Why Algorithmic Stablecoins Need Control Theory, Not Just PID Loops
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
- A Primer on Optimal Control
- The Token Economy as a Dynamical System
- Control Design Methodology
- Strategic Pricing: A Game-Theoretic Analysis
- Experiments
- Discussion and Future Work, and References
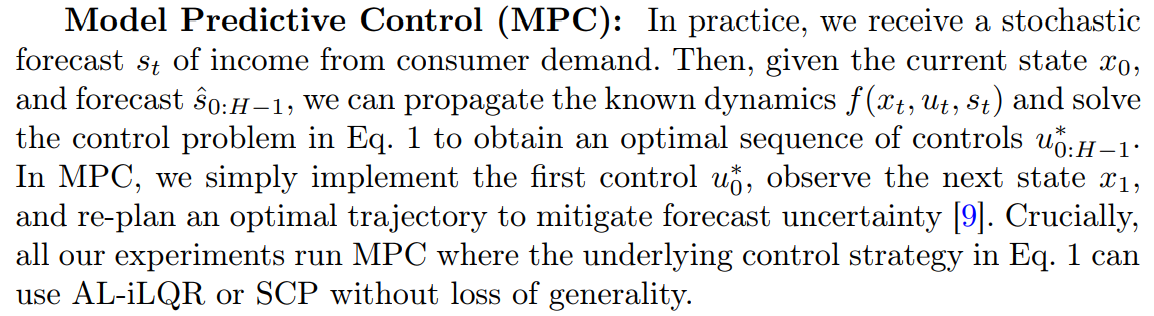
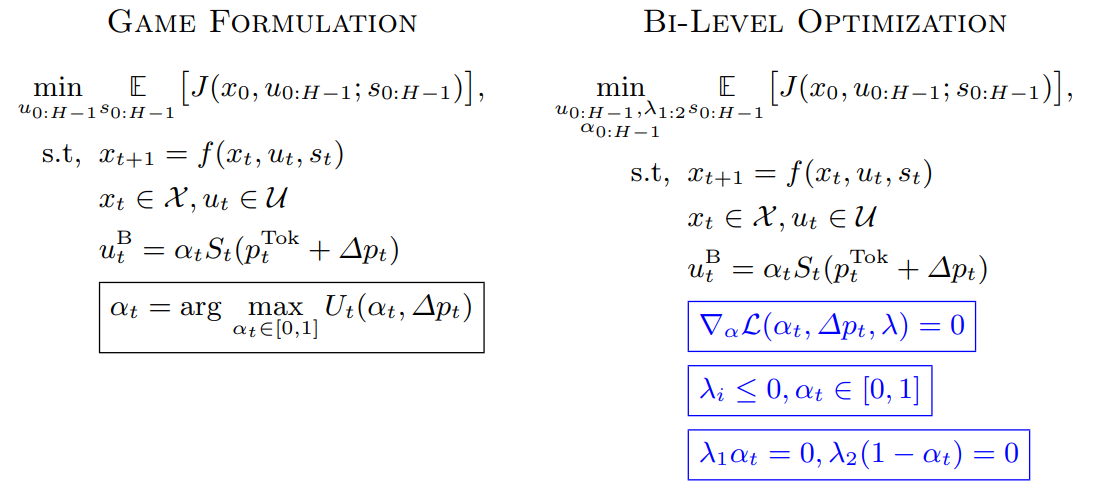
4 Control Design Methodology
We now illustrate methodologies that solve our formal control problem Eq. 1 by outlining techniques from nonlinear optimal control theory.
