Here’s Why AI Researchers Are Talking About Sparse Spectral Training
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Related Work
-
Low Rank Adaptation
3.1 LoRA and 3.2 Limitation of LoRA
3.3 ReLoRA*
-
Sparse Spectral Training
4.1 Preliminaries and 4.2 Gradient Update of U, VT with Σ
4.3 Why SVD Initialization is Important
4.4 SST Balances Exploitation and Exploration
4.5 Memory-Efficient Implementation for SST and 4.6 Sparsity of SST
-
Experiments
5.1 Machine Translation
5.2 Natural Language Generation
5.3 Hyperbolic Graph Neural Networks
-
Conclusion and Discussion
-
Broader Impacts and References
Supplementary Information
A. Algorithm of Sparse Spectral Training
B. Proof of Gradient of Sparse Spectral Layer
C. Proof of Decomposition of Gradient of Weight
D. Proof of Advantage of Enhanced Gradient over Default Gradient
E. Proof of Zero Distortion with SVD Initialization
F. Experiment Details
G. Singular Value Pruning
H. Evaluating SST and GaLore: Complementary Approaches to Memory Efficiency
I. Ablation Study
A Algorithm of Sparse Spectral Training
B Proof of Gradient of Sparse Spectral Layer
We can express the differential of W as the sum of differentials:
\ \ 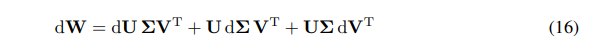
\ \ We have chain rule for the gradient of W:
\ \ 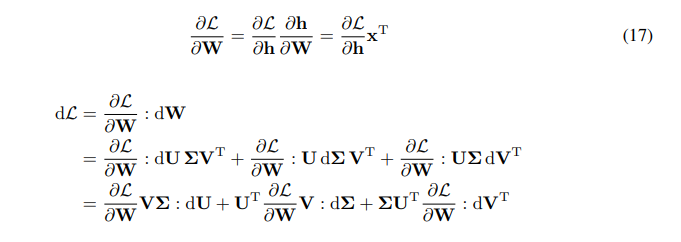
