How Block-Based Parallelization Cuts IO and Computation Overhead
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Preliminaries and Related Work
-
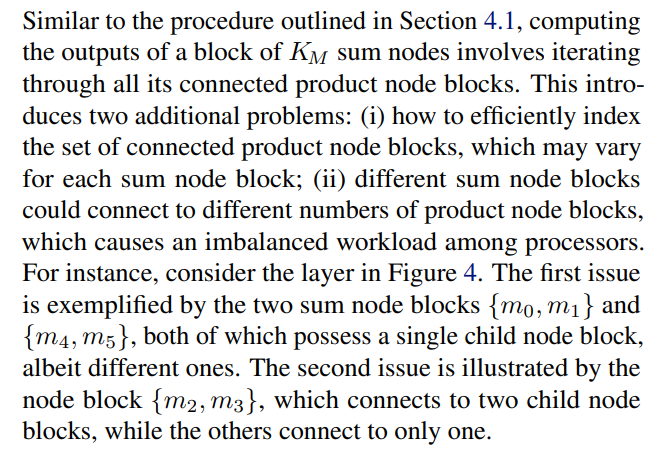
Key Bottlenecks in PC Parallelization
-
Harnessing Block-Based PC Parallelization
4.1. Fully Connected Sum Layers
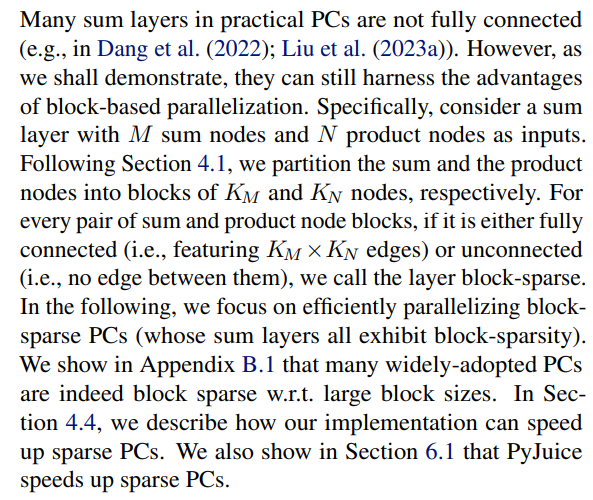
4.2. Generalizing To Practical Sum Layers
4.3. Efficient Implementations by Compiling PC Layers
4.4. Analysis: IO and Computation Overhead
-
Optimizing Backpropagation with PC Flows
-
Experiments
6.1. Faster Models with PyJuice
6.2. Better PCs At Scale
6.3. Benchmarking Existing PCs
-
Conclusion, Acknowledgements, Impact Statement, and References
A. Algorithm Details
B. Additional Technical Details
C. Experimental Details
D. Additional Experiments
\
4. Harnessing Block-Based PC Parallelization
This section takes gradual steps toward demonstrating how we can reduce both the IO and computation overhead using block-based parallelization. Specifically, we first utilize a fully connected sum layer to sketch the high-level idea (Sec. 4.1). Consequently, we move on to the general case, providing further details of the algorithm (Secs. 4.2, 4.3).
4.1. Fully Connected Sum Layers
Consider a fully connected sum layer comprised of M sum nodes, each connected to the same set of N product nodes as inputs. Under the parallelization strategy mentioned in
\ 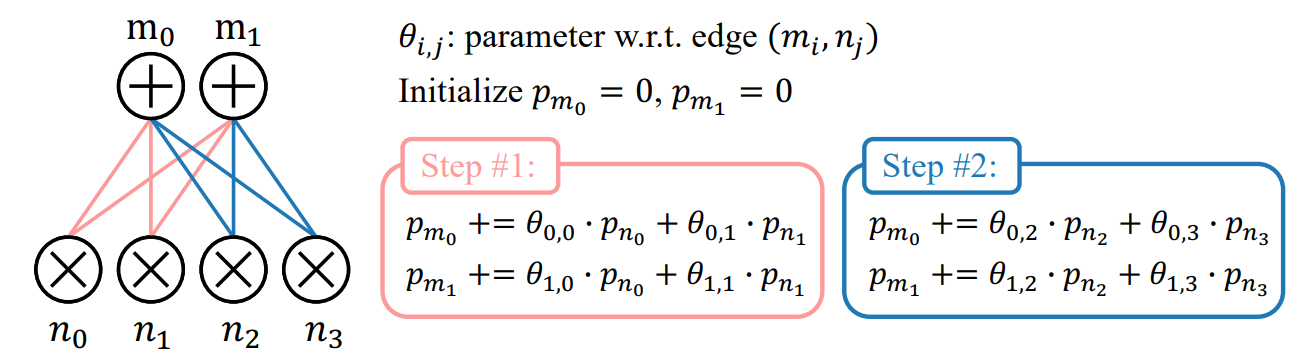
\ Section 3, with a single sample, we have M processors each computing the output of a sum node. Since the layer is fully connected, every processor loads all N input log-probabilities, which results in M reloads of every input.