\ 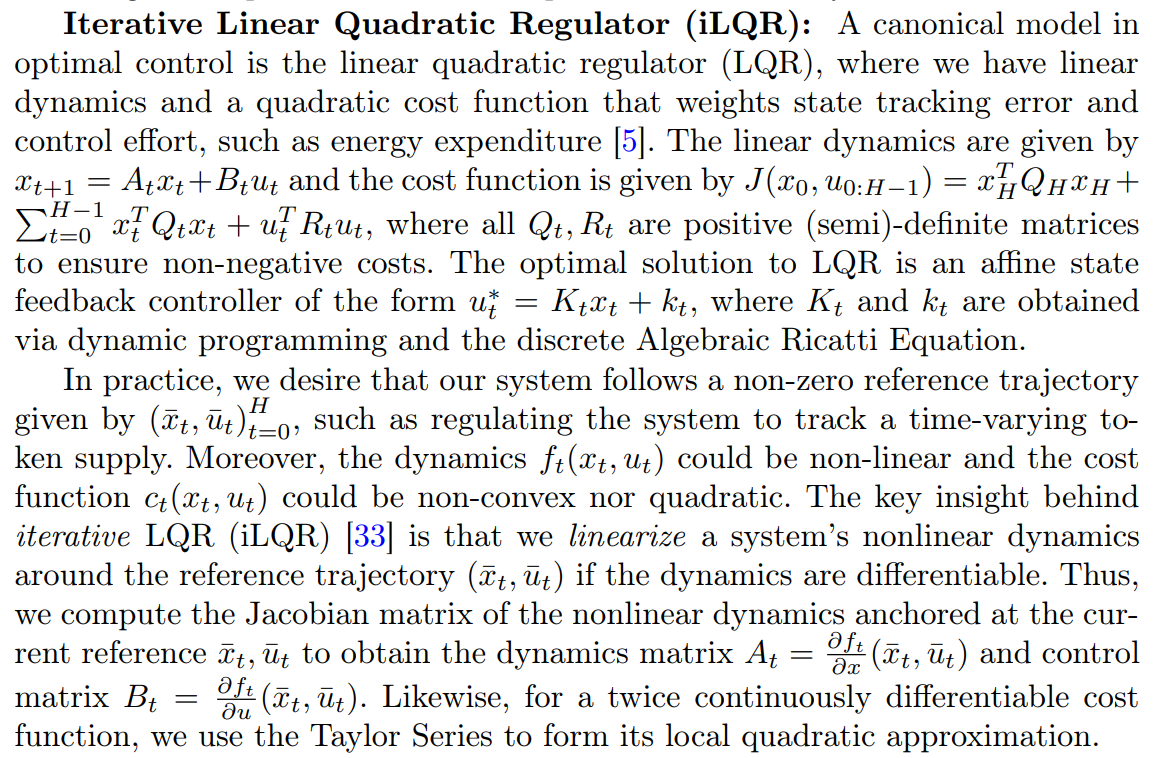
\ Given a nominal reference trajectory, linearized dynamics, and a quadratic approximation of the cost, we can simply invoke LQR to improve our nominal reference trajectory. The process repeats until the control cost converges, which is analagous to Newton’s method. We can incorporate strict state or control constraints by adding them as penalties to iLQR’s cost function using Augmented Lagrangian iLQR (AL-iLQR) methods. Crucially, AL-iLQR is our solution method of choice for tokenomics, since we have smooth nonlinear dynamics, a quadratic cost function, a well defined reference trajectory for the token price/circulating supply, and strict constraints for non-negative treasuries.
\ Sequential Convex Programming (SCP): SCP extends the core ideas behind iLQR to control problems with strict state or control constraints [8,23]. First, we linearize the dynamics around a reference trajectory, just as in iLQR. Then, we form a convex approximation of the cost function, often using a local quadratic approximation. Thus, we recover a constrained convex optimization problem, which we solve to obtain a new nominal trajectory. We then re-linearize around the updated nominal trajectory until the control cost saturates.
\ 
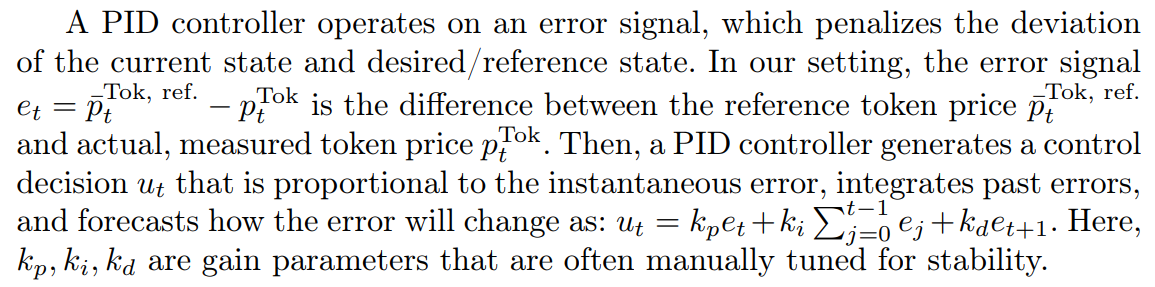
\ Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) Control: Our proposed solution uses AL-iLQR and SCP since we can model the token dynamics and explicitly desire to optimize a cost function. We compare these methods to a benchmark proportional integral derivative (PID) controller. While PID controllers achieve stability [5], they do not explicitly optimize a cost function like iLQR/SCP, and often require extensive tuning and can overshoot a reference trajectory. PID is a fitting benchmark due to its simplicity and the fact that recent algorithmic stablecoins, such as the RAI index [2], use PID.