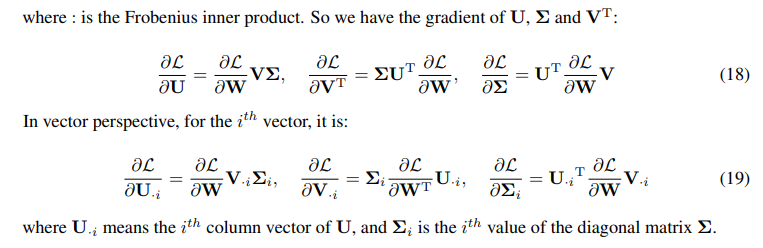
\ \ \ 
\
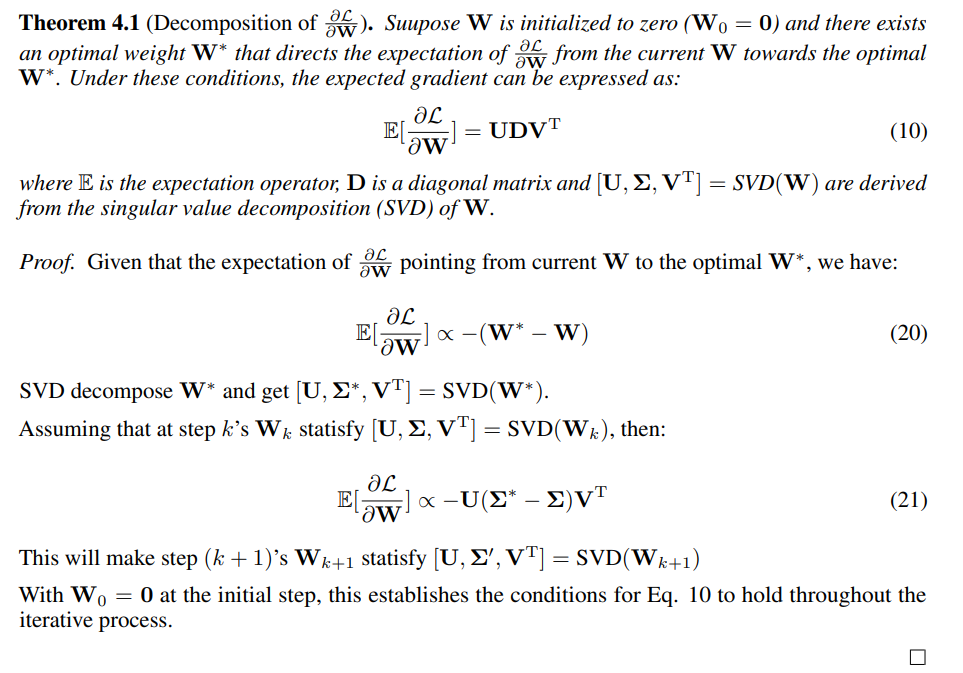
C Proof of Decomposition of Gradient of Weight
\ 
\
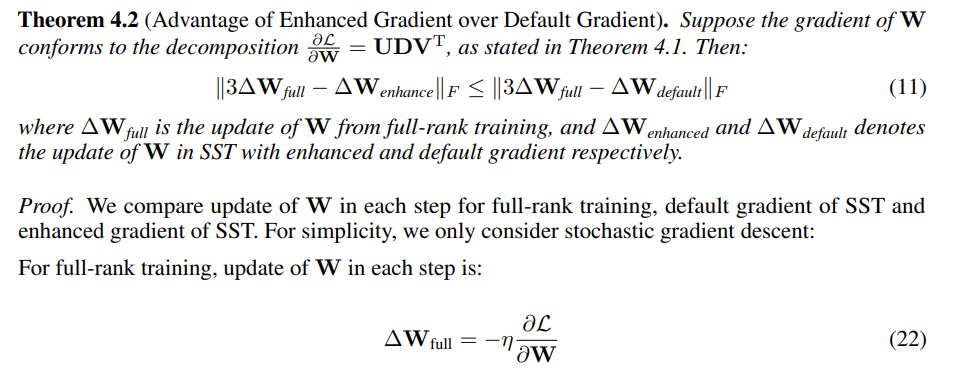
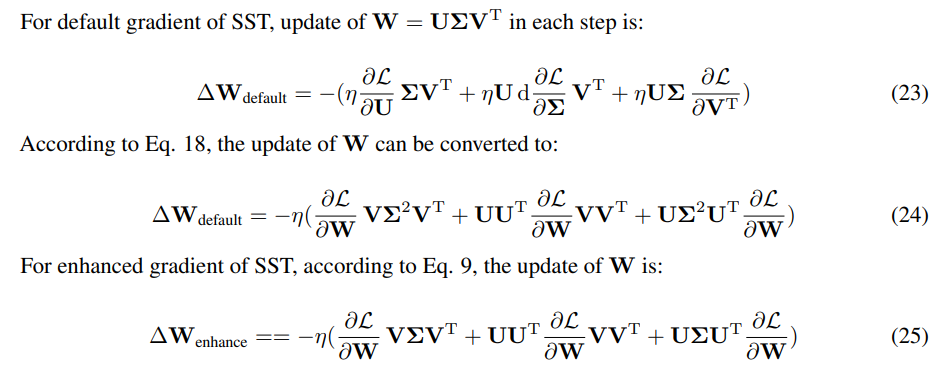
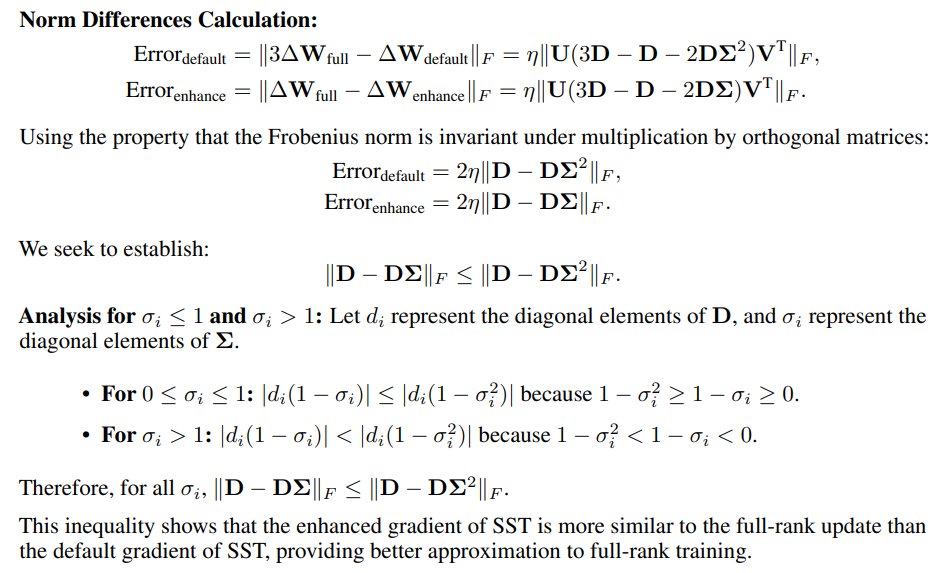
D Proof of Advantage of Enhanced Gradient over Default Gradient
\ 
\ \ \ 
\ \ \ 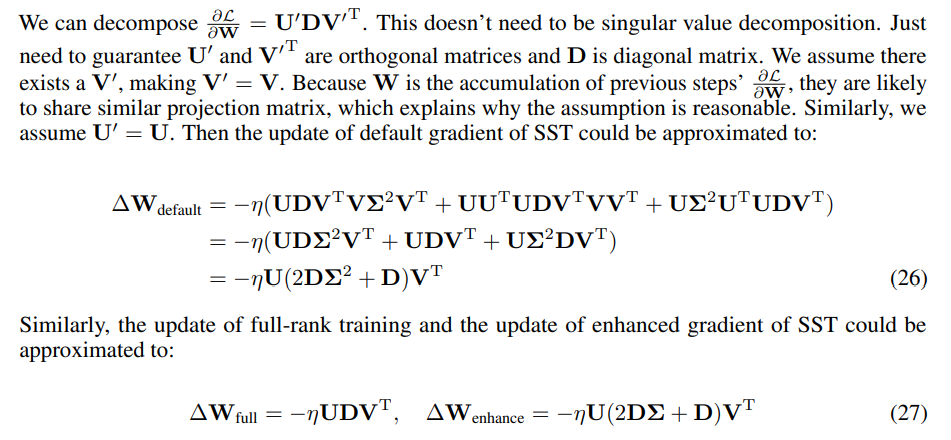
\ \ As only the direction of update matters, the scale of update can be adjusted by changing learning rate. We measure similarity using the Frobenius norm of the differences between SST updates and 3 times of the full-rank update.
\ \ 
\
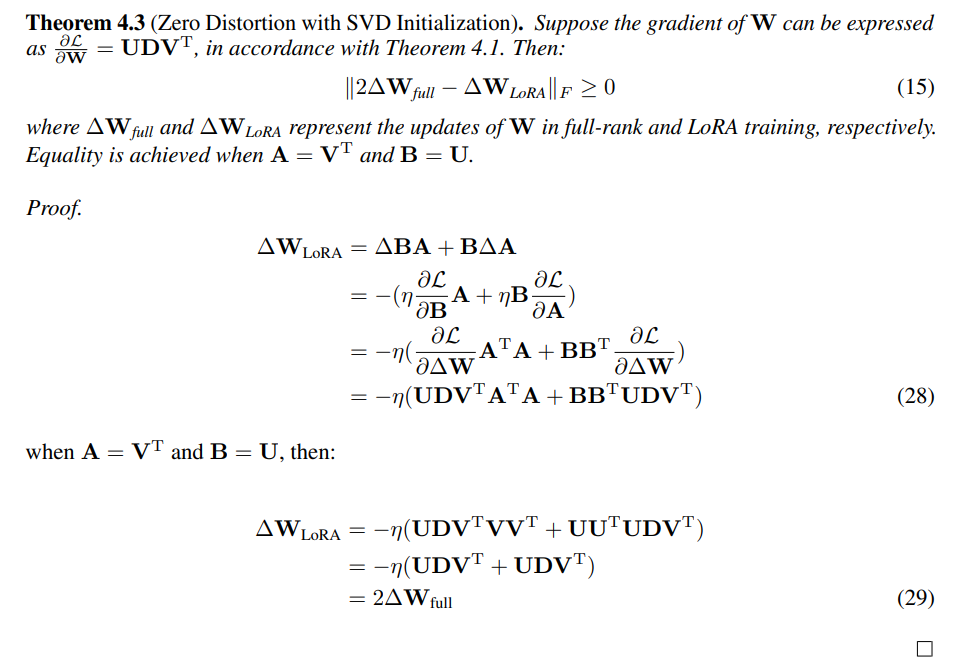