\ 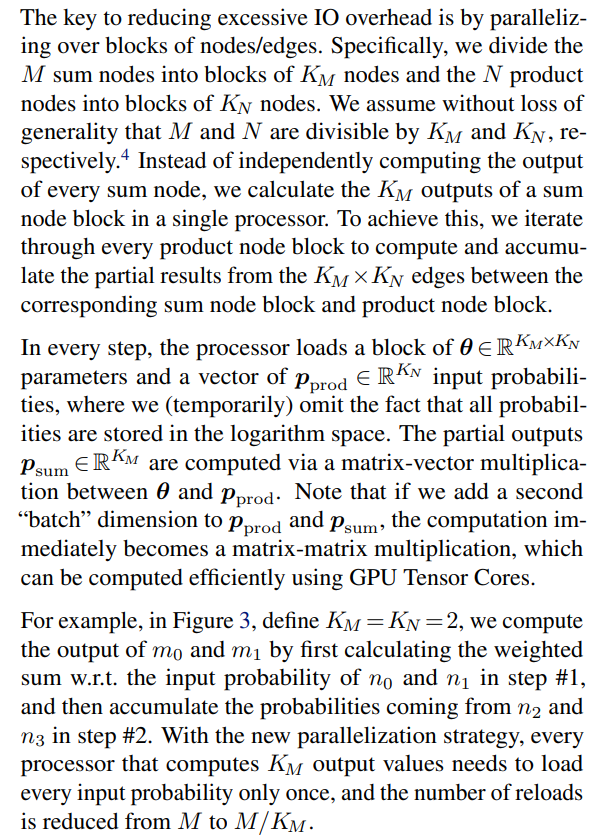
4.2. Generalizing To Practical Sum Layers
\ 
\ \ \ 
\ \ \ 
\ \ \ 
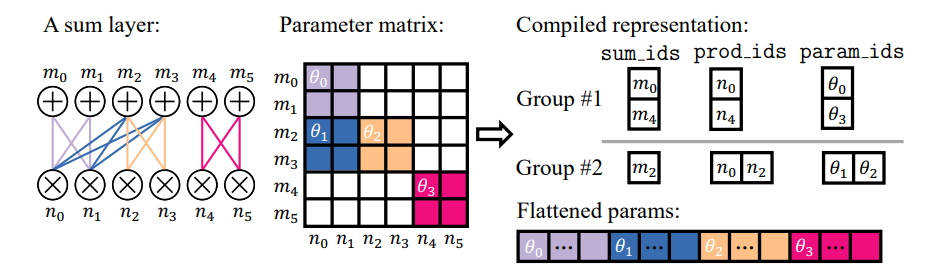
4.3. Efficient Implementations by Compiling PC Layers
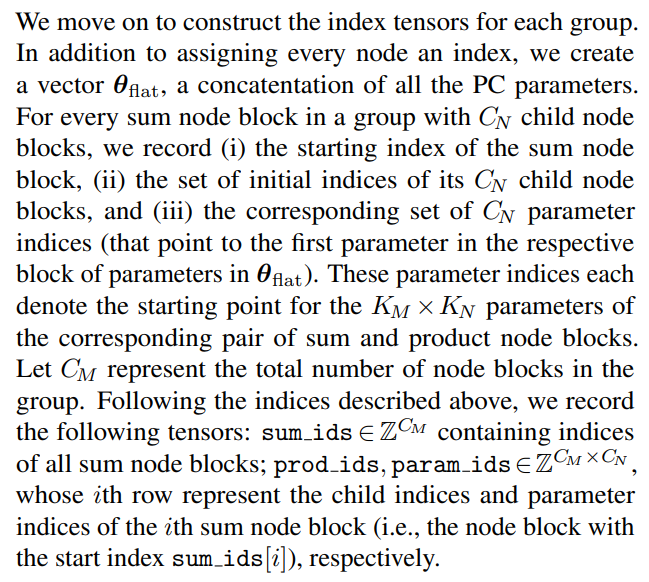
We address both problems through a compilation process, where we assign every node an index, and precompute index tensors that enable efficient block-based parallelization. The first step is to partition the sum node blocks into groups, such that every node block within a group has a similar number of connected child node blocks. We then pad the children with pseudo-product node blocks with probability 0 such that all sum node blocks in a group have the same number of children. The partition is generated by a dynamic programming algorithm that aims to divide the layer into the smallest possible number of groups while ensuring that the fraction of added pseudo-node blocks does not exceed a predefined threshold. Due to space constraints, we elaborate the node block partitioning algorithm in Appendix A.1. We also discuss its optimality and time/memory efficiency.