\ 
\
5 Strategic Pricing: A Game-Theoretic Analysis
In our control-theoretic formulation, we assume token owners will gladly sell their tokens to the reserve when it offers to buy back tokens with an incentive price of ∆pt. However, as shown in Fig. 2, strategic token owners might only sell a fraction of their tokens for immediate revenue and retain the rest for their future expected value. As such, the reserve must offer a sufficiently high incentive ∆pt to goad token owners to sell their valuable tokens so that the circulating token supply is regulated to avoid inflation. Our key insight is that strategic pricing can be formulated as a two-player Stackelberg game (see [28]).
\ \ 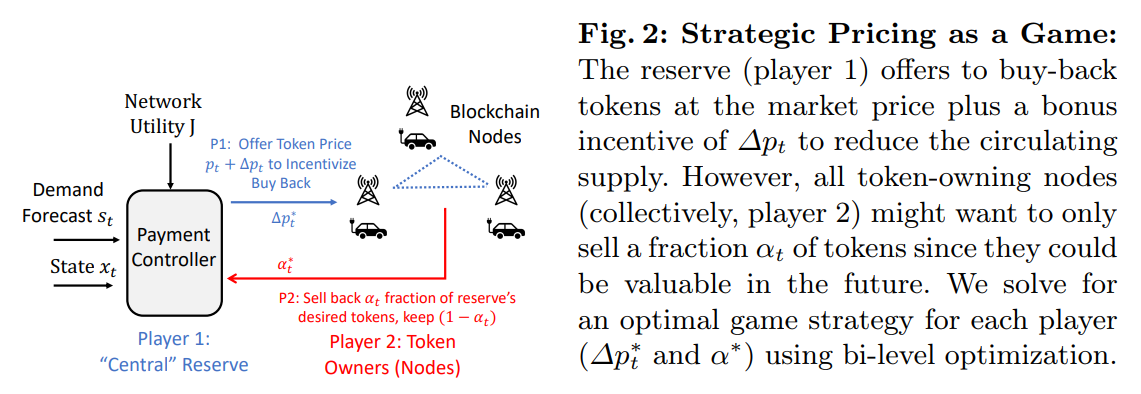
\ \ Market Dynamics The market dynamics arise from the selfish behavior of rational consumers. At each timestep, we have a two-step sequential game of complete information between the reserve’s controller (player 1) and all tokenowning nodes (player 2). The controller optimizes program (1) and the consumers seek to maximize the value of their token holdings over the time horizon. By complete information, we mean that facts about the opponent respectively are common knowledge. For example, token owners are aware of the controller’s strategy, which is encoded in smart contracts distributed across the blockchain. Likewise, each player can also perfectly observe the token price and supply.
\ \ 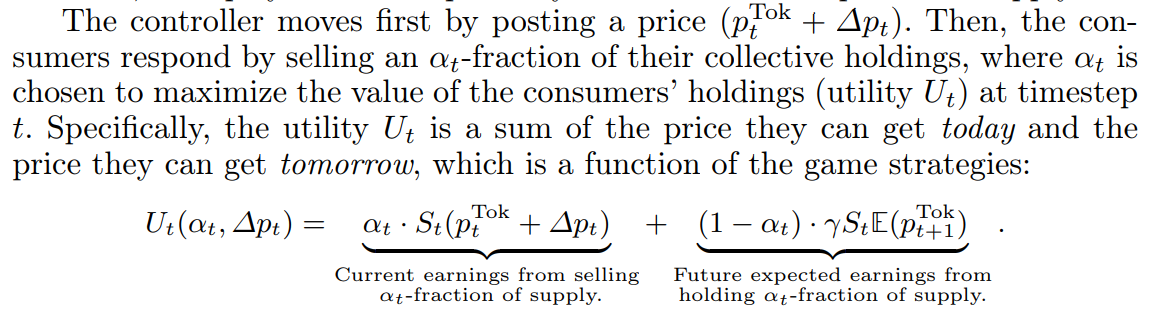
\ \ In the above, γ is a risk factor attenuating the expected future earnings from not selling. Further, the randomness in the expectation is due to forecasting noise as our controller is not randomized. Thus, for any controller-chosen incentive ∆pt, the nodes’ optimal strategy is to choose αt such that:
\ \ 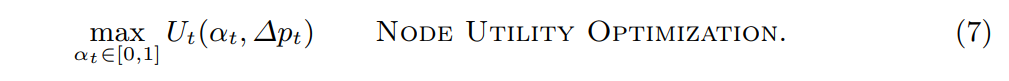
