Detailed explanation of how BIO Protocol and DeSci projects are revolutionizing the new paradigm of scientific research development
Author: Bankless
Compiled by: Felix, PANews
On the eve of the BIO Protocol token issuance, the price of tokens in the DeSci (decentralized science) ecosystem soared.
As the boundaries between cutting-edge technologies such as DeSci and AI gradually blurred, this craze continued until the launch of BIO and was reflected in the tokens related to these technologies. As a key hub for DeSci's financing, the launch of BIO brought hope to DeSci, spawned the outside world's enthusiasm for this highly experimental field, and attracted more attention and capital to DeSci over time.
This article will take a deep dive into how BIO Protocol works, the challenges it seeks to solve, and the DAOs that operate under its umbrella. It will then explore how other projects can fill out the DeSci narrative and provide additional tools or use cases to transform the way science is collaborated and funded.
BIO Protocol
BIO Protocol is essentially a decentralized, token-managed platform that supports and incubates specialized BioDAOs. By bringing funding decisions, intellectual property ownership, and governance on-chain, BIO directly addresses several long-standing obstacles in the biotech space:
- Help early-stage projects escape the “valley of death” where insufficient funding often prevents promising ideas from coming to fruition
- Tokenizing research results to promote open access and transparent collaboration, and combating data and intellectual property silos
- Replace opaque R&D with real-time on-chain funding and results tracking
To achieve these goals, BIO implements several core mechanisms:
Curation
BIO holders lock up their tokens (vBIO) to help determine which new BioDAOs are allowed to join the network. This process ensures that only the most promising or community-backed ventures join, as those who pledge their support must stake BIO for a certain period of time. If approved, stakers have exclusive access to the BioDAO's funding rounds.