\ \ 
\ \ \ 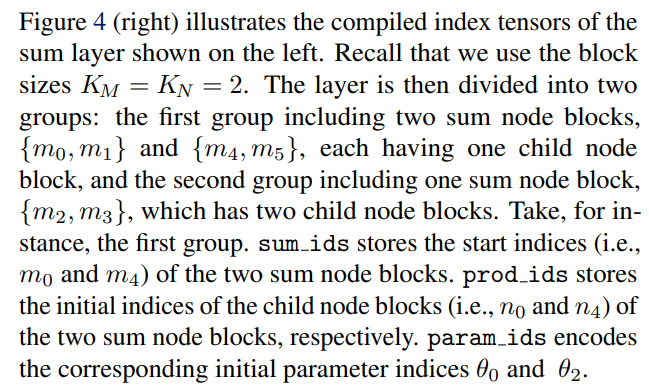
\ \ Partitioning a layer into groups with the same number of children allows us to use different kernel launching hyperparameters according to the specific setup of every node group (e.g., number of nodes) to achieve better performance.
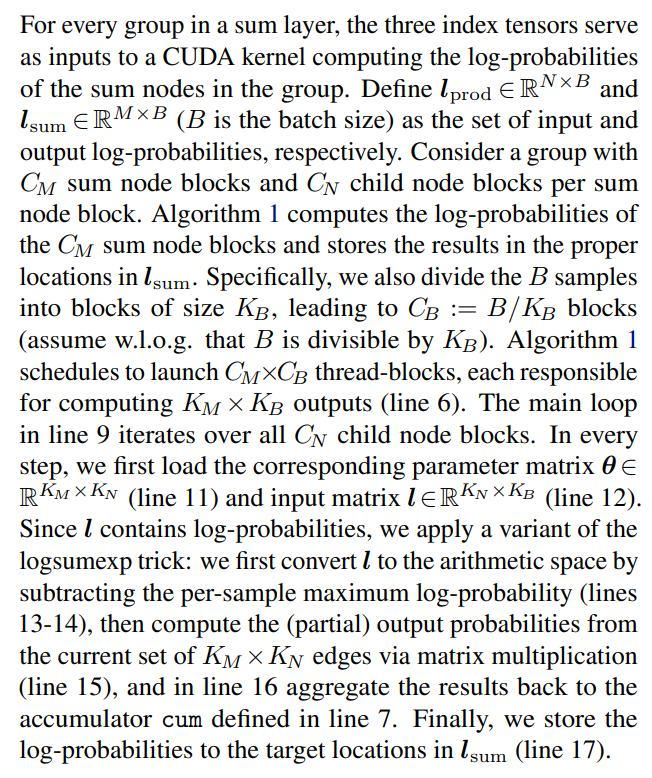
\ \ 
\ \ \ 
\
4.4. Analysis: IO and Computation Overhead
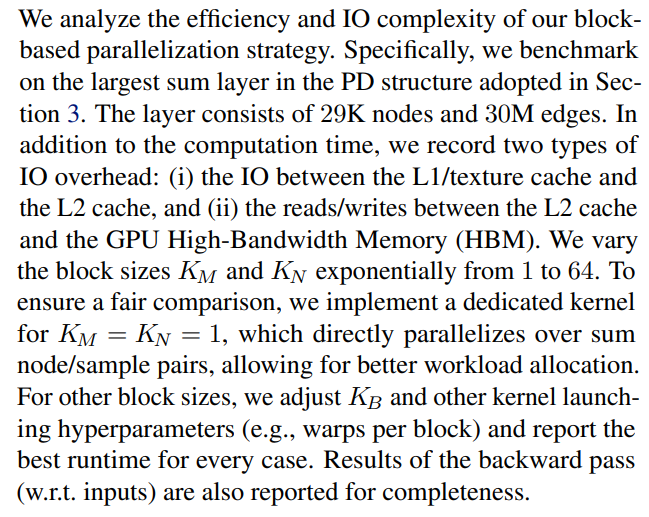
\ 
\ \ \ 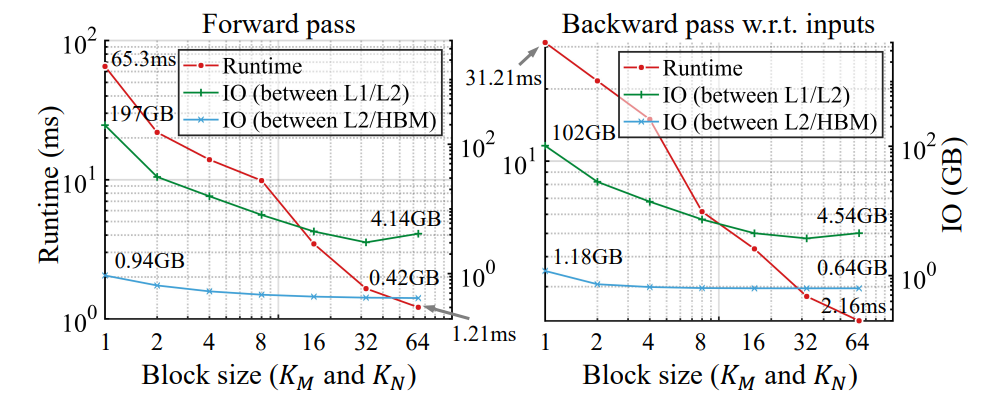
\ \ Results are shown in Figure 5. As the block size increases, both the forward and the backward pass become significantly faster. Notably, this is accompanied by a significant drop in IO overhead. Specifically, with a large block size, the kernel consumes 2x fewer reads/writes between the L2 cache and the HBM, and 25-50x fewer IO between the L1 and L2 cache. This corroborates the hypothesis stated in Section 3 that the extensive value reloads significantly slow down the computation.