E Proof of Zero Distortion with SVD Initialization
\ 
F Experiment Details
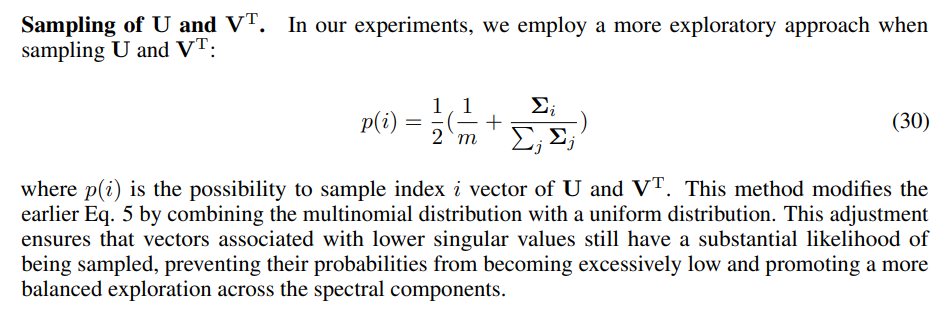
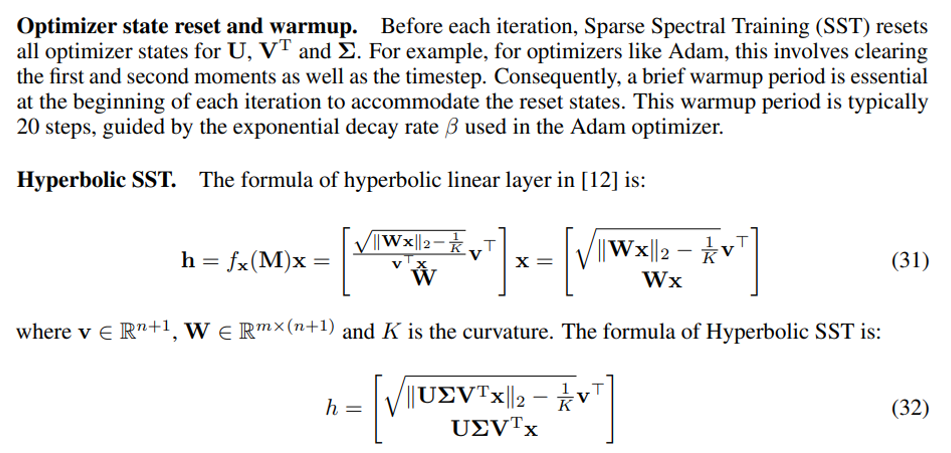
F.1 Implementation Details for SST
\ 
\ \ \ 
\
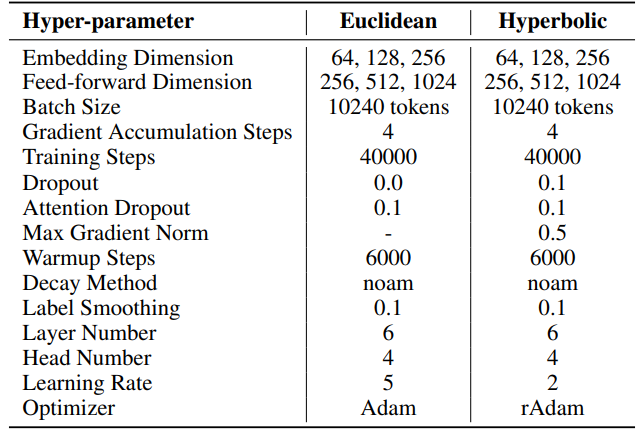
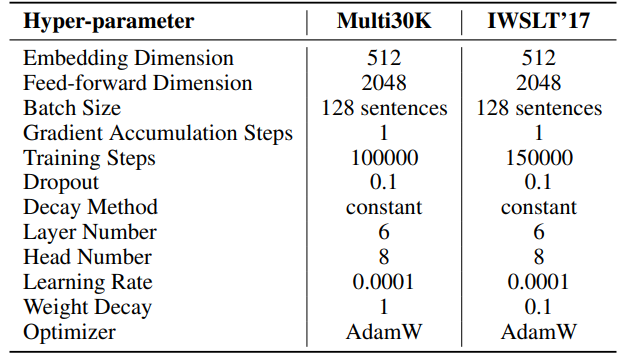
F.2 Hyperparameters of Machine Translation
IWSLT’14. The hyperparameters can be found in Table 6. We employ the same codebase and hyperparameters as those used in HyboNet [12], which is derived from OpenNMT-py [54]. The final model checkpoint is utilized for evaluation. Beam search, with a beam size of 2, is employed to optimize the evaluation process. Experiments were conducted on one A100 GPU.