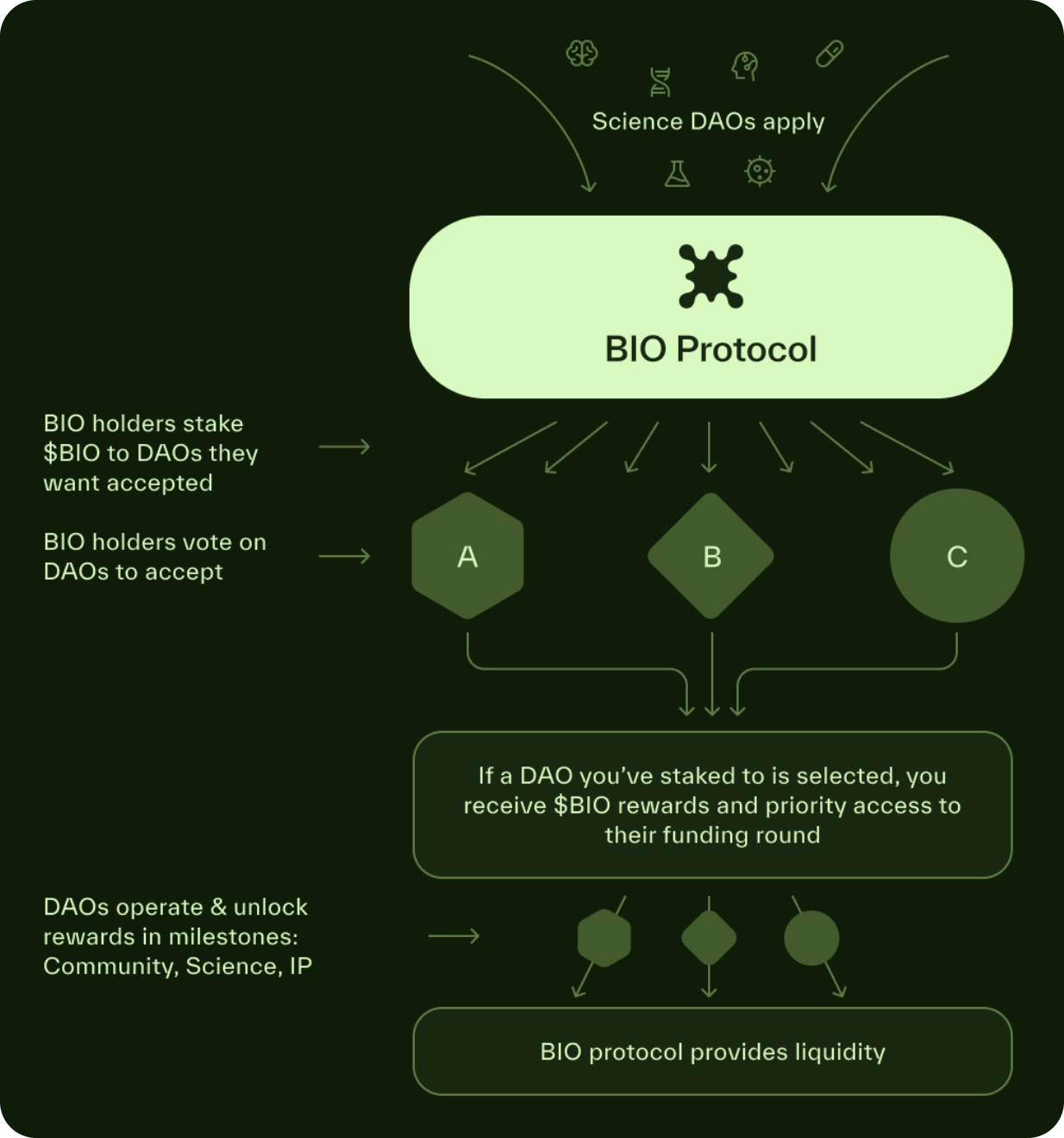
Funding and Liquidity
After completing the curation phase, BioDAO opens a private pre-seed auction for those who lock in vBIO.
This allows early backers of the DAO and the BIO community to invest in early scientific research on terms traditionally reserved for VCs. At the same time, the BIO Protocol manages liquidity on behalf of these BioDAOs, eliminating the need to monitor secondary markets. The BIO Treasury pairs tokens (i.e. VITA/BIO or HAIR/BIO) with ETH or other assets, generating fees for the protocol while ensuring stable trading pairs. This arrangement allows BioDAOs to focus on advancing research rather than being busy with market operations.
Meta-governance
Because the BIO Treasury holds a portion of every BioDAO token, BIO holders collectively gain influence within the broader DeSci ecosystem.
This meta-governance structure enables them to guide multiple BioDAO decisions, whether it’s determining research priorities or highlighting synergies between projects. Additionally, by diversifying the assets held in the treasury, the protocol enhances its ability to invest in new projects and reinvest in existing ones, enabling seamless coordination across an ever-expanding scientific research landscape.
Providing benefits
To incentivize clear, measurable contributions to its network, BIO issues “bio/acc rewards” in the form of additional BIO tokens to BioDAOs that achieve key milestones. In addition to these incentives, BioDAOs can tokenize their IP, from research data to patents. By issuing IP tokens, BioDAOs can grant partial ownership of their research results, allowing more stakeholders to benefit from future scientific breakthroughs, while retaining control over key decisions and potentially earning revenue from the use of their data.
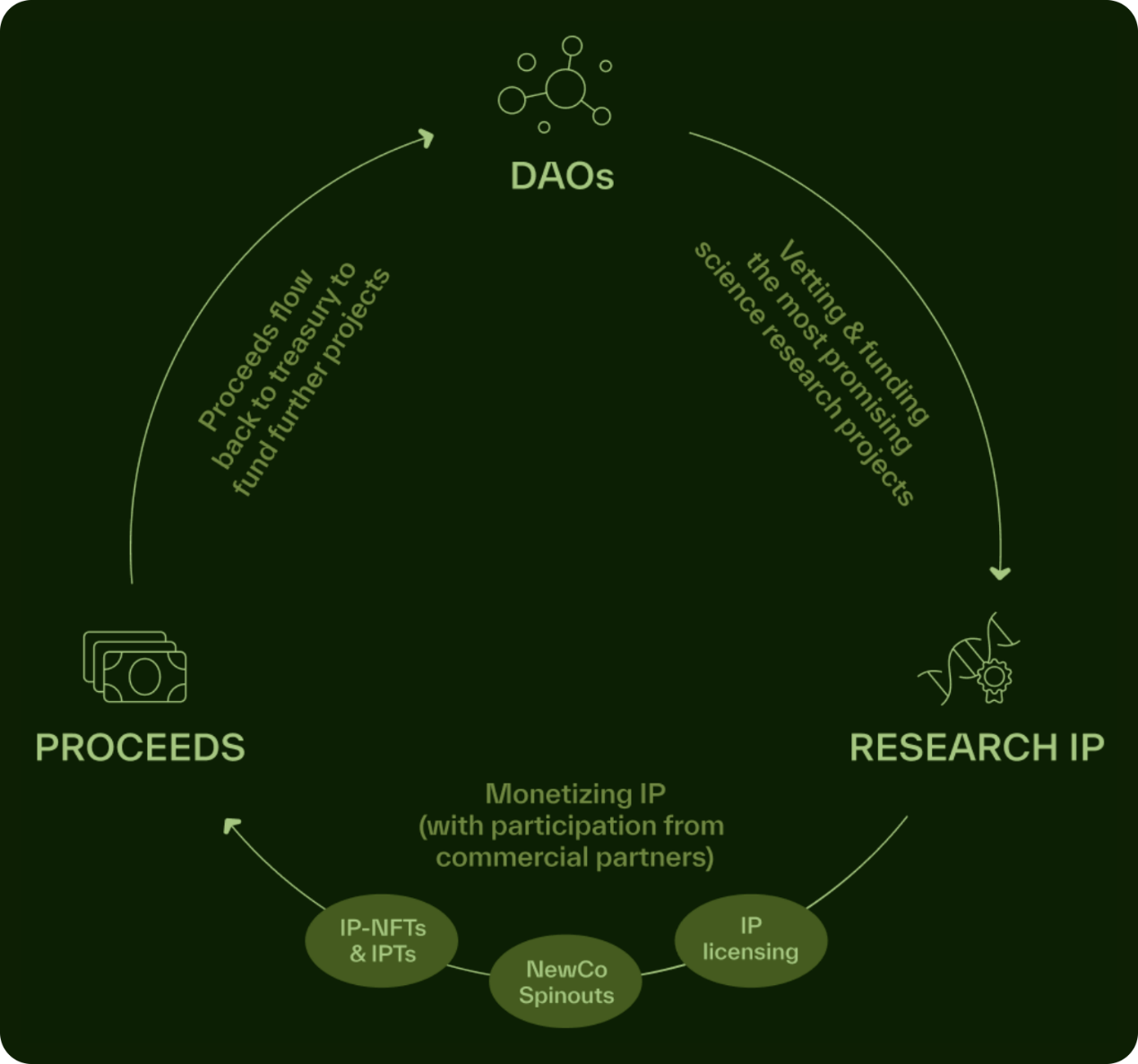
