A Brief Review of Modern Shortest Path Algorithms and Graph Optimization Techniques
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
1.1 Our Contribution
1.2 Setting
1.3 The algorithm
-
Related Work
-
Algorithm
3.1 The Structural Decomposition Phase
3.2 The Routing Phase
3.3 Variants of WormHole
-
Theoretical Analysis
4.1 Preliminaries
4.2 Sublinearity of Inner Ring
4.3 Approximation Error
4.4 Query Complexity
-
Experimental Results
5.1 WormHole𝐸, WormHole𝐻 and BiBFS
5.2 Comparison with index-based methods
5.3 WormHole as a primitive: WormHole𝑀
References
2 RELATED WORK
There is a vast body of research on shortest paths and distances, spanning over many decades, and including hundreds of algorithms and heuristics designed for a variety of settings. Here, we only review several works that are most closely related to ours. For a more comprehensive overview, see the surveys [42, 55] and references therein.
\ Index-based approaches. As mentioned earlier, a ubiquitous set of algorithms are based on landmark/sketch approaches [37, 61, 62], with Pruned Landmark Labeling (PLL) [5] being perhaps the most influential one. These algorithms follow a two-step procedure: the first step generates an ordering of the vertices according to importance (based on different heuristics), and the the second step generates labeling from pruned shortest path trees constructed according to the ordering. Then the shortest distance between an arbitrary pair of vertices 𝑠 and t can be answered quickly based on their labels. However, even with pruning, PLL requires significant setup time. Hence, there have been many attempts to parallelize it [29, 37, 39].
\ Embedding based approaches. Some recent approaches leverage embeddings of graphs to estimate shortest paths. Likein representation learning, they seek to find efficient representations of distances between pairs of nodes [64, 65]. A modern line of work also considers hyperbolic embeddings of the graphs, that are closely related to tree decompositions, to answer shortest path inquiries [11, 33]. Recent work has also looked at accelerating this process by using GPU based deep learning methods [35, 47, 48]. Query-by-Sketch [57] considers the, related but incomparable, task of answering shortest-path-graph inquiries, where the goal is to compute a subgraph containing exactly all shortest paths between a given pair of vertices. They propose an alternative labeling scheme to improve the scalability and inquiry times.
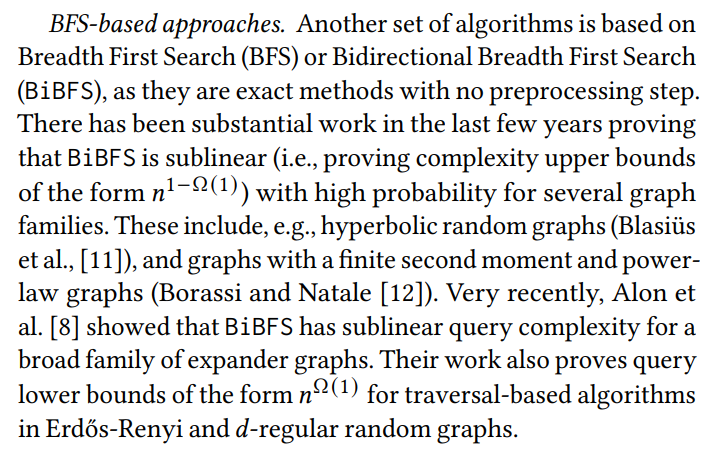
\ 
\ Core-periphery based approaches. Several other works exploit the core-periphery structure of networks [6, 13, 38]. Brady and Cohen [13] use compact routing schemes to design an algorithm with small additive error based on the resemblance of the periphery to a forest. Akiba, Sommer and Kawarabayashi [6] exploit the property of low tree-width outside the core, and in [38], the authors design a Core-Tree based index in order to improve preprocessing times on massive graphs. We note that in all these results, the memory overhead is super-linear.
\ Worst case graphs. On the theoretical side, there have been many results on exact and approximate shortest paths in worst-case graphs, e.g., [19, 20, 22, 49, 51, 67], with improvements as recently as the past year. Most of these focus on the 2-approximation case, first investigated in the seminal work of Aingworth et al. [4]. We point the readers to Zwick’s survey [66] on exact and approximate shortest-path algorithms, and Sen’s survey [53] on distance oracles for general graphs with an emphasis on lowering pre-processing cost. Notably, because we make a beyond worst case structural assumption that is common in large networks, namely, a core-periphery structure, both our results and algorithm substantially differ from the worst-case theoretical literature.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Talya Eden, Bar-Ilan University (talyaa01@gmail.com);
(2) Omri Ben-Eliezer, MIT (omrib@mit.edu);
(3) C. Seshadhri, UC Santa Cruz (sesh@ucsc.edu).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Analyst Ignores Bitcoin (BTC) Price Crash Narratives, Points to Hidden Bull Signals That May Matter More

Pundit Describes How $10,000 In XRP Could Become $1,000,000
