Breaking Down Low-Rank Adaptation and Its Next Evolution, ReLoRA
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Related Work
-
Low Rank Adaptation
3.1 LoRA and 3.2 Limitation of LoRA
3.3 ReLoRA*
-
Sparse Spectral Training
4.1 Preliminaries and 4.2 Gradient Update of U, VT with Σ
4.3 Why SVD Initialization is Important
4.4 SST Balances Exploitation and Exploration
4.5 Memory-Efficient Implementation for SST and 4.6 Sparsity of SST
-
Experiments
5.1 Machine Translation
5.2 Natural Language Generation
5.3 Hyperbolic Graph Neural Networks
-
Conclusion and Discussion
-
Broader Impacts and References
Supplementary Information
A. Algorithm of Sparse Spectral Training
B. Proof of Gradient of Sparse Spectral Layer
C. Proof of Decomposition of Gradient of Weight
D. Proof of Advantage of Enhanced Gradient over Default Gradient
E. Proof of Zero Distortion with SVD Initialization
F. Experiment Details
G. Singular Value Pruning
H. Evaluating SST and GaLore: Complementary Approaches to Memory Efficiency
I. Ablation Study
3 Low Rank Adaptation
This section introduces the fundamentals and limitations of Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) [4] and ReLoRA [5]. These limitations are addressed by Sparse Spectral Training (SST) in Section 4.
3.1 LoRA
3.2 Limitation of LoRA
3.3 ReLoRA*
\ 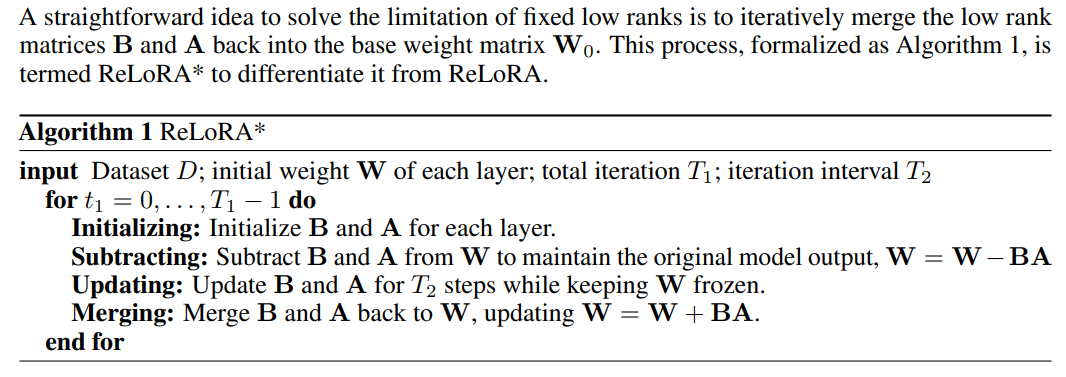
\ \ This improvement theoretically permits LoRA to transcend the limitations of a predetermined rank r. ReLoRA [5] and COLA [6] represent specific implementations of this strategy, where they employ LoRA’s initialization techniques—B initialized to zero and A with a Gaussian distribution [30]. The initial zero setting for B allows the subtracting step to be skipped. ReLoRA* thus serves as an end-to-end memory-efficient methodology, differing from ReLoRA, which incorporates a period of full-rank training initially. Notably, the optimizer states for B and A are reset after merging step (99% optimizer state is pruned in ReLoRA).
\ However, each iteration of ReLoRA* learns only a small subset of singular values. Additionally, its reliance on random initialization can lead to stucking at saddle points, as discussed in Section 4.3. These issues hinder ReLoRA* from achieving the convergence speed and training quality of full-rank training.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Jialin Zhao, Center for Complex Network Intelligence (CCNI), Tsinghua Laboratory of Brain and Intelligence (THBI) and Department of Computer Science;
(2) Yingtao Zhang, Center for Complex Network Intelligence (CCNI), Tsinghua Laboratory of Brain and Intelligence (THBI) and Department of Computer Science;
(3) Xinghang Li, Department of Computer Science;
(4) Huaping Liu, Department of Computer Science;
(5) Carlo Vittorio Cannistraci, Center for Complex Network Intelligence (CCNI), Tsinghua Laboratory of Brain and Intelligence (THBI), Department of Computer Science, and Department of Biomedical Engineering Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed (Attribution 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Why This New Trending Meme Coin Is Being Dubbed The New PEPE After Record Presale

Real estate, crypto, bonds, AI stocks and gold defined global market trades in 2025