In addition to direct incentives, the overall value of the network grows through token distribution and the liquidity owned by the protocol. Grants to new BioDAOs are exchanged for a small stake in their tokens, while liquidity pool fees flow back into the treasury. As BioDAOs mature and produce tangible results, the total value of these assets increases, reinforcing a virtuous cycle of funding, growth, and innovation.
BioDAO in BIO
Currently, there are eight BioDAOs active in the BIO Network, each focusing on a specific area of research.
- VitaDAO | $VITA
VitaDAO launched in 2021 to support research into extending human lifespan. Funded by Pfizer Ventures and Balaji Srinivasan, it explores the biological mechanisms of aging, including neurodegenerative diseases.
- Quantum Biology DAO
Quantum Biology DAO studies how weak magnetic fields affect cells at the quantum level. In collaboration with the Institute for Quantum Biology, it aims to develop quantum microscopes to open up new avenues for longevity research, drug discovery, and more.
- HairDAO | HAIR
HairDAO unites patients, researchers, and funders to address the under-resourced issue of hair loss.
- ValleyDAO | $GROW
ValleyDAO is working to pursue synthetic biology solutions to climate change, such as engineering microbes to capture carbon dioxide or produce biodegradable materials.
- AthenaDAO | $ATH
AthenaDAO is focused on women’s health, filling a gap that traditional funding has neglected. Through a decentralized community of patients, scientists, and advocates, it supports projects in reproductive health, hormonal imbalance, and other under-researched topics in female biology.
- CryoDAO | $CRYO
CryoDAO directs funding toward cryopreservation research to improve organ and tissue storage, a potentially life-saving option.
- PsyDAO | $PSY
PsyDAO focuses on psychedelic research for mental health issues such as depression, addiction, and PTSD. It uses a decentralized funding model and AI-based auditing to accelerate the discovery of new compounds, while on-chain governance ensures transparency in resource allocation.
