11 Overlooked HTML Tags That Can Make Your Pages Pop
I know I think a lot about HTML, but honestly, I have to say it's an incredible markup language to get accustomed to programming. Even though it doesn't follow many standards like a semicolon at the end, it's still a good intro that teaches you about proper syntax and logic.
If you don't know how HTML works, then why are you here? But to put it simply: if we think of a web page like a human being, HTML would be the skeleton that holds everything together. JavaScript would be the organs that make the body work, and CSS would be like the hair, eye color, and the clothes that it's wearing. Elements are HTML's way of telling it what to do.
For example, if I want a heading, I'd put an H1 or an H2 for a subheading. If I wanted a paragraph here, I'd put a p element. If I wanted to combine all of these together, I'd wrap them in a div element, and so on and so forth.
We can see that there are more specific tags than just text. The div tag, for example, creates a sort of box. Other tags, such as strong and em, not only alter the look of the text but also tell the website that they mean something—either they should be emphasized or have bigger importance than the rest of the text. However, there are some HTML tags that not many people know. Which ones are they? Well, let's find out.
1. The abbr Tag
Also called the abbreviation tag, this is used for when you want to display the meaning of an acronym or abbreviation. To use it, simply wrap the word or acronym in the abbr tag and add a title attribute to it.

- The
<abbr>tag wraps the acronym "WHO." - The
titleattribute specifies what "WHO" stands for: "World Health Organization." - When you hover over "WHO" with your cursor, the full meaning ("World Health Organization") is displayed as a tooltip.
The title attribute works with every element, but in this case, type what the acronym or abbreviation stands for. Now, when you hover your cursor over that abbreviation, it shows you the title you set. This is great for buttons or icons for further accessibility. However, be careful with mobile users—they can’t hover over objects.