\ \ 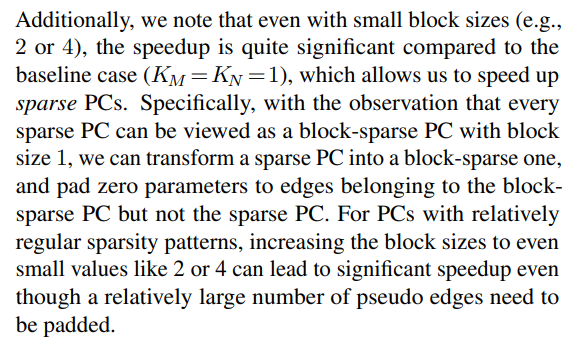
\ \ the speedup obtained by having a larger block size outpaces the overhead caused by padded edges with zero parameters, which leads to speed-ups.
\ \
:::info Authors:
(1) Anji Liu, Department of Computer Science, University of California, Los Angeles, USA (liuanji@cs.ucla.edu);
(2) Kareem Ahmed, Department of Computer Science, University of California, Los Angeles, USA;
(3) Guy Van den Broeck, Department of Computer Science, University of California, Los Angeles, USA;
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::

You May Also Like

Zero Knowledge Proof’s 200M Daily Presale Auction Is Driving The Rush, While ZCash and Hedera Look Lost

U.S. Court Finds Pastor Found Guilty in $3M Crypto Scam