- CerebrumDAO | $NEURON
CerebrumDAO convenes a global community to prevent neurodegeneration and prolong brain health. It studies diseases such as Alzheimer's, focusing on inflammation, metabolic issues, the blood-brain barrier and their impact.
Other DeSci Projects
In addition to the BIO Protocol ecosystem, there are many interesting DeSci projects that bring new platforms or tools for scientific research discoveries.
ResearchHub Foundation
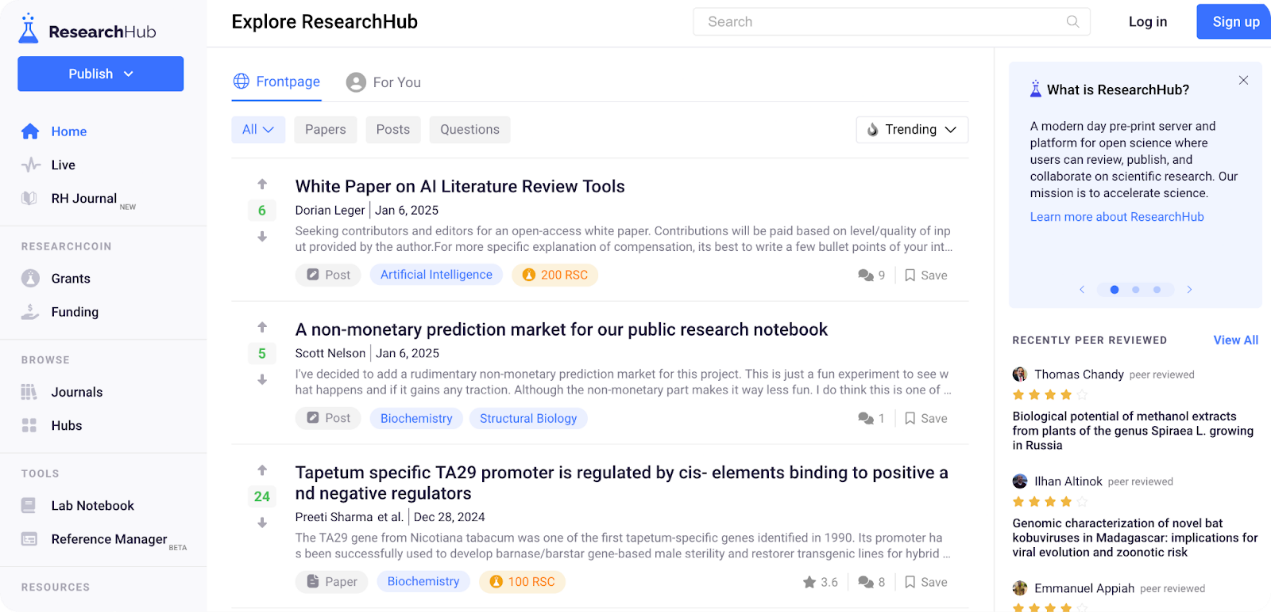
Founded by Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong and Patrick Joyce, the ResearchHub Foundation uses RSC to create an open platform for publishing and reviewing science. Contributors earn RSC by publishing research, curating content, or promoting discussions. The platform aims to build a "GitHub" for scientific research, aiming to simplify peer review, encourage open sharing, and bring real-time accountability to academic publishing, all through token incentives. RSC holders can also vote on platform improvements and reward distribution.