2. The code Tag
This is extremely useful for transmitting code blocks to users. You could use CSS and a normal p element to make it look like a code block, but why do that when the code tag is made for this exact purpose?
Wrap the string you want to transform in the code tag, and the browser will automatically display it in a monospace font. You can then use CSS to make it prettier. 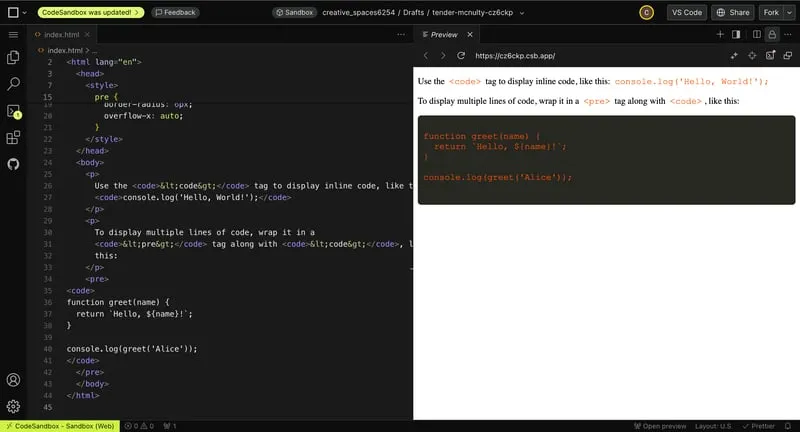
3. The kbd Tag
\  Also known as the keyboard tag, this is much like the
Also known as the keyboard tag, this is much like the code tag. Wrap designated keyboard keys in the kbd tag, and the browser will automatically display them in a monospace font. Use CSS to make it look like keyboard buttons.
4. The datalist + option Tags
These are super useful for displaying recommendations or an option menu. It’s easier than you think!
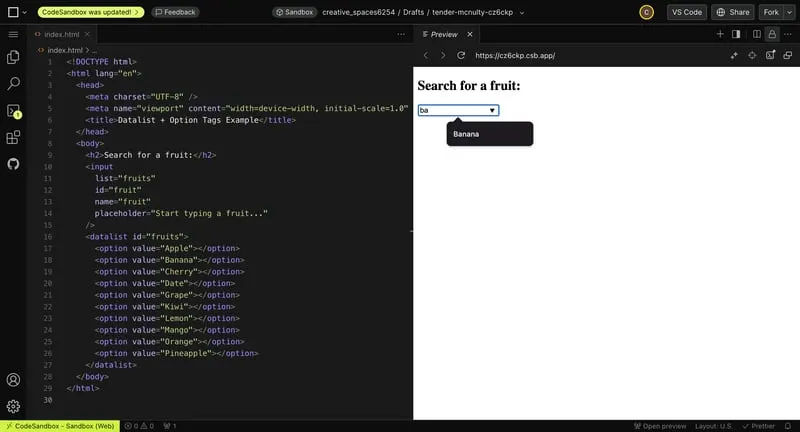
- Create an
inputelement with the input tag where users can write. - Add the
listattribute to it and give it a name. - Create your
datalistelement with thedatalisttag and set itsidattribute equal to the list attribute’s name. - Inside the
datalist, addoptiontags for recommendations. Use thevalueattribute for the options.
Now, when users start typing, options pop up based on the letters typed.
5. The dialog Tag
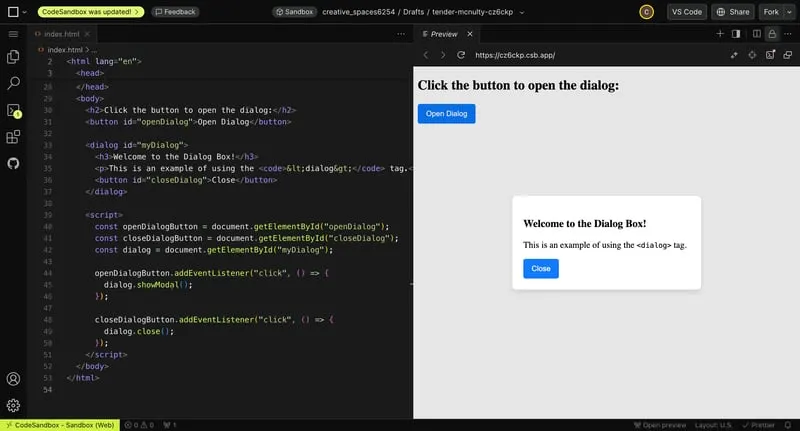
This tag is a quick and easy way to create a pop-up or modal. Simply create your dialog box with the dialog tag and add content inside it. When you add the open attribute, the dialog box will show. You can use simple JavaScript to control it further.
6. The details + summary Tags
These are perfect for creating native dropdown menus without CSS or JavaScript.
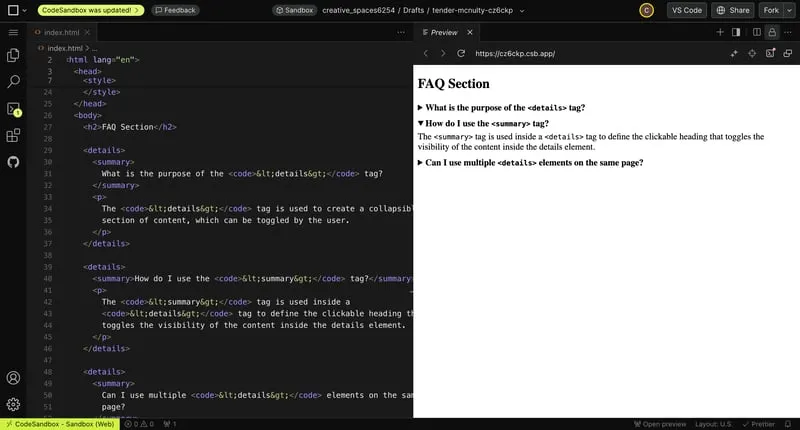
- Use the
detailstag to create the container. - Add a
summarytag inside it for the clickable title. - Place any content inside the
detailstag, and it will toggle visibility when clicked.
This is especially useful for FAQ sections.
7. The time Tag