\ \ Moreover, due to program (7), the controller can compute the consumer strategy for any incentive price ∆pt. This means that we can transition the control problem (1) into the setting with incentives by equating the amount of tokens the controller buys back to the amount of tokens the nodes agree to sell:
\ \ 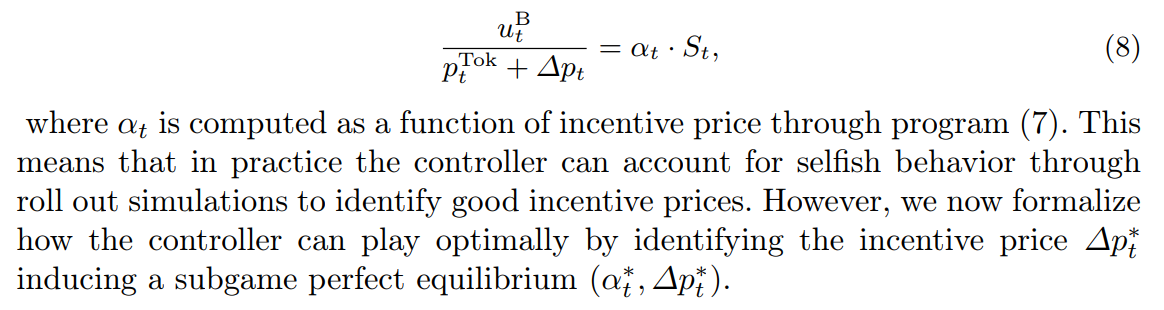
\ \ A Stackelberg Game for Strategic Pricing Since the controller first posts a price ∆pt and the nodes respond with the fraction αt of the holdings they wish to sell, we naturally have a leader-follower (Stackelberg) game. As mentioned above, we use (8) to constrain the tokens bought back by αt. Then, recalling that the node’s strategy is given by (7), the controller’s optimization problem is:
\ \ 
\ \ \ 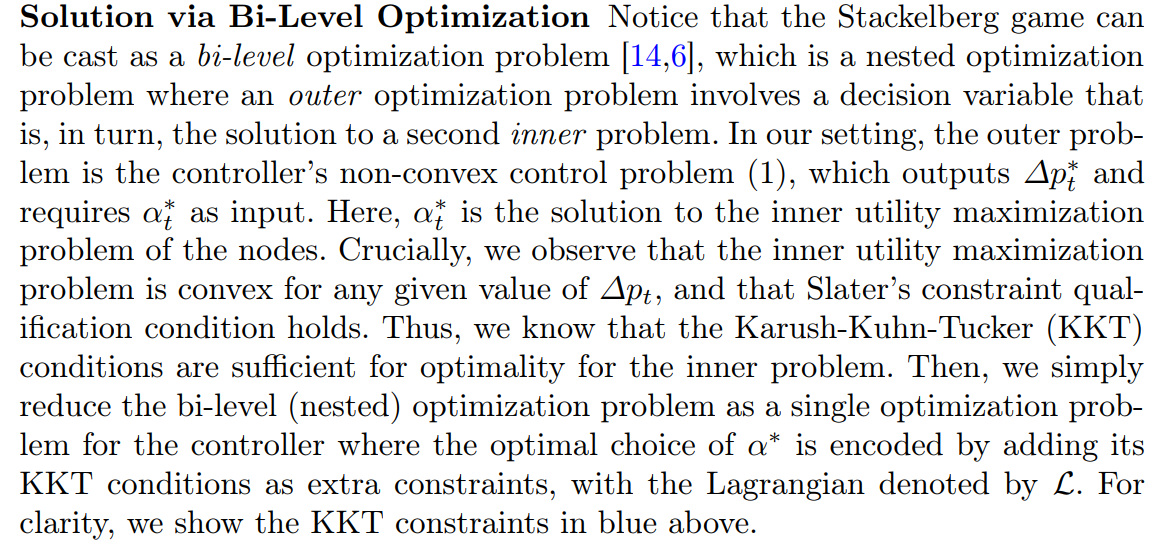
\ \ Remark 2. Since we have a Stackelberg Game, the horizon is finite and a subgame perfect equilibrium can be found via backward induction. First, the best response function of the nodes is calculated. Then, the controller picks an action maximizing its utility, anticipating the follower’s best response. For more details, see [28]. Then it is clear that our method finds a subgame perfect equilibrium since the KKT conditions of the inner problem give a certificate of optimal play on the nodes part. Encoding them as extra constraints on the part of the controller simply gives an explicit route for backward induction in this game.
\ \
:::info Authors:
(1) Oguzhan Akcin, The University of Texas at Austin (oguzhanakcin@utexas.edu);
(2) Robert P. Streit, The University of Texas at Austin (rpstreit@utexas.edu);
(3) Benjamin Oommen, The University of Texas at Austin (baoommen@utexas.edu);
(4) Sriram Vishwanath, The University of Texas at Austin (sriram@utexas.edu);
(5) Sandeep Chinchali, The University of Texas at Austin (sandeepc@utexas.edu).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Fed Decides On Interest Rates Today—Here’s What To Watch For

Robinhood Chain Public Testnet Launch: A Strategic Pivot into Ethereum’s Layer 2 Ecosystem