yesnoerror
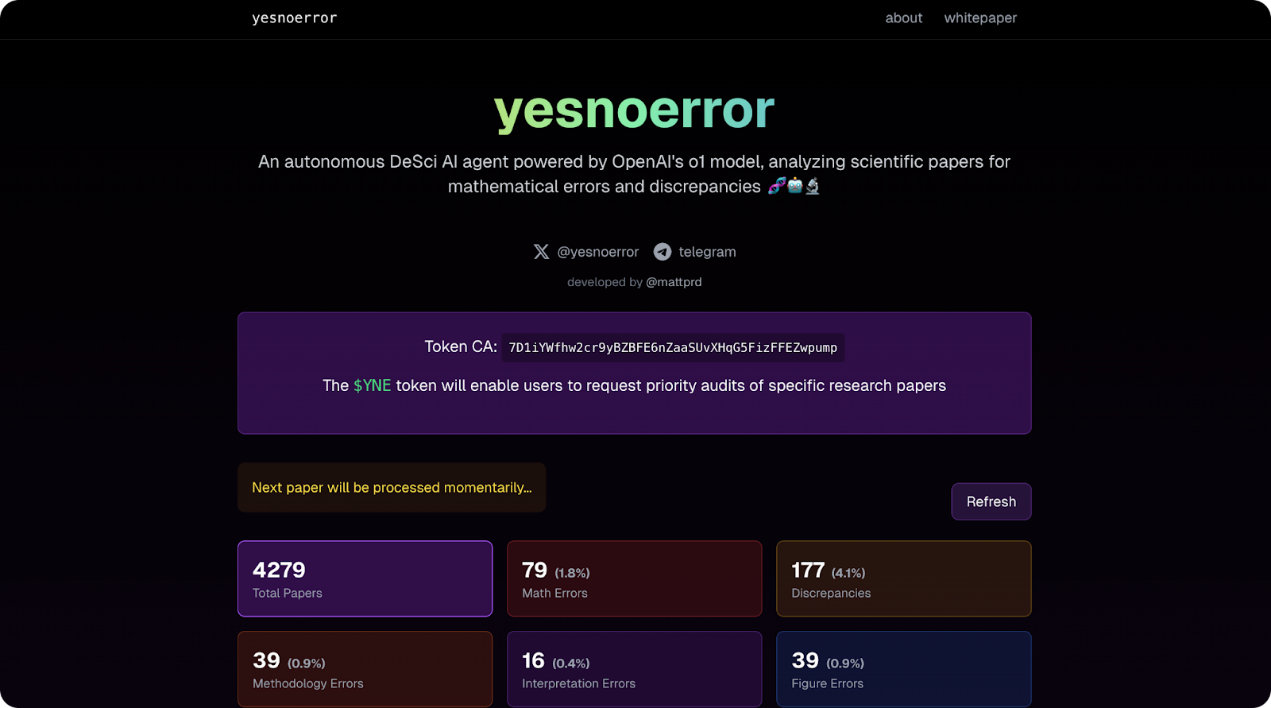
Yesnoerror is a decentralized platform that combines AI with community-driven oversight to improve the reliability of scientific research papers. Its AI engine constantly scans for inaccuracies in research (whether in data, statistical analysis, or references) and flags potential issues for further review. Community members who verify or correct these errors will receive YNE tokens, creating intrinsic incentives for thorough review and timely feedback.
Overall, YNE hopes to detect problems early to prevent false theories, reduce the risk of poor policy decisions and wasted research, and develop an AI that can learn from users to better detect problems across a range of different scientific fields.
pump.Science

Pump.science is a DeSci platform that aims to identify and develop chemicals that can extend healthy human lifespan. It hopes to gamify research by enabling low-cost testing on simple organisms (worms, flies) before using complex models (mice). This approach could allow for early identification of promising interventions, using cryptocurrency-based funding to propose or invest in new compounds. By live-streaming experiments, the protocol provides real-time data, allowing researchers and speculators alike to track results and potentially adjust their support as research progresses.
Conclusion
BIO Protocol’s token launch puts the DeSci space in the spotlight, showcasing how a new generation of on-chain initiatives can reshape R&D in biotech and beyond.
Outside of the BIO ecosystem, other DeSci projects demonstrate complementary strategies for enhancing scientific research through blockchain. From ResearchHub's open collaboration platform to yesnoerror's AI-based paper audits and pump.science's gamified longevity experiments, these projects explore the intersection of science and crypto from different perspectives. Taken together, they point to a rapidly evolving DeSci landscape where shared governance, financial coordination, and real-time data sharing may lead to new breakthroughs.
Whether it’s solving funding bottlenecks, streamlining peer review, or discovering molecules that extend lifespan, DeSci’s solutions have the audacious goal of empowering a broad, motivated community to pursue discovery, ultimately accelerating the speed at which the world benefits from the next wave of scientific innovation.
Related reading: BIO Protocol in-depth research report: Decentralized Science (DeSci) platform supported by Binance
You May Also Like

U.S. Moves Grip on Crypto Regulation Intensifies

Trading time: Tonight, the US GDP and the upcoming non-farm data will become the market focus. Institutions are bullish on BTC to $120,000 in the second quarter.