Though it doesn’t visually do much, this tag allows browsers and search engines to read time values. Wrap time values in the time tag to improve SEO.
8. The ruby + rt + rp Tags
These are used for Ruby notation, commonly in Asian typographies. They display small text above a word or character.
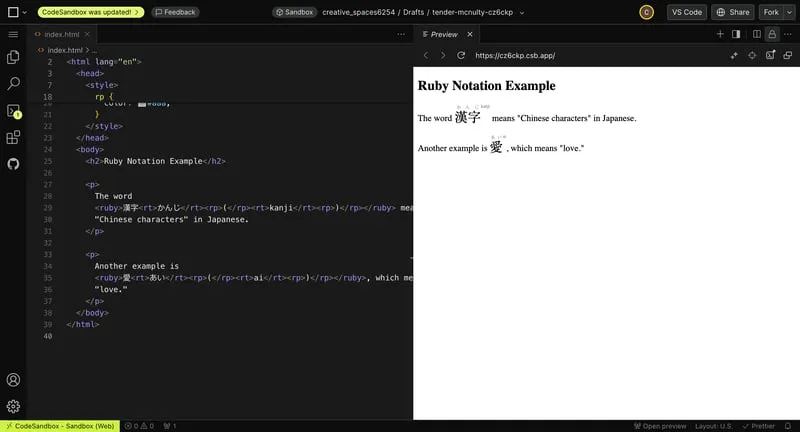
- Wrap your text in the
rubytag. - Use the
rttag for the smaller text. - Add
rptags for browsers that don’t support Ruby notation.
9. The progress Tag
This tag creates a progress bar without CSS.

- Use the
progresstag. - Add the
maxattribute for the maximum value. - Use the
valueattribute for the current value.
The bar adjusts automatically.
10. The meter Tag
Similar to the progress tag, the meter tag represents a scale.
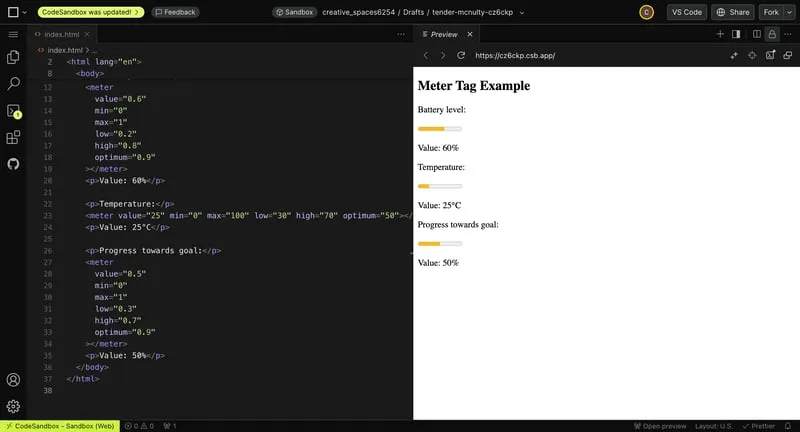
- Add
min,max, and value attributes for the range and current value. - Use the
low,high, andoptimumattributes for thresholds that change the bar's color.
11. The fieldset + legend Tags
These tags create a box to group objects.

- Use the
fieldsettag to create the container. - Add a title with the
legendtag. The legend automatically positions itself in the margins of the box.
Outro
If you learned something new today, let me know by absolutely destroying that like button! If you enjoy this type of content, consider subscribing. I post videos on programming, web development, and my journey of learning how to code.
That’s all for today’s list of hidden HTML tags. Thank you so much for reading to the end, and I’ll see you in the next one. Bye-bye!
You May Also Like

XRP Delivers Impressive ETF Volumes But Digitap ($TAP) is the King of Cross-Border Payments in 2026

Strive Completes Acquisition of Bitcoin Treasury Firm Semler

Wormhole token soars following tokenomics overhaul, W reserve launch
Wormhole’s native token has had a tough time since launch, debuting at $1.66 before dropping significantly despite the general crypto market’s bull cycle. Wormhole, an interoperability protocol facilitating asset transfers between blockchains, announced updated tokenomics to its native Wormhole (W) token, including a token reserve and more yield for stakers. The changes could affect the protocol’s governance, as staked Wormhole tokens allocate voting power to delegates.According to a Wednesday announcement, three main changes are coming to the Wormhole token: a W reserve funded with protocol fees and revenue, a 4% base yield for staking with higher rewards for active ecosystem participants, and a change from bulk unlocks to biweekly unlocks.“The goal of Wormhole Contributors is to significantly expand the asset transfer and messaging volume that Wormhole facilitates over the next 1-2 years,” the protocol said. According to Wormhole, more tokens will be locked as adoption takes place and revenue filters back to the company.Read more