\ For SST, number of steps per iteration (T3) is set to 200. Each iteration begins with a warmup phase lasting 20 steps. The number of iterations per round (T2) is determined by the formula T2 = d/r, where d represents the embedding dimension and r denotes the rank used in SST.
\ \ 
\ \ \ 
\ \ For SST, number of steps per iteration (T3) is set to 200 for Multi30K and 400 for IWSLT’17. Each iteration begins with a warmup phase lasting 20 steps. The number of iterations per round (T2) is determined by the formula T2 = d/r, where d represents the embedding dimension and r denotes the rank used in SST
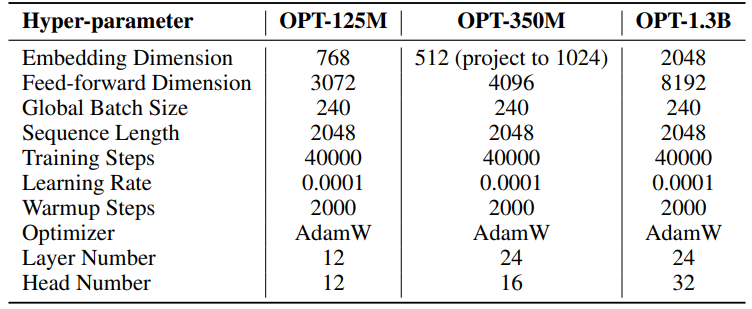
F.3 Hyperparameters of Natural Language Generation
The hyperparameters for our experiments are detailed in Table 8. We employ a linear warmup of 2000 steps followed by a stable learning rate, without decay. A larger learning rate (0.001) is used for only low rank parameters (U, VT and Σ for SST, B and A for LoRA and ReLoRA*. The total training tokens for each experiment is 19.7B, roughly 2 epochs of OpenWebText. Distributed training is facilitated using the Accelerate [55] library across four A100 GPUs on a Linux server.
\ For SST, number of steps per iteration (T3) is set to 200. Each iteration begins with a warmup phase lasting 20 steps. The number of iterations per round (T2) is determined by the formula T2 = d/r, where d represents the embedding dimension and r denotes the rank used in SST.
\ \ 
\ \ \ 
\
F.4 Hyperparameters of Hyperbolic Graph Neural Networks
We use HyboNet [12] as full-rank model, with same hyperparameters as those used in HyboNet. Experiments were conducted on one A100 GPU.
\ For SST, number of steps per iteration (T3) is set to 100. Each iteration begins with a warmup phase lasting 100 steps. The number of iterations per round (T2) is determined by the formula T2 = d/r, where d represents the embedding dimension and r denotes the rank used in SST.
\ We set dropout rate to 0.5 for the LoRA and SST methods during the node classification task on the Cora dataset. This is the only one deviation from the HyboNet configuration.
\ \ \
:::info Authors:
(1) Jialin Zhao, Center for Complex Network Intelligence (CCNI), Tsinghua Laboratory of Brain and Intelligence (THBI) and Department of Computer Science;
(2) Yingtao Zhang, Center for Complex Network Intelligence (CCNI), Tsinghua Laboratory of Brain and Intelligence (THBI) and Department of Computer Science;
(3) Xinghang Li, Department of Computer Science;
(4) Huaping Liu, Department of Computer Science;
(5) Carlo Vittorio Cannistraci, Center for Complex Network Intelligence (CCNI), Tsinghua Laboratory of Brain and Intelligence (THBI), Department of Computer Science, and Department of Biomedical Engineering Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed (Attribution 4.0 International) license.
:::
\

You May Also Like

Stand Out And Boost Brand Recognition With High-Quality Tag Choices

Highlights of Stanford HAI's 2025 Artificial Intelligence Index Report
