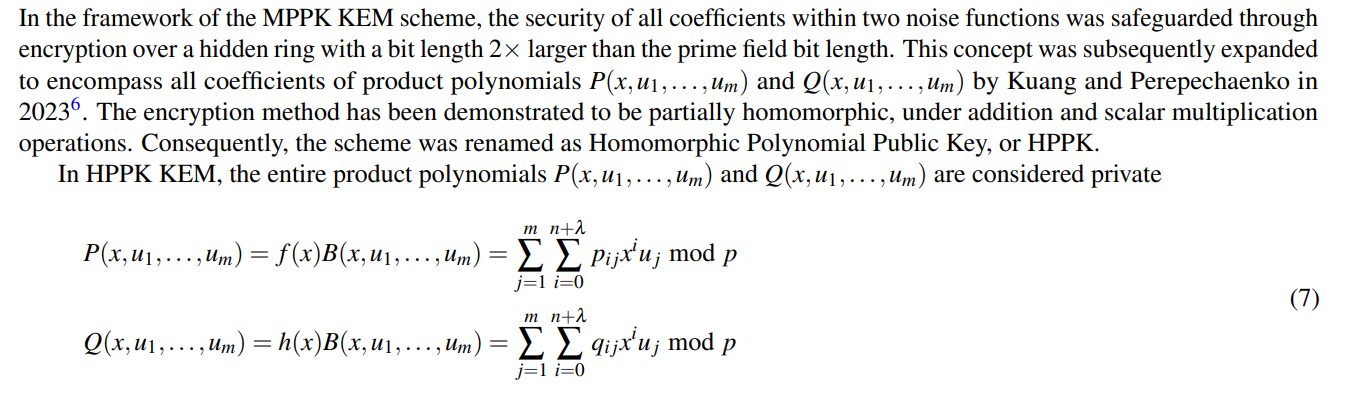
4.3 HPPK KEM
\ 
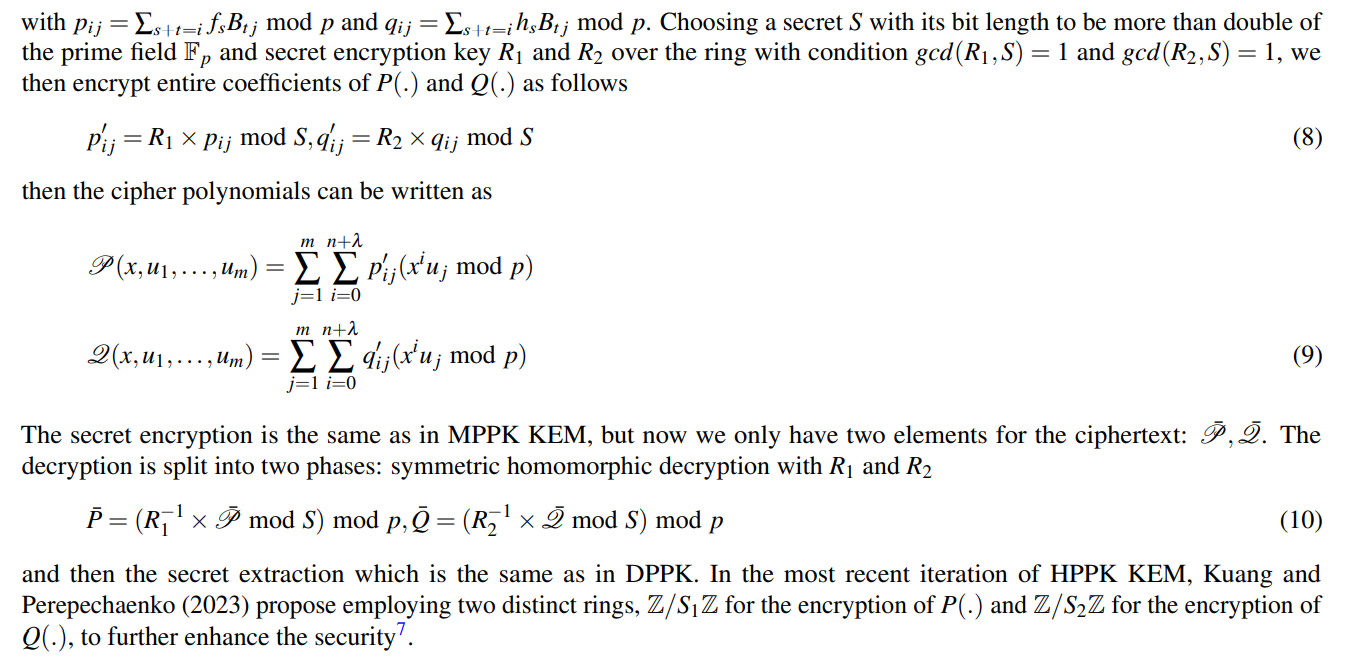
\ \ \ 
\
4.4 MPPK DS
A digital signature scheme based on MPPK has been proposed by Kuang, Perepechaenko, and Barbeau in 2022[8] and later optimized variant was proposed by Kuang and Perepechaenko in 2023[9]. MPPK digital signature scheme originated from MPPK over a single prime field[3, 4]. The signature verification equation stems from the identity equation
\ \ 
\ \ \
:::info Authors:
(1) Randy Kuang, Quantropi Inc., Ottawa, K1Z 8P9, Canada (randy.kuang@quantropi.com);
(2) Maria Perepechaenko, Quantropi Inc., Ottawa, K1Z 8P9, Canada;
(3) Mahmoud Sayed, Systems and Computer Engineering, Carleton University, Ottawa, K1S 5B6, Canada;
(4) Dafu Lou, Quantropi Inc., Ottawa, K1Z 8P9, Canada.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under ATTRIBUTION-NONCOMMERCIAL-SHAREALIKE 4.0 INTERNATIONAL license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

A whale traded ETH and made another $1.13 million, bringing its total profit to $76.05 million.

Sonami Token Ön Satışı S Staking Ödülleriyle Başladı, Solana Katman-2 Ağ Vizyonunu Güçlendiriyor